Logic tree and the Answer First Methodology
(→In relation to other tools with a hierarchical structures) |
(→Context and Application) |
||
| Line 98: | Line 98: | ||
Other relevant and popular tools like the root cause analysis and work breakdown structure also use a hierarchical structure to visualise dependencies and hierarchy. While they definitely carry resemblance in the way they are used to breakdown something complex into easier to manage elements, they have different abstraction levels and are also different in what they are trying to communicate As such they should be used differently. In order to distinguish between them a summary and a collection of use cases are presented below: | Other relevant and popular tools like the root cause analysis and work breakdown structure also use a hierarchical structure to visualise dependencies and hierarchy. While they definitely carry resemblance in the way they are used to breakdown something complex into easier to manage elements, they have different abstraction levels and are also different in what they are trying to communicate As such they should be used differently. In order to distinguish between them a summary and a collection of use cases are presented below: | ||
| − | '''Root-cause:''' | + | '''Root-cause analysis:''' |
| − | The | + | The Root-cause analysis tree is mostly used in the context where the goal is to find the root cause for a particular error or undesired state of something, often leading to a very deep dive into a very specific and detailed level |
*A production where the end-product experiences too many errors during production (Ishakawa) | *A production where the end-product experiences too many errors during production (Ishakawa) | ||
*A mechanical problem on a complex machine | *A mechanical problem on a complex machine | ||
*Why you are still single | *Why you are still single | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Work-structure breakdown:''' | ||
| + | |||
== In conjunction with system-oriented problem solving == | == In conjunction with system-oriented problem solving == | ||
Revision as of 14:42, 24 February 2021
Dear Reviewer
If you would be so kind to also assess how you think the structure of the big idea paragraph is
Thank you
Jonas
Contents |
Abstract
Problem solving in a company is difficult: Not only do you first have to identify a problem, but the company may also be so deeply entrenched in the way that they are doing things that they cannot possibly consider doing it differently. Developed by highly respected consultancy firms, The answer first methodology is a proven way of structuring a problem and the subsequent project activities in a way that is communicable, coherent, and thorough. By defining a problem as a primary assertion and working out from that, it is broken down into smaller, test-able fragments. What follows is a testing of the sub-assertions and whether proposed solutions will have an effect on the sub-assertion and through that the primary assertion. This breakdown enables a methodical, solution oriented and coherent project work where the main problem is always in focus. Framing the project around a primary assertion also creates a narrative that presentable and easy to follow for stakeholders. This article will briefly explain the birth of this methodology. Subsequently it will explain how it fits into the contemporary bigger picture of business management. What follows will be a crash-course in working with projects using the answer first methodology. This article will also highlight the pitfalls one can encounter when using this methodology as well as provide a general example throughout the presentation of the tool.
Introduction
Sooner or later, each and every one of us will have to be presented with the task of communicating a complex problem and its' solution to important people. Unfortunately, solving and communicating complex problems is not easy. As a company machine grows, the cogs and gears comprising the engine are increasingly interconnected - as such the complexity of problems are bound to increase. This further complicates concise and logical communication of the problem.
In order to tackle the problem of solving problems of increased complexity and avoid situations described above some of the worlds biggest management companies McKinsey and Bain & Co. developed a structured problem solving methodology (Bain, McKinsey). The methodology, despite having distinct names, follow the same principles - understand and frame the problem and context, define an initial hypothesis/answer, break down the answer into analysable elements and lastly validate or invalidate the initial hypothesis/answer.
This article will present the Big Idea of the methodology, followed by a crash-course in the application and context to other contemporary approaches like systems-oriented problem solving. Lastly limitations and further reading will be discussed.
