Quality Gates in Project Management
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
== Big idea == | == Big idea == | ||
Text | Text | ||
| − | === | + | === 5 Ws + 1H of Quality Gates === |
'''Who?''' Project Manager, Process Manager, Project Owner <br /> | '''Who?''' Project Manager, Process Manager, Project Owner <br /> | ||
'''What?''' Designing, embedding and checking quality criteria <br /> | '''What?''' Designing, embedding and checking quality criteria <br /> | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
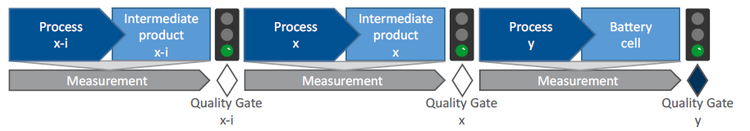
| − | [[File:BatteryQG.png||center|thumb| | + | [[File:BatteryQG.png||center|thumb|750px|Figure 1: Quality gates for the production chain of battery cells, aggregating measurement of the relevant process parameters and intermediate product properties. <ref name = "3-TUMBat"/>]] |
=== Quality Control in Project Management === | === Quality Control in Project Management === | ||
Revision as of 20:20, 21 February 2021
Contents |
Abstract
Projects are temporary and unique endeavors and require active management of their integration, scope, schedule, cost, quality, resources, and communication according to the Project Management Institute. [1]
One tool to control project management is the Stage Gate approach that divides projects into stages with gates and tracks their progress and success. In the 1990s a modification to focus on especially schedule, cost, and quality was established known as Quality Gates. A quality gate represents a checkpoint of predefined criteria set by the project manager to evaluate the current progress of a project. Hereby a focus lies on the three aspects of time and cost, both resource-related and quality (2). After assessing the specified benchmarks and standards, an evaluation of passing or failing the gate is made.
This article sets the quality gate model into the picture with other phase gate models and points out its differences, benefits, and limitations. More weight lies on the quality criteria and its control in project management and its lifecycles. Besides, how four main tenets set, assess, and complete gates together with intermediate milestones. [2] The article also explains the required steps a project manager needs to take in order to introduce quality gates for projects. A proposal of applying the quality gates by segmenting projects into the three stages of front-end, middle, and back-end gates for different project stages [3][4] is suggested with a detailed successive explanation. Finally, the concern of resource-intensity in quality gate processes is discussed whereby more focus on scoping and lean management for projects is recommended. Also, the development from sequential towards iterative quality control is elaborated along with expanding the application from product-only towards service-oriented sectors.
Abb. Quality Gate Process: QGP
Big idea
Text
5 Ws + 1H of Quality Gates
Who? Project Manager, Process Manager, Project Owner
What? Designing, embedding and checking quality criteria
When? Whole lifecycle – from initiation to closing
Where? Developments and processes, e.g. in new product development (NPD), manufacturing, IT software, finance, M&A
Why? Gain control over quality development, status and state of the art
How? Define and assess quality criteria, milestones and gates
Example of quality gates from practice:
Quality Control in Project Management
- Outline the three main factors of schedule, cost and quality in project management - Describe the impact of the three factors - Give examples of possible management ways of the three factors
Quality Gates
- Outline main differences between quality gates and other phase gate models - Schedule, cost and quality aspects with QGP in project management - 4 essential tenets (performance standards, milestone criteria, criteria control, gate completions)
Application
- Set the project scope - Set quality requirements
Introduction of Quality Gates
- How to determine, define, measure and evaluate quality gates in project management
Application of Quality Gates
Front-end Gates
- Invest, Commit, Design
Middle Gates
- Implement, Integrate, Validate
Back-end Gates
- Try, Introduce, Release
Limitations
Resource Requirements
- QGP is time and labour intense, project manager is required - Project needs to be of a certain size, otherwise it is not worthwhile - Maybe mention lean possibilities; adopt the amount of quality gates to the project scope
Sequentiality/Waterfall Model
- Often it is claimed and critized that phase gate models such as the QGP are due to their native sequential developments harming (product and/or service) development - Show that QGP can also be iterative processes
Non-product Realization Projects
- Critics say QGP are mainly used in physical product realization projects because of quality nature - Give examples of software, service, IT applications
Annotated Bibliography
(1) PMI Guide - Project Management
(2) PMI Symposium – Quality Control with Quality Gates
(3) Quality Gates Concept in Battery Production
References
- ↑ Project Management Institute, Inc.. (2017). Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide) (6th Edition). Project Management Institute, Inc. (PMI). Retrieved from https://app.knovel.com/hotlink/toc/id:kpGPMBKP02/guide-project-management/guide-project-management
- ↑ Achieving Total Project Quality Control Using The Quality Gate Method, Presented at the 1993 PMI Annual Symposium;, John M. Aaron, Cesare P. Bratta, D. Paul Smith
- ↑ Achieving Total Project Quality Control Using The Quality Gate Method, Presented at the 1993 PMI Annual Symposium;, John M. Aaron, Cesare P. Bratta, D. Paul Smith
- ↑ Quality Management for Battery Production: A Quality Gate Concept Joscha Schnell, Gunther Reinhart Procedia CIRP 57 ( 2016 ) 568 – 573 49th CIRP Conference on Manufacturing Systems (CIRP-CMS 2016) Institute for Machine Tools and Industrial Management (iwb), Technical University of Munich (TUM)
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs named3-TUMBat
- - ex1