Conflict ladder
(→Application) |
(→Application) |
||
| Line 119: | Line 119: | ||
Active Listening Techniques, Constructive communication, (Self-Awareness) and Choosing the appropriate medium (oral- written – hybrids). | Active Listening Techniques, Constructive communication, (Self-Awareness) and Choosing the appropriate medium (oral- written – hybrids). | ||
| − | [http://wiki.doing-projects.org/index.php/Active_Listening_Technique Active Listening Techniques] | + | [http://wiki.doing-projects.org/index.php/Active_Listening_Technique Active Listening Techniques], [http://wiki.doing-projects.org/index.php/Constructive_communication Constructive communication], [http://wiki.doing-projects.org/index.php/Self-Awareness link Self-Awareness], [http://wiki.doing-projects.org/index.php/Choosing_the_appropriate_medium_(oral_%E2%80%93_written_%E2%80%93_hybrids) Choosing the appropriate medium (oral- written – hybrids)]. |
=== The good conflict within a team === | === The good conflict within a team === | ||
Revision as of 20:22, 21 February 2021
Contents |
Abstract
One of the most important things in good management is good and clear communication, both when it comes to working in a team and if you are working as a consultant and your relationship with a client. Good communication is important within all types of management - project, program and portfolio. Basically, every time more than one person is working together in solving a problem, and no matter if you are a leader, manager or coworker.
A good way to start having good communication is to avoid bigger conflicts and misunderstandings. Conflicts can occur for many reasons, if not on behalf of unclear goals or misunderstandings, then it often comes from differentiations within perceptions, values and backgrounds [1]. To help control conflicts The Conflict Ladder is a good tool to use.
Conflict in itself is not a bad thing but escalating conflicts are bad. Actually, if all members of a team always agree, then the work can be unnuanced and going in a wrong direction – so conflicts are good when being controlled [1]. But what is a conflict exactly and what does it mean when a conflict is escalating, and how can it be avoided? This will be described in this article together with the principles of The Conflict Ladder. The Conflict Ladder describes the different stages that exist if a conflict is allowed to escalate fully with anger, blame and personal attack, and the aim is to keep the conflict at lowest possible stage. To keep the conflict at the same stage or to get it to lower stages, there are some tools to manage the conflict.
Not all persons react with anger to a conflict, some will try to avoid the conflict, and here The Conflict Avoidance Ladder will describe the different stages of the conflict. Here the tools to solve the conflict will be different [2].
Different examples of conflicts at different stages and managing tool to use in different relations will be illustrated, so it will be easier for you to incorporate The Conflict Ladder in not only your daily work life but also your personal life.
The big idea
When talking about managing, no matter if it is project, program or portfolio management, good communication is the key. In every type of managing information have to be gathered from different actors, agreements have to be made between parts, a solution have to be researched and analyzed by a various of team members. Every time two individuals have to communicate different parameters can cause a conflict - here the challenge lies in keeping it as a good conflict with a useful outcome for both sides. If the conflict escalates drastic it can have large consequences for the harmony in a team. To keep conflicts at a compatible level sometimes requires clever managing.
What is a conflict?
To know how to keep a good conflict it is essential to know exact what a conflict is. There are many formulations and definitions of what a conflict is. In the DS Handbook 185:2007[1] it is defined as: “An interactive process manifested in incompatibility, disagreement or dissonance within or between social entities.” When trying to straighten out a conflict it is crucial to know the context and what it is about. When it comes to working in a team there are five main types of conflict contexts: methods, resources, values, personal and system. These are described by The Sector of Working Environment (BFA) as following [3]:
Method conflicts: “Is about goals, means, structure and procedures. Professional questions about how the work is carried out and what methods are used to solve the task.”
Resource conflicts: “Emerging from competition for money, time, space, materials and staff.”
Value conflicts: “Is about culture and about personal values and attitudes. What is right and what is wrong? Moral and ethical disagreements, traditions, etc. Here, conflicts can arise between different professional groups, and in cultural clashes between, for example, new and experienced employees.”