Big Idea
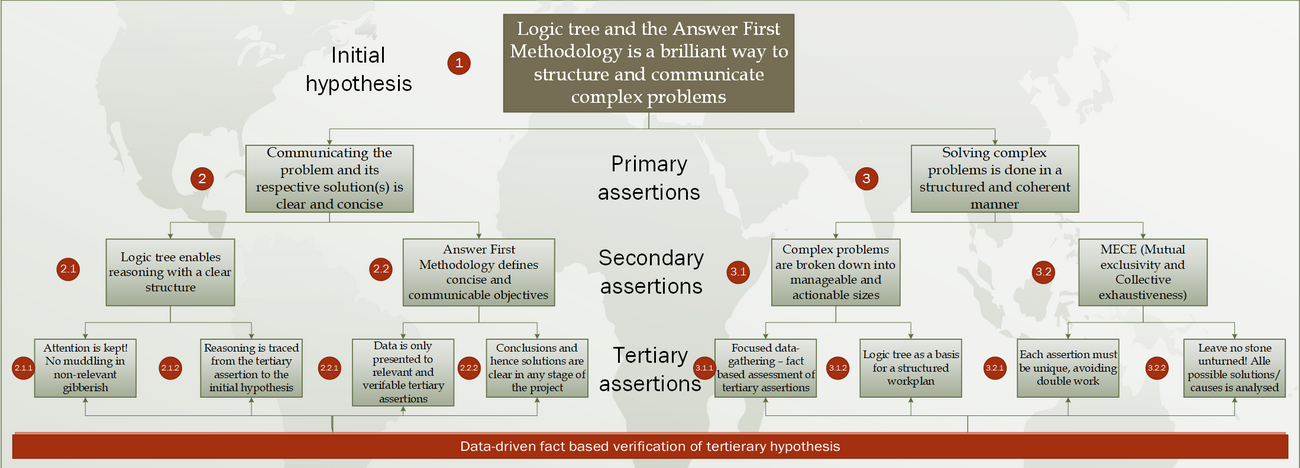
1: The Logic Tree and The Answer First Methodology is a brilliant way to structure and communicate complex problems
What better way to further communicate and exemplify that the Logic tree and the Answer First Methodology is a brilliant way to structure and communicate complex problems, than use the methodology as a framework to explain itself! If this methodology is successful in communicating itself, it will no doubt be a useful tool to managers or prospective engineers too.
What comes first is the Initial hypothesis. This hypothesis not only lays a foundation for further exploration within the problem owners’ area of solution, but also provides a solution to the problem from the get-go. That's right - you answer the problem before you have even done any analysis or research!
2: Communicating the problem and its respective solution(s) is clear and concise
A paramount facet of dealing with business problems, and one of which the success of the project according to PMI standards [PMI Project standard] is contingent on, is communicating them to stakeholders and the project team. The elevator test [McKinsey way] states that a problem solver post-analysis should strive to be able to communicate a complex problem and its’ solutions over the course of an elevator ride. For you ‘stair people’ out there that is approximately 30 seconds. ‘Why?’ You may ask. The reason is two-fold: 1. For you to be able to boil a complex problem and its’ solutions down to 30 seconds requires a thorough comprehension of the essentialities within each of them. 2. Important stakeholders as well as the problem owner, be it manager or executive, whom are either responsible for change or can give you the mandate to implement a change simply does not have time to engage in the problem like you have. It is your job to present to him/her the essentialities of your findings [Mckinsey]. This methodology enables exactly that.
2.1: Logic tree enables reasoning with a clear structure
Using a model as an illustration will greatly aid your communicative efforts to get your point across by illustrating complex interrelated information in a simple way (In the company of others). The Logic Tree is no different. Providing a hierarchy and structure to your communication that can at all times be referred to enables the target audience to clearly follow the points of your presentation and the thought process behind different assertions and how they relate (the pyramid principle).
2.1.1: Attention is kept! No muddling in non-relevant gibberish
In a study, 182 senior managers were interviewed in a range of industries, 71% said meetings are often unproductive (HBR). Using this tool, only stuff that is has an impact on the initial hypothesis is communicated. This avoids the communicator and the conversation straying into non-relevant gibberish, staying on topic. The overview the Logic Tree provides serves as a brilliant guide as to how the project is progressing (eg. We are currently examining this tertiary hypothesis) to and what the goal of a given meeting is, keeping attention on the problem at hand. [Mckinsey]
2.1.2: Reasoning is traced from the tertiary assertion to the initial hypothesis
Throughout the communication the reasoning is traced from the Initial hypothesis down the Logic Tree all the way to the Tertiary assertions. What follows is a data-driven and fact-based verification in order to analyse to what extent these assertions hold true. If they do, logical conclusions can now be made from the tertiary assertions all the way to the initial hypothesis. In this case – if data or facts support that 2.1.1 and 2.1.2 is true, a logical conclusion follows that 2.1 is true.
