Situational leadership - Hersey and Blanchard
Stefaniaosk (Talk | contribs) |
Stefaniaosk (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Abstract == | == Abstract == | ||
| − | The Hersey-Blanchard Situational Leadership is a theory designed to help leaders finding the most effective leadership style from different circumstances they find themselves in. The theory was developed by author Paul Hersey and leadership expert Ken Blanchard, first introduced in late 1960s as Life Cycle Theory of Leadership but renamed in the mid-1970 as Situational Leadership Model <ref name="blanchard" /> . | + | The Hersey-Blanchard Situational Leadership is a theory designed to help leaders finding the most effective leadership style from different circumstances they find themselves in. The theory was developed by author Paul Hersey and leadership expert Ken Blanchard, first introduced in late 1960s as ''Life Cycle Theory of Leadership'' but renamed in the mid-1970 as Situational Leadership Model <ref name="blanchard" /> . |
The theory was inspired by the changing leadership needed by parents as a child grows up from infancy to adulthood. An infant needs a different leadership style than as a young adult, so Hersey and Blanchard felt as the same logic held true for managing new, developing and experienced workers. <ref name="blanchard" /> | The theory was inspired by the changing leadership needed by parents as a child grows up from infancy to adulthood. An infant needs a different leadership style than as a young adult, so Hersey and Blanchard felt as the same logic held true for managing new, developing and experienced workers. <ref name="blanchard" /> | ||
| − | In 1980s Blanchard made a number of changes to the original model which is now called Situational Leadership II or SLII. [heimild minute manager, Blanchard]. This article will focus on this new and improved Situational Leadership model, the SLII. | + | In 1980s Blanchard made a number of changes to the original model which is now called Situational Leadership II or SLII. [heimild minute manager, Blanchard]. (This article will focus on this new and improved Situational Leadership model, the SLII. ) |
| − | + | The theory contains a flexible style, whereas the manager adapts their management style to situational factors in the workplace. By understanding, recognizing, and adapting to these situational factors, the leaders will be able to influence their surroundings and followers much more successfully than if these factors are ignored <ref name= "PM_Situational_Leadership" /> . The fundamental foundation of the theory is that there is no single best style of leadership and the most effective leadership varies on the project and the employees working on the project <ref name= "PM_Situational_Leadership" /> . | |
| + | == Big Idea == | ||
SLII proposes that there are four primary leadership styles that are suitable for four different followers’ directive behavior, often called the four development levels. The leadership styles are Directing, Coaching, Supporting and Delegating. SLII helps the leader answer the questions on what the right form of leadership for this person is, in a specific context. The context is the task, and a task can be defined as a project from a project management perspective. Further on, this article will relate the SLII to project managers and why this technique is effective and important in project management. | SLII proposes that there are four primary leadership styles that are suitable for four different followers’ directive behavior, often called the four development levels. The leadership styles are Directing, Coaching, Supporting and Delegating. SLII helps the leader answer the questions on what the right form of leadership for this person is, in a specific context. The context is the task, and a task can be defined as a project from a project management perspective. Further on, this article will relate the SLII to project managers and why this technique is effective and important in project management. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=== Leadership Styles === | === Leadership Styles === | ||
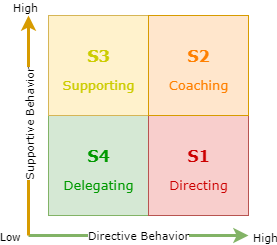
| + | The model that Hersey and Blanchard developed contains four leadership styles. The updated model from SLII in figure 1 shows how the different leadership styles is placed depending on its behavior. X-axis shows the degree of Directive Behavior that the leader must exhibit with each style of leadership, while the Y-axis shows the degree of Supportive Behavior. | ||
| + | [[File:LeadershipStyles.png|right|325px|Situational Leadership Model]] | ||
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" style="width: 70%; height: 14em;" | |
| − | + | |+ style="text-align: center;" |Description of the leadership styles | |
| − | === | + | |- style="height: 7em;" |
| − | Managers are high on directive behavior but low on supportive behavior. The manager tells the person what the goal is and what a good job looks like, but he also lays out a step-by-step plan about how the project is to be completed <ref name="OneMinuteManager"/> . | + | ! scope="row" style="width: 7em;" | S1 Directing |
| − | == | + | | Managers are high on directive behavior but low on supportive behavior. The manager tells the person what the goal is and what a good job looks like, but he also lays out a step-by-step plan about how the project is to be completed <ref name="OneMinuteManager"/>. || |
| − | Coaching combines both direction and support. The manager provides a lot of support, listens well and encourages. This type of leadership teaches the follower how to evaluate their own work. | + | |- style="height: 7em;" |
| − | + | ! scope="row" | S2 - Coaching | |
| − | = | + | | Coaching combines both direction and support. The manager provides a lot of support, listens well and encourages. This type of leadership teaches the follower how to evaluate their own work. || |
| − | Opposite of directing, managers are high on supportive behavior but low on directive behavior. The manager supports the employees’ efforts, listen to suggestions and builds up their confidence in their competence. | + | |- style="height: 7em;" |
| − | == | + | ! scope="row" | S3 - Supporting |
| + | | Opposite of directing, managers are high on supportive behavior but low on directive behavior. The manager supports the employees’ efforts, listen to suggestions and builds up their confidence in their competence. || | ||
| + | |- style="height: 7em;" | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | S4 - Delegating | ||
| + | | delegating || | ||
| + | |} | ||
=== Development Levels === | === Development Levels === | ||
| − | ==== D1 - Enthusiastic Beginner | + | {| class="wikitable" style="width: 70%; height: 14em;" |
| − | An enthusiastic beginner is an employee that has low competence and high commitment. Eager to learn, curios and fairly confident that learning won’t be difficult. | + | |+ style="text-align: center;" |Description of the development levels |
| − | == | + | |- style="height: 7em;" |
| − | This type of an employee has low to some competence and confidence, meaning that he knows what he is supposed to be doing, but still lacks the confidence. [one-minute] Now the enthusiastic beginner is a disillusioned learner where he has gained more skills and knowledge about the project, but still want to know all about the whats, hows, and whys. | + | ! scope="row" style="width: 7em;" | D1 - Enthusiastic Beginner |
| − | == | + | | An enthusiastic beginner is an employee that has low competence and high commitment. Eager to learn, curios and fairly confident that learning won’t be difficult. || |
| − | The capable but cautious contributor has demonstrated some competence and experience, but lack confidence in doing that project alone. | + | |- style="height: 7em;" |
| − | == | + | ! scope="row" | D2 - Disillusioned Learner |
| − | A self-reliant achiever has high competence, high confidence and need little to no direction from their manager. This best describes an employee who has a lot of experience and has been performing a job for a while. | + | | This type of an employee has low to some competence and confidence, meaning that he knows what he is supposed to be doing, but still lacks the confidence. [one-minute] Now the enthusiastic beginner is a disillusioned learner where he has gained more skills and knowledge about the project, but still want to know all about the whats, hows, and whys. || |
| + | |- style="height: 7em;" | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | D3 - Capable but Cautios | ||
| + | | The capable but cautious contributor has demonstrated some competence and experience, but lack confidence in doing that project alone. || | ||
| + | |- style="height: 7em;" | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | D4 - Self-Reliant Achiever | ||
| + | | A self-reliant achiever has high competence, high confidence and need little to no direction from their manager. This best describes an employee who has a lot of experience and has been performing a job for a while. || | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | == Application == | ||
=== How to identify a suitable leadership style === | === How to identify a suitable leadership style === | ||
[[File:StylevsDev.png|left|80px|caption= Figure 2 - Matching leadership styles with development levels ]] | [[File:StylevsDev.png|left|80px|caption= Figure 2 - Matching leadership styles with development levels ]] | ||
When deciding a suitable leadership style there are a few things that need to be considered. | When deciding a suitable leadership style there are a few things that need to be considered. | ||
| − | A directing style is a good match when a decision has to be made quickly and the stakes are high. It is also suitable for when a follower with little work experience for a specific project, but you as a manager see a lot of potential in. Directing is therefore also suitable for inexperienced employees that the manager thinks have the potential to be self-directed. Therefore S1 applies well with D1. | + | A directing style is a good match when a decision has to be made quickly and the stakes are high. It is also suitable for when a follower with little work experience for a specific project, but you as a manager see a lot of potential in. Directing is therefore also suitable for inexperienced employees that the manager thinks have the potential to be self-directed. Therefore S1 applies well with D1 since D1 has commitment but lacks competence and therefore the leader needs to provide direction. |
| + | |||
| + | When determining what style to use with what development level, leaders need to do what the people they are leading can’t do for themselves at the present moment. [one minute] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === Developing people as a leader === | ||
== Why Situational Leadership is important in project management == | == Why Situational Leadership is important in project management == | ||
| Line 50: | Line 71: | ||
Blanchard, K., Zigrami, P., & Zigrami, D. (2013). Leadership and the One Minute Manager (pp. 20-25). William Morrow & Company. | Blanchard, K., Zigrami, P., & Zigrami, D. (2013). Leadership and the One Minute Manager (pp. 20-25). William Morrow & Company. | ||
| − | |||
Hersey, P. & Blanchard, K. H. (1969). "Life cycle theory of leadership". Training and Development Journal. | Hersey, P. & Blanchard, K. H. (1969). "Life cycle theory of leadership". Training and Development Journal. | ||
| + | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 14:20, 24 February 2021
Contents |
Abstract
The Hersey-Blanchard Situational Leadership is a theory designed to help leaders finding the most effective leadership style from different circumstances they find themselves in. The theory was developed by author Paul Hersey and leadership expert Ken Blanchard, first introduced in late 1960s as Life Cycle Theory of Leadership but renamed in the mid-1970 as Situational Leadership Model [1] . The theory was inspired by the changing leadership needed by parents as a child grows up from infancy to adulthood. An infant needs a different leadership style than as a young adult, so Hersey and Blanchard felt as the same logic held true for managing new, developing and experienced workers. [1]
In 1980s Blanchard made a number of changes to the original model which is now called Situational Leadership II or SLII. [heimild minute manager, Blanchard]. (This article will focus on this new and improved Situational Leadership model, the SLII. ) The theory contains a flexible style, whereas the manager adapts their management style to situational factors in the workplace. By understanding, recognizing, and adapting to these situational factors, the leaders will be able to influence their surroundings and followers much more successfully than if these factors are ignored [2] . The fundamental foundation of the theory is that there is no single best style of leadership and the most effective leadership varies on the project and the employees working on the project [2] .
Big Idea
SLII proposes that there are four primary leadership styles that are suitable for four different followers’ directive behavior, often called the four development levels. The leadership styles are Directing, Coaching, Supporting and Delegating. SLII helps the leader answer the questions on what the right form of leadership for this person is, in a specific context. The context is the task, and a task can be defined as a project from a project management perspective. Further on, this article will relate the SLII to project managers and why this technique is effective and important in project management.
Leadership Styles
The model that Hersey and Blanchard developed contains four leadership styles. The updated model from SLII in figure 1 shows how the different leadership styles is placed depending on its behavior. X-axis shows the degree of Directive Behavior that the leader must exhibit with each style of leadership, while the Y-axis shows the degree of Supportive Behavior.
| S1 Directing | Managers are high on directive behavior but low on supportive behavior. The manager tells the person what the goal is and what a good job looks like, but he also lays out a step-by-step plan about how the project is to be completed [3]. | |
|---|---|---|
| S2 - Coaching | Coaching combines both direction and support. The manager provides a lot of support, listens well and encourages. This type of leadership teaches the follower how to evaluate their own work. | |
| S3 - Supporting | Opposite of directing, managers are high on supportive behavior but low on directive behavior. The manager supports the employees’ efforts, listen to suggestions and builds up their confidence in their competence. | |
| S4 - Delegating | delegating |
Development Levels
| D1 - Enthusiastic Beginner | An enthusiastic beginner is an employee that has low competence and high commitment. Eager to learn, curios and fairly confident that learning won’t be difficult. | |
|---|---|---|
| D2 - Disillusioned Learner | This type of an employee has low to some competence and confidence, meaning that he knows what he is supposed to be doing, but still lacks the confidence. [one-minute] Now the enthusiastic beginner is a disillusioned learner where he has gained more skills and knowledge about the project, but still want to know all about the whats, hows, and whys. | |
| D3 - Capable but Cautios | The capable but cautious contributor has demonstrated some competence and experience, but lack confidence in doing that project alone. | |
| D4 - Self-Reliant Achiever | A self-reliant achiever has high competence, high confidence and need little to no direction from their manager. This best describes an employee who has a lot of experience and has been performing a job for a while. |
Application
How to identify a suitable leadership style
When deciding a suitable leadership style there are a few things that need to be considered. A directing style is a good match when a decision has to be made quickly and the stakes are high. It is also suitable for when a follower with little work experience for a specific project, but you as a manager see a lot of potential in. Directing is therefore also suitable for inexperienced employees that the manager thinks have the potential to be self-directed. Therefore S1 applies well with D1 since D1 has commitment but lacks competence and therefore the leader needs to provide direction.
When determining what style to use with what development level, leaders need to do what the people they are leading can’t do for themselves at the present moment. [one minute]
Developing people as a leader
Why Situational Leadership is important in project management
Limitations & Reflections
Limitations
Annotated Bibliography
Zuest, Project Management Institute. Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, 2017. Project Management Institute.
Blanchard, K., Zigrami, P., & Zigrami, D. (2013). Leadership and the One Minute Manager (pp. 20-25). William Morrow & Company.
Hersey, P. & Blanchard, K. H. (1969). "Life cycle theory of leadership". Training and Development Journal.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Blanchard, K., Zigarmi, D., Nelson, R. (1993). Situational Leadership after 25 Years: A Retrospective. 1(1), 22-28. https://www.academia.edu/3431281/Situational_Leadership_After_25_Years_A_Retrospective
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Situational Leadership. (2016). Retrieved 21 February 2021, from https://www.projectmanagement.com/contentPages/wiki.cfm?ID=293293&thisPageURL=/wikis/293293/Situational-Leadership#_=_
- ↑ Blanchard, K., Zigrami, P., & Zigrami, D. (2013). Leadership and the One Minute Manager (pp. 20-25). William Morrow & Company.