Personal conflicts: “Is about identity, self-esteem, loyalty, trust and rejection.” “Here, deep and unconscious feelings are activated, which are about friendship, sympathy and care, which can be difficult to deal with in a workplace, but are crucial for how the individual employee or manager experiences his or her work situation.”
System conflicts: “Is about allocating rights, responsibilities and obligations. The system conflicts arise from the contradictions that arise between employees and managers when legislation, party agreements and professional practices are established in general.”
More than one of these types of conflicts can occur in one conflict, so it is important to detangle a conflict and find a solution to all parts of the conflict. To find a solution to a conflict it is important that the involved parts in the conflict are able to keep the good communication and keep the conflict from escalating. Here The Conflict Ladder is a great tool to understand the different stages in a conflict and which signs to look for at which stages, so it can be avoided to take the step up and escalate the conflict even more.
The Conflict Ladder
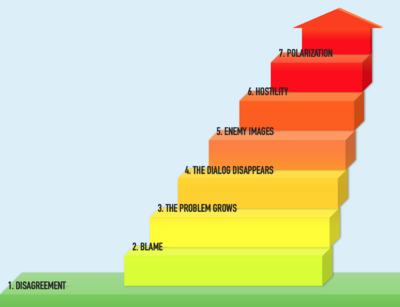
The Conflict Ladder consists of seven main steps divided into three colors – the green area, the yellow and the red. When stepping up the ladder into another color means that it will be very hard to deescalate the conflict back down again. The green area is where both parts of the conflicts can win something from the conflict, and this will be a healthy conflict. When stepping up to the yellow steps means that the situation changes and only one part will win something – both parts will try to win whatever it takes. When reaching the red area, it will be a loose-loose and either part will not get anything positive out of the conflict – here the conflict will be more like a warfare[5]. Each step of the ladder represents a way of acting, thinking or reacting.
Step 1 - Disagreement
A disagreement appears and is solved easy and constructively between the involved parts because both remains focused by listening and keep being open for other opinions[6].
Step 2 - Blame
The situation changes so instead of aiming for the ball the aim is now the other part, so the blaming starts. Either part will not get something good out of the blaming, and the conflict is no longer constructively[7].
Step 3 - The problem grows
Other problems and disagreements will be put on the table – other unsolved disagreements no matter if they are new, old or other straight out of context[7].
Step 4 - The dialogue disappears
The original disagreement is now shaded and almost forgotten, overshined by all the negative and the dialogue fades out. Instead of communicating with the other part the energy is transferred into talking about the other part instead[7].
Step 5 - Enemy images
The communication has stopped, and the original disagreement totally forgotten. Instead, the other part has become more like an enemy and the aim only is to be right and to get the other part to surrender[8].
Step 6 - Hostility
Now the other part is the enemy and a war is started. The aim of being right is forgotten and taken over by anger so the goal is to hurt the other part – no matter the cost[4].
Step 7 - Polarization
Ending up at this step means that the parts can no longer be in the same room, and the conflict has reached the top[4].
When knowing the different kinds of conflicts and what parameters characterizing the different steps of The Conflict Ladder, then the theory is that it is easier to avoid escalating conflicts. It is used as a tool in many workplaces to keep the good and constructive communication, because all will know how to keep the conflicts positive with a useful outcome. This is specially applying where the agile way of working is applied.
Not all conflicts will be escalated by blame and emotions and follow the steps of The Conflict Ladder. Some conflicts will be avoided instead if one part has a shy personality or just want to turn the other cheek to a conflict[2]. When this is the case the conflict will follow The Conflict Avoidance Ladder instead, and here the case is a bit different.
Application
When using The Conflict Ladder there is some tools to use at the different steps of the ladder to deescalate the conflict and to get to the lower steps. The aim for every escalated conflict is to get back to step 1 again, to be able to get a healthy conflict with a beneficial outcome.
Conflict management tools
First step when noticing a conflict is to detect the stage, and from here to use the following tools to control the conflict.
Tools to the green area:
At step 1 it is important to stay cool and stick to the topic. Show respect and listen to the other part when using push and pull communication. If the conflict is hard to solve a tool like negotiation can be useful to reach an agreement. In the DS Handbook 185:2007[1] it stands: “Negotiation is, amongst other things, a key tool for conflict resolution. (…) When entering a negotiation, consider what is relevant to you, prepare strong arguments and an attractive BATNA (best alternative to non-agreement). Ideally, negotiations should be shaped as a problem-solving instead of a bargaining task.”