2.2: Answer First Methodology defines concise and communicable objectives
The Answer First Methodology utilizes deductive reasoning to arrive at a pressure-tested and actionable solution. Deductive reasoning sets itself apart by being thoughts that yield a conclusion from assertions being valid or not. This way of reasoning is very familiar because we do it every single day when considering day-to-day choices: “I don’t want to arrive late to work tomorrow, so I better set an alarm and mentally prepare my morning routine”. Here it is implied that the general conclusion one is not late to work is true if the premises that one sets ones’ alarm and one mentally prepare ones’ morning routine are valid. This methodology hereby presents general conclusions – assertions – that when broken down are proven and as such affirm the assertions higher levels or dis-proven and in this case require a re-formulation or a complete dismissal of the assertion.
2.2.1: Data is only presented to relevant and verifable tertiary assertions
Data is only presented to relevant and verifiable tertiary assertions To drive a concise communication it can be assessed which tertiary assertion that has the highest impact on the initial hypothesis (Mckinsey) – and then the data for this assertion can be put forward to prove why a certain assertion is valid. The Logic Tree also clearly presents what assertion the shown data verifies – avoiding the pitfall of showing data that confuses the audience more than it backs up your points.
2.2.2: Conclusions and hence solutions are clear in any stage of the project
A major strength of this methodology is that solutions are always present, just under different degrees of verifiability (Mckinsey). This means that, in principle, at any point stakeholder can inquire into the findings of your analysis and get a usable answer. In contrast, problems solving that is done by way of inductive reasoning need to have a high degree of the quantitative analysis done in order to draw any valid conclusion (Pyramid).
3: Solving complex problems is done in a structured and coherent manner
Solving multi-faceted, complex problems is not easy. By using this methodology, clear objectives – goals - with their relations are clearly presented. The closer to the main hypothesis, the more vague and general the assertions are – as such these cannot be evidently dis-proven or proven [Mckinsey] but have to be broken down into smaller, testable tertiary assertions. They do, however, tie the logic between the initial hypothesis and the factually verified tertiary assertions to create a coherent and easy-to-follow reasoning.
3.1: Complex problems are broken down into manageable and actionable sizes
A recognized method to solve complex problems (also seen in System-oriented problem solving and the Black-box tool [no more muddling through]) is breaking it down into smaller, more manageable sizes. To do so we must deduct, discuss, and investigate with colleagues – what is they key element of each hypothesis? For this, a good question to for each step to ask is ‘Why?’. Assertion: Why does the Logic Tree and the Answer First Methodology ensure problem solving is done in a structured and coherent manner? …. Answer: The problems are broken into manageable sizes. And why does this fact ensure the former… ->
3.1.1: Focused data gathering - fact based assessment of tertiary assertions
The search for solutions is only manageable if it is known what to look for.” (No more muddling through) When the problem has been properly de-constructed, focused data-gathering is commenced. Making sure to only do data-collection for the ‘lowest’ level of problems ensures a clear objective when gathering and analysing data that can validate or invalidate an assertion. Not only that, but a sensitivity assessment can also be assigned to each tertiary assertion determining how much they affect the parent assertions and in turn the initial hypothesis.
3.1.2: Logic tree as a basis for a structured workplan
As a framework for a detailed workplan in line with the WBS, the Logic tree can be utilized to manage a teams toward a solution. By using the Logic Tree as roadmap of activities, a project manager can utilize Tertiary assertions as as scopes for a further work breakdown (Bain). It is important to note, however, that this methodology is not a project management tool per se. To properly manage a project it is therefore recommended to use other managerial tools such as the GANNT chart or SCRUM to manage the completion of tasks and day-to-day activities in conjunction with this methodology.
3.2: MECE
A term leading consultancy companies using this tool swear by is MECE. At McKinsey, It is hammered into every graduate’s brain [Mckinsey]. In context of this methodology, the use is straightforward - in the development of the logic tree, each assertion must address the previous one in a unique way. Not only that, but the sum of all sub-assertions under every assertion must also be Collectively Exhaustive of all relevant impacts. [McKinsey]
3.2.1: Each assertion must be unique – avoid double work!
