Brain Storming Technique
Contents |
Abstract
- History:
Brainstorming as an idea for the first time emerged back in 1942. The term was introduced by Alex Faickney Osborn, founder and advertising executive of the US advertising agency BBDO. In fact, brainstorming was introduced as a creative technique inspired by the working atmosphere in BBDO. Namely, during his time in the company, Osborn’s observations of the everyday work in the office took him closer to developing this creative technique. He found out that during the company’s meetings and discussions, all employees were not proposing creative ideas, methods or solutions, which resulted in poor meetings’ closings.
Business meetings are supposed to be an opportunity to set goals and objectives, present and define problems, propose and discuss ideas, and in the end, work toward realizing them. Osborn was aware that the conventional business meetings he and his colleagues held didn’t include an exchange of fruitful ideas and were usually suppressing people’s spontaneity and the ability of free-thinking. This inspired him to establish new basic principles of conducting effective meetings that will be based on freedom of mind and creative thinking. [1]
Purpose
The purpose of brainstorming is to generate ideas and share knowledge to solve a particular commercial or technical problem. The participants are encouraged to think freely without interruption.
Having a clear idea of the topic to be addressed is critical to creating a successful brainstorming session. A topic that is too specific can restrict thinking, while an ill-defined topic will not produce enough directly applicable ideas.
Big Idea
- Defnition:
The concept of brainstorming includes defining a simple or a complex problem for which solutions are generated from different ideas that are later accepted or rejected. The participants in the process of brainstorming present and reveal new ideas as potential solutions for a specific problem. In this process, brainstorming helps the stimulation of the human mind towards creative problem-solving.
Osborn’s approach to brainstorming and his few simple rules from the beginning until this moment have helped in solving many important issues. Brainstorming as a group activity has become a revolutionary technique that can find its use in both small and large enterprises regardless of the industry in which they are operating. Moreover, it can be beneficial for individuals who are in need of a solution for a specific problem.
This creative thinking technique as a group activity usually starts with a gathering of a group of people. As an informal method of problem-solving, group brainstorming stimulates creative thinking. The proposals that come up in these constructive meetings can provoke interesting and unusual ideas that later could become a creative solution to a problem. [2]
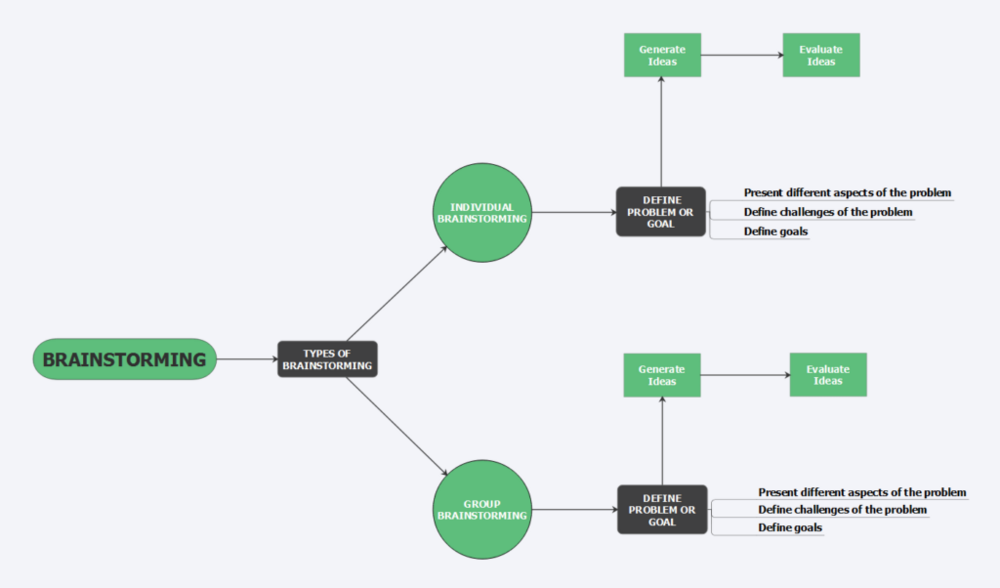
- Types of brainstorming:
1- individual Brainstorming:
Self Brainstorming includes storming by yourself, it takes a different approach than group storming as it opens the space and opportunities for those introverts who experience idea blockage in group work to produce a wider and bigger variety of ideas. Being on your own can give the sense of flexibility and comfort also giving the space to discover a variety of simple, weird or complex ideas which usually would have felt afraid to present in order not to get judged or criticized.
2-Group Brain Storming:
consisting of a group of people and while keeping it within the rules, group brainstorming is the most efficient as it generates a wider and bigger quantity of possible solutions to the facing problem, the more the group members the more ideas available to build up upon and in the end more areas and possibilities to discover. opposite to individual Brainstorming, group brainstorming clears the way for those individuals who face idea blockage during self idea generation, which in this case will limit the creativity or passion towards generating possible outcomes and solutions.
Figure 1:Types of BrainStorming.[3]
- Advantages:
There are many benefits to brainstorming as it is one of the most useful tools for problem-solving process and helping in achieving better communication in the meanwhile, one of the major benefits:
1-Encourages Creativity:
Brainstorming creates a lot of ideas and promotes organizational innovation. It broadens members' thinking so that they can come up with the most creative solutions to the problem.
It can provide a variety of options since Ideas are formed in groups rather than individually.
2-Generates bigger quantity of ideas:
Since the process is made by a group, and if the moderator motivates the members to produce the most amount of ideas in the shortest timeframe, This creates the maximum amount of ideas possible and guarantees a good quantity.
3-Participation builds Responsibility:
Since the process is a collaborative experience, all members of the meeting will participate in the idea generation. This creates a sense of ownership and responsibility towards the issue or project. Which will then increase the passion and motivation to reach even a higher point of creativity and production.
4-Easy to setup:
The brainstorming techniques which will be mentioned below, are once acquired easy to set up, understand and use. which reduces the sense of confusion and time-wasting.
5-Saves Resources:
Since most of the brainstorming techniques are digital or basic office material, in addition to not requiring much time and resources to set up. it guarantees saving time and money other than other consulting options.
-In order to make sure that these Benefits are established and acquired several steps or rules has to be done.
These rules and Suggestions are carried out or set by the organiser which can be the team leader, supervisor or even a Manager, they are made to make sure to get the most out of the brainstorming session.
An example of some of the rules:
1-set a deadline: Setting a deadline helps improve the speed of the idea generation process
2-Define the main problem/goal: Start the process with a clear definition of the needed goal to achieve or problem to solve, in order to focus the ideas on the desired outcome.
3-Deny or block any Idea criticism: By working with the principle that there are no bad ideas, the members involved would not feel shy or preserve some of the ideas, which might define the needed solution. in addition to removing chances of conflicts or bad feelings in working the environment.
4-Quanitity over quality: Keep motivating even the simplest ideas in order to produce the biggest number of possible solutions which will be later on filtered in the process.
5-use variety of tools: By using the big variety of tools in hand and digitally the members can achieve better and more organised solutions, this also helps to structure the thought process and solution filtering in the next steps such tools are: SWOT which will be discussed in the Applications part.
Application
Phase 1: GENERATION OF IDEAS:
1. Preparation. Know your goals. Clearly define where you are now and where you want to be.
2. Prepare an executive summary that can be quickly scanned for the key points you need your team to focus on.
3. Now decide whom to invite.
4. Provide the executive summary with the meeting request, and ask them to bring three ideas to share during the session.
5. Reserve ample time for your group to be effective, yet focused. Motivation decreases with each follow-up session you have to add.
Phase 2: DISCUSSION OF THE PRODUCED IDEAS:
1. Facilitation. Like any meeting, a brainstorming session needs structure. Designate a facilitator to encourage participation, act as a timekeeper.
2. Have a note-taker write ideas on a whiteboard or easel pad. This will have one major positive consequence – visual proof of progress.
3. Before ending the session, make sure there are clear, agreed-upon takeaways and next steps. Everyone needs to leave the session knowing his or her role in the next phase.
Phase 3: FINAL EVALUATION OF THE PRESENTED IDEAS:
1. Follow Through. After the session, share the most viable ideas, separating them by those more easily implemented vs. those tabled for further discussion. If possible, take action on one or two ideas immediately, so everyone can see the result of their work.
2. Don’t let the good ideas fall into a black hole. Make sure a single person, strong in follow-through, is responsible for advancing the ideas and achieving your original goals. This person might be you, but can be a key staff person.
3. Communicate progress with the entire team, even those who have no further role after the session. Keeping colleagues informed shows them you value their time and knowledge. [4]
Examples of Brainstorming uses:
1- Problem Solving
2- Marketing advertisements
3- Project Management
4- Process Management
5- Management Planning
6- any other obstacle-solution scenario in real life.
Limitations
Annotated Bibliograhpy
- ↑ [Brainstorming iMind] https://www.imindq.com/brainstorming/
- ↑ [BrainStorming iMind] https://www.imindq.com/brainstorming/
- ↑ [BrainStorming iMind] https://www.imindq.com/brainstorming/
- ↑ [Three phases of effective brainstorming]https://www.memphisdailynews.com/news/2016/feb/17/three-phases-of-effective-brainstorming/