Risk
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
| − | [[File:Steps.png| | + | [[File:Steps.png|400x350px|thumb|right|'''Figure 1''': The seven steps in FMEA (own figure)]] |
'''The FMEA consists of 7 steps:''' | '''The FMEA consists of 7 steps:''' | ||
Revision as of 18:53, 21 February 2021
By Shakila Khan Malik s173780
Contents |
Abstract
Risk is associated with everything, even when we talk about projects. It is important to keep risk in mind when working on a project, program and portfolio and identify them, as risk can lead to large costs, losses and project failures. The purpose of the article is to identify potential risks and put them into perspectives using risk management tools.
In order to identify and prevent risks in a project, it is necessary to have risk management. Risk management is a process for identifying risks in a project. Multiple tools can be used to reduce and prevent risks and uncertainties during a process or project. The aim is to ensure successful projects without major risks and unexpected events leading to high costs.
One of the risk management tools is “Failure mode and effects analysis” (FMEA). The FMEA is a process that identifies how and where the project might fail and assesses the different failures to identify which parts are most in need of change [1]. In addition, another management tool, the “fishbone diagram” can be used to track the causes of deficiencies or failures in the project. Some other risk management tools are “Post-project review” (PPR) and “Potential problem analysis” (PPA). The PPR analysis identifies potential failures and successes in a project where the PPA determines what may go wrong in a process or development phase.
Tools
As mentioned earlier, this wiki article contains several risk management tools, that can be used to manage a project. These tools can be adopted by the managers in any organization as the tools are guidance how to tackle and prevent risks and uncertainties in a project or program.
Failure Mode and Effects analysis (FMEA)
The FMEA was developed in 1940s when the U.S. military systems became too complex. The FMEA tool identifies where the project might fail, and which parts are most in need of change to prevent risks and uncertainties. The FMEA tool can solve several risks in a manageable way. The failures are prioritized by their consequences and frequency, starting with the highest priorities [2].
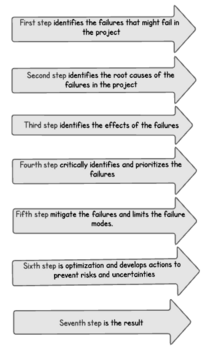
The FMEA consists of 7 steps:
- The first step identifies the failures that might fail in the project. The management team has to define the scope.
- The second step identifies the root causes of the failures in the project. All processes are divided into subsequent steps.
- The third step identifies the effects of the failures. Each failure is analysed separately to identify the largest failures.
- The fourth step critically identifies and prioritizes the failures, starting with the highest priority.
- The fifth step mitigate the failures and limits the failure modes.
- The sixth step is optimization and develops actions to prevent risks and uncertainties. The actions reduce the likelihood of failures and improve processes, products and services.
- The seventh step is the result, where the results of the FMEA are documented.
When and why should the tool be used
The FMEA tool is often used through a product, process and service design phase, before modifying an existing process in a different way and generally to analyse the failures of a project.
The benefits of using the tools are that the failures are identified in an early stage and prevent risks and uncertainties. Furthermore, the FMEA allows to a greater extent changes in the processes, products and services as it is possible to mitigate the risks. Moreover, it is cheaper solutions. [3].
References
- ↑ http://www.innovation-portal.info/toolkits/fmea-failure-mode-effect-analysis/
- ↑ ASQ. (2020). Learn about quality. Retrieved from Failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA): https://asq.org/quality-resources/fmea
- ↑ Quality-One International - Discover the value. (2020). Quality-One International - Discover the value. Retrieved from Introduction to Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA): https://quality-one.com/fmea/