By having every assertion be unique, the problem-solving group mitigates the risk of double work, or even worse, that two non-unique tertiary assertions validates contradicting assertions.
3.2.2: Leave no stone unturned – all possible solutions/causes are analysed
By having a Collectively Exhaustive list of assertion, no stone is left unturned. This means that all possible solutions are pressure-tested for impact on assertions.
Context and Application
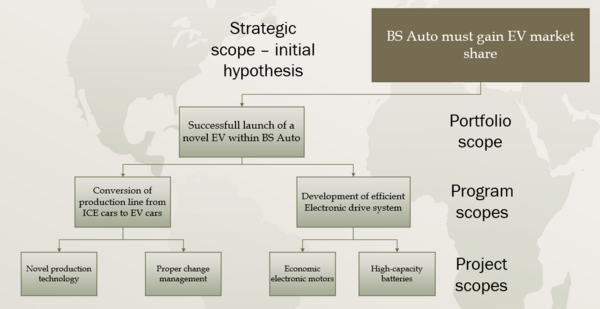
A strength of this tool is its' scalability, allowing it to be utilized in both project, program and portfolio management. Being able to adjust the generalization level of the initial hypothesis to the level of the problem can scope this tool to fit the it [McKinsey].
In this example, the scope of programs, portfolios and projects in this makeup car manufacturer BS Auto is derived from the overall strategic/business goal of wanting to gain EV (Electronic Vehicles) market share within the car industry eg. the portfolio scope should be 'Model insert-fancy-model-name-here'. Similarly, program and project scopes can be derived from the logic tree that is developed from the answer-first assertions in the logic tree.
In relation to other tools with a hierarchical structures
Other relevant and popular tools like the root cause analysis and work breakdown structure also use a hierarchical structure to visualise dependencies and hierarchy. While they definitely carry resemblance in the way they are used to breakdown something complex into easier to manage elements, they have different abstraction levels and are also different in what they are trying to communicate As such they should be used differently. In order to distinguish between them a summary and a collection of use cases are presented below:
Root-cause analysis: The Root-cause analysis tree is mostly used in the context where the goal is to find the root cause for a particular error or undesired state of something, often leading to a very deep dive into a very specific and detailed level
- A production where the end-product experiences too many errors during production (Ishakawa)
- A mechanical problem on a complex machine
- Why you are still single
Work-structure breakdown:
In conjunction with system-oriented problem solving
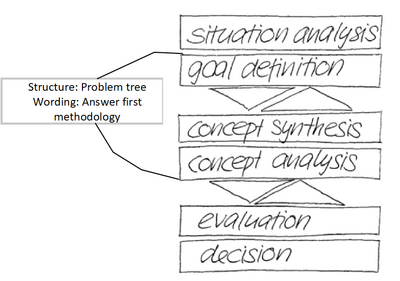
As it happens, this methodology fits neatly into the system-oriented problem solving method. In fact, literature suggests that Answer First principles and structure Logic Tree brings to the table is a good idea to implement while approaching goal definition and concept synthesis in the system-oriented project solving process:
"The result of the goal definition is a structured catalogue of objectives. This catalogue of objectives is further used in the concept analysis and selection" Page 91. No more muddling through
As such, it is recommended to use the Logic Tree as a way to clearly structure objectives, worded in answer first principle, in the goal definition stage. Note that the objectives in this case should be the primary and secondary assertions, and not the tertiary as these are concrete, testable solutions.
"In the first step of a synthesis-analysis-cycle, a wide and comprehensive range of solutions is developed with only a shallow description of the details. This first step aims at completely covering the field of possible solutions" Page 95. No more muddling through
Utilizing MECE, the Tertiary assertions here represents the wide and comprehensive range of concrete and validate-able solutions. This falls perfectly in line with purpose of the concept synthesis that is to find diverse and concrete solutions which are related to our objectives (Primary and secondary assertions).