Tools to the yellow area:
If the other part in the conflict starts crossing the line to the yellow area, it is important not to follow. Stay cool and let the accusation pass. Avoid discussing other problems being brought to the table by the other part but without ignoring them. Phrases like “let us solve one problem at a time” can be useful[2].
Tools to the red area:
When the conflict reaches this area a third part is necessary to get the conflict under control. The uninvolved part will have a mediating role. The goal for the mediator is to create a safe room to reestablish the contact between the involved parts[9].
In general these tools can be helpful to keep a conflict in the green area:
Active Listening Techniques, Constructive communication, (Self-Awareness) and Choosing the appropriate medium (oral- written – hybrids).
Active Listening Techniques, Constructive communication, link Self-Awareness, Choosing the appropriate medium (oral- written – hybrids).
The good conflict within a team
Keep a good relationship to your client
Limitations
Not all conflicts can be solved
It takes time
Good communication is necessary
Annotated bibliography
The Conflict Ladder - How to prevent and manage conflicts, BFA Handel, 2020 [2]. This leaflet is produced by the industry community of working environment within trade, finance and offices to improve the customer contact in the industry. It is like a handbook where The Conflict Ladder and The Conflict Avoidance Ladder is discribed, and different tools to use.
Arts in Psychotherapy - Unlocking conflict through creative expression [10].
PMBOK Guide - A guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge [11].
Five types of conflicts [3].
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 J. Geraldi, C. Thuesen, J. Oehmen & V. Stingl. (2017). Doing Projects - Nordic flavour to managing projects. Danish Standards Foundation. 97.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 BFA Handel,\& Marianne Lassen (Stockfleth & Lassen). (2020). The Conflict Ladder - How to prevent and manage conflicts. http://bfahandel.dk/Files/Filer/BFAHandel/English/Trapned-pjece-eng-FINAL.pdf Visited: 08/02/2021.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Branche Fællesskab Arbejdsmiljø (BFA). Fem typer af konflikter. https://www.arbejdsmiljoweb.dk/trivsel/konflikter/fem_typer_konflikter Visited: 10/02/2021.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Krifa. Når konflikten topper. https://krifa.dk/inspiration/kolleger/naar-konflikten-topper Visited: 10/02/2021.
- ↑ Branche Fællesskab Arbejdsmiljø (BFA). Konflikttrappen - Konflikters udvikling. https://www.arbejdsmiljoweb.dk/trivsel/konflikter/saadan_udvikles_konflikter/konflikttrappen-konflikters-udvikling Visited: 10/02/2021.
- ↑ Branche Fællesskab Arbejdsmiljø (BFA). Grøn konflikt - fokus på sagen. https://www.arbejdsmiljoweb.dk/trivsel/konflikter/saadan_udvikles_konflikter/konflikttrappen-konflikters-udvikling/gron_konflikt Visited: 10/02/2021.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Branche Fællesskab Arbejdsmiljø (BFA). Gul konflikt - fokus på personen. https://www.arbejdsmiljoweb.dk/trivsel/konflikter/saadan_udvikles_konflikter/konflikttrappen-konflikters-udvikling/gul_konflikt Visited: 10/02/2021.
- ↑ Branche Fællesskab Arbejdsmiljø (BFA). Rød konflikt - fokus på krigsførelse. https://www.arbejdsmiljoweb.dk/trivsel/konflikter/saadan_udvikles_konflikter/konflikttrappen-konflikters-udvikling/rod_konflikt Visited: 10/02/2021.
- ↑ L. Christy. "Grib konflikten". 3rd edition (2012). Det Kriminalpræventive Råd. 18-22.
- ↑ R. Goldblatt, D. Elkis-Abuhoff, M. Gaydos, S. Rose & S. Casey. (2011). Arts in Psychotherapy - Unlocking conflict through creative expression.
- ↑ The Project Management Institute (PMI). 6th edition (2017). A guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide).