MTA (Milestone trend analysis)
created by Luisa Buchta
Abstract
Within project, program and portfolio management, the Milestone Trend Analysis (MTA) can be found under the section Uncertainty. It is a tool for Monitoring that is mainly used for Project Controlling. According to ISO 21502 Project Controlling covers monitoring and measuring performance against an agreed plan of projects, including phases and work packages. This also includes authorized changes. [1] [2]
The MTA is an effective tool to visualize the milestones within a project. It helps controlling the project by showing which milestone is ahead of, on, or behind schedule. The MTA uses different timelines: the reporting dates and the milestone dates. [2] [3] [4] The curves express the projects‘ performance. A horizontal line means that the milestone is on time, an increasing line reflects that the milestone is later than planned and the decreasing line shows that it is earlier than planned. [2]
The MTA supports the project managers in that sense that it provides simple trend analysis charts with an overview of bottlenecks, already in the early stages. It also allows a realistic forecast of the progression of the project. [4] It therefore is a combination of history and forecast since it shows time-related discrepancies. It assesses the project’s health by allowing insights into the schedule. This can be seen as one of the MTA’s biggest advantages. [5] [6]
Those advantages are only applicable when regular reporting dates are set as well as the milestones for the subcategories of the project. Here it is important that the milestones as well as the dates are well defined. [6] The method has its drawbacks in the lack of objectiveness that requires the projects participants trust towards each other. [7] [8]
Contents |
Main Concept
Definition of Milestone and Trend analysis
Since the term MTA itself consists of different aspects that form crucial parts for a MTA, it is necessary to briefly explain the term milestone and milestone schedule as well as trend analysis before giving more insights on the MTA. Milestone: A Milestone is defined as a significant point or event in a project, program or portfolio, that marks the completion of key activities. [9] [10] Those key activities can be from different natures like completing a work package, a delivery step or a management stage. [11] In addition a milestone must be defined, understood, measurable and quantifiable. [12]
Milestone Schedule: A milestone schedule is described as a type of schedule that presents milestones with planned dates. [9] The milestone schedule is sometimes also referred to as a milestone plan. Information to be included is the project start date, project end date, other major milestones and data items like deliverables or reports. [13] Trend Analysis: Trend Analysis makes use of mathematical models to forecast future outcomes based on historical results. [9], [14] The main advantage of trend analysis is its key function of being an early warning system and therefore allowing managers to take preventive measures.[13] Hence it is based on the idea that what has happened in the past will continue happening in the future.[14]
Description of MTA
„The MTA is a special form of the trend analysis based on the milestone plan.” [2] It shows the project’s development over time. [6] Combining milestone schedules with trend charts leads to MTA. It is a tool to keep track of the project milestones and therefore also the project schedule. It can therefore be found under the knowledge area of time management. [15] The term Milestone Trend Chart (MTC) is often used in the context of milestones and scheduling techniques, and it might appear to be similar to the MTA. [12] It has to be distinguished between the two terms though because the MTA uses the typical triangle shape whereas a MTC in general can be a flow chart as well. [16] The tool allows a visual overview of the milestones within a project and is a combination of history and forecast. It shows time-related discrepancies and therefore assesses the health of a project and allows insights into the schedule. This is achieved by estimating the date on which the future milestone will be done for every reporting period. The software should generate new estimated completion dates of all future milestones by taking into account the completed milestones and the revised completion dates for the milestones. [12] The MTA supports the project managers in that sense that it provides simple trend analysis charts with an overview of bottlenecks, already in the early stages. It also allows a realistic forecast of the progression of the project. [2] It is up to the project managers to decide how detailed the milestones will be but one important milestone that should always be looked at is the completion date of the project.[12]
Importance and relevance of performing MTA
Since milestones express important states which the projects should pass, they also represent important results and have more value besides being a checkpoint. [7] The purpose of breaking plans into smaller intervals with milestones gives a better overview over the project schedule and allows project managers to deal with schedule issues faster. [11] Monitoring the progress of smaller milestones within a project is an important factor to the project’s success. [12] Reporting completion dates of milestones forms an important part of project control. It allows to decide between different possibilities of what to do in case the reporting reveals a lapse in project process. This can be moving the completion date, lowering the level of ambitions, bringing in additional resources and rearranging the workload. [7] The completion dates are important, but it shouldn’t be the reason why delays aren’t being reported. It has to be kept in mind that the project will be assessed on whether or not the project is on schedule. Reporting anticipated variance from completion dates helps the project by being able to find the causes for those occurrences. Therefore, it is equally important to aim for completion within time as to constantly report delayed completion dates. [7] Trend analysis is especially important in long-term projects to take corrective action in case of mayor delays within a project. [13] Furthermore, trend analysis is seen to be the most important information in project control since predicting via trends is more helpful than “just watch it happen”. [16] Unfortunately forecast to predict future performance is left out in a lot of projects, but in industries where time to market is a competitive advantage it is crucial to perform trend analysis. [16] Since every project is different, it can be difficult to set a standard of how often a MTA should be performed, but the general rule is that a major milestone should be scheduled at least once each month. The consequence is that in order to perform a meaningful MTA it should also be conducted once a month. [17] This frequency of performing MTA is common practice in all sorts of different companies. The milestone status should then be reported in milestone meetings with those responsible and those involved. [2]
Application
Graphical Background and Functionality
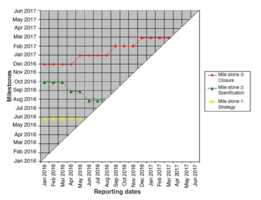
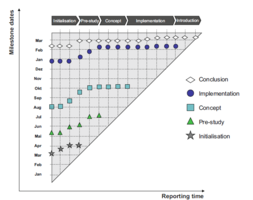
Another important part of the topic is how MTA works. This section is about the graphical background of the chart and the data that is necessary to use it. As already mentioned, enough milestone dates must be available to perform MTA in the first place. This is also important for the graphical background of the chart, that’s why it is stressed again in this section. [6] The MTA uses a simple graphical methodology where the horizontal axis represents the reporting time and the vertical axis the milestone dates. [2], [6] This is also the reason why there is no information on the lower right side of the chart, since the dates progress, which leads to its typical triangle shape.[18] Once the line of a work package hits the angle bisector the task is done. [8] The two different example graphs show how a MTA could look like. Design wise each MTA can differ a lot. In Figure 1 the different dots are connected to each other with a line, whereas Figure 2 only shows the symbols, which are also different to each other. To make it graphically even more interesting it is also possible to already include bigger symbols with the different milestone stages in the top horizontal axis. It should be mentioned that the Figure 1 show a MTA that has already been performed for a longer period of time. When initially starting the MTA only the dates on the very left side are visible like it can be seen in Figure 2.
For every reporting date a cross will be added at the respective coordinate for the milestone. After several reporting dates, those coordinates then build a trend line.[2], [6]. This line is then used to interpret the course of the milestones. [2], [12] - Horizontal: no deviation, project is within schedule - Decreasing: milestone earlier than planned, potentially too much buffer - Increasing: milestone later than planned, postponed several times
It can also occur that the trend line is alternately decreasing and increasing. This is an indication of high uncertainty of the date statements.[8] Another possibility can be that two lines with different milestones that are dependent on each other cross. This indicates a clash of dates which should be compensated by reducing the agreed output with the customer early enough.[8] The graph can consist of different lines representing various milestones with diverse topics within the same project. [2], [6] Those different lines can include different work packages that depend on each other. This then also means that if a previous milestone is already late, the dependent milestones should also be updated in time. Here it is quite important to mention that the project manager should be able to identify those delays and update the time delay of the dependent milestones as soon as possible.[8] If that is not the case this slow reaction towards the delays will be visible in the MTA for people who have common understanding of the chart. Regarding the number of different lines in one chart it should be mentioned that although it helps in general to have more than one different milestone in one chart, too many milestones also make the chart confusing and this should be avoided. [19] It becomes clear, that the amount of data that is needed to do MTA is relatively low. It consists of the pre-defined milestones at the beginning of the project and the deadline forecasts for the awarded milestones as of the respective cut-off date. Those dates don’t require more information since it is based on the assessment of the project manager.[2], [7] There are a lot of different tools which help to implement a MTA, like Microsoft Project or Microsoft Excel. [18] It is highly recommended to use a tool for MTA since it saves a lot of time and effort by automating the task. Also, because the other alternative of drawing on paper doesn’t fit modern reporting standards anymore. The important basic information that all the different tools have in common and use to generate the MTA graph is a simple table. It contains information of the status date which will be the current date or the so called reporting date and the date of the milestone is necessary. [19] Such a table is presented in the picture (benennen). For this specific table it becomes clear that at the reporting dates of 4.2. and 4.3 the completion date of the milestone was the 10.10, whereas at the next reporting date (4.4.) the milestone completion date had to be adjusted by 5 days.
Application possiblities
Discussion
Advantages
Limitations
Annotated Bibliography
References
- ↑ International Organization for Standardization, "ISO 21502:2020 Project, programme and portfolio management — Guidance on project management", 2020
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 M. D. Alam and U. F. Gühl, “Project Phases,” in Project-Management in Practice, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2016, pp. 55–121. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-52944-7_3.
- ↑ P. Stoemmer, “Milestone Trend Analysis.” https://www.project-management-knowhow.com/milestone_trend_analysis.html (accessed Feb. 10, 2022).
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 S. Reister, “Milestone Trend Analysis - Free Tool for MS Project.” https://www.theprojectgroup.com/blog/en/milestone-trend-analysis-ms-project/ (accessed Feb. 10, 2022).
- ↑ M. Waida, “What is a Milestone Trend Analysis?,” Jul. 17, 2020. https://www.wrike.com/blog/what-milestone-trend-analysis/ (accessed Feb. 10, 2022).
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 J. Kuster et al., Project Management Handbook. Springer-Verlag, 2015. [Online]. Available: http://www.springer.com/series/10101
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 E. S. Andersen, K. v. Grude, and Tor. Haug, Goal directed project management: effective techniques and strategies. Kogan Page Ltd, 2009.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 R. Fiedler, Controlling von Projekten - Mit konkreten Beispielen aus der Unternehmenspraxis - Alle Aspekte der Projektplanung, Projektsteuerung und Projektkontrolle, 7th ed. Würzburg: Springer Vieweg, 2016.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Project Management Institute, The Standard for Project Management and A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK guide), 7th ed. 2021..
- ↑ Nicholas, John M, Steyn, and Herman, Project Management for Engineering, Business and Technology, 6th ed. New York: Routledge, 2021.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 AXELOS, Managing Successful Projects with PRINCE2 2017 Edition, 2017th ed. TSO, 2018.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 12.4 12.5 R. K. Wysocki, Project Management Process Improvement. 2004.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 H. Kerzner