" The concept analysis aims at identifying unsuited solutions or individual deficiencies selecting and improving ideas and solutions and narrowing down the spectrum of alternatives in the process of the analysis" Page 95. No more muddling through
" In principle, the concept analysis is about examining ‘validity’ of the individual solutions. For this purpose, the solutions have to be analysed under different aspects." Page 103. No more muddling through
The general concept analysis aims to validate these solutions by way of critically examining and whether they fulfil and affirm the parent assertion. Concrete Data and facts should support the decision whether the tertiary assertion is either valid or invalid.
To sum up, it is recommended to use Logic Tree for its structural and complexity reducing capabilities as an alternative to the Black Box method in conjunction with the Answer First Methodology for its communicative benefits. More specifically, in the system-oriented problem solving context, it is desirable to use the methodology in the recursive procedure in the steps of Goal Definition, concept analysis and the general concept analysis.
How-to-use handbook
What is presented here is a complete step-by-step guide on how to implement this tool in the field:
- Workshop setting with Project team and problem owners - Frame the problem the Initial hypothesis solves and explain present an initial plan of the problem solving procedure. :
- Firstly, we need to understand the context of the problem the initial hypothesis addresses (Pyramid). For this, scoping tools like the Task analysis and/or System Demarcation can be used in a workshop setting to illustrate and facilitate and understand of context.
- Consider if there are elements in the environment that can cause complications
- Make efforts to understand industry specific particularities
- Map important stakeholders including the problem owner
- Develop a fact-base to support a concrete problem statement (eg. Financial statement supports that Revenue has declined by X in the recent year)
- Develop initial hypothesis (IH) within the project team´:
- Develop an initial hypothesis that solves the problem
- Consider whether your IH is your general enough - rather be too general and scope down later, than too narrow and missing important aspects.
- Be as concise as possible - the IH should not be the length of a novel, but rather a sentence.
- Consider whether
- Avoid outside influence: The problem owners may already have an idea for a solution or the root of a problem. Put this aside, as it will bias your search for solution
- Develop an initial hypothesis that solves the problem
- 2 Workshop: Break down initial hypothesis´ with your project team: Break down your IH into its central components - what facts must be valid for the IH to be true?
- Remember the MECE principles: Develop Mutually Exclusive and Collective Exhaustive assertions
- Consider at what time an assertion is difficult to reasonably break down anymore. Is it verifiable? If yes, it is a tertiary assertion (McKinsey)
- Enable a idea-rich environment: Use brainstorming techniques for assertion generation! And remember - no idea is inherently bad. You can always discard the idea later if it is not relevant.
- Consider your team and their skills and knowledge. Are you well covered within this problem and industry scope? If not, consider acquiring expertise to help the breakdown of the problem
- Stakeholder meeting: Communicate your Logic tree to stakeholders:
- Stakeholders management is an important aspect of any P/P/P (Project). Communicate your answer-first Logic tree to stakeholders to inform them of your initial draft of a solution.
- Bring them into the discussion: If they can find inconsistencies in the reasoning between assertion or additional assertions consider adding them to the model.
- Gauge their satisfaction and compromise if necessary: Not all solutions, even though they might technically be the best solutions, is the best for the problem owner and other important stakeholders for various reasons (Stakeholder engagement).
- Stakeholders management is an important aspect of any P/P/P (Project). Communicate your answer-first Logic tree to stakeholders to inform them of your initial draft of a solution.
- Create a detailed workplan that aims to validate or invalidate tertiary assertions
- Consider incorporating other task management tools like GANNT charting, weekly meetings, SCRUM
- Set clear deliverables for each tertiary assertion and assess how much data is sufficient to properly analyse it
- Workshop: Consolidate validity of tertiary assertions and re-evaluate Logic Tree
- Next is bringing the data to work. The goal of this workshop for your project team is to consider what impact the data-gathering and analysis have on the coherence and reasoning in the Logic Tree
- Does the invalidation of some assertion require a dismissal or reformulation of some assertions?
- Reconsider the IH based on the Logical conclusions that comes from the bottom-up from the primary, secondary and tertiary assertions. Does it still hold truth or should it be changed? Does the potential change imply new assertions that need validation?
- Next is bringing the data to work. The goal of this workshop for your project team is to consider what impact the data-gathering and analysis have on the coherence and reasoning in the Logic Tree
Limitations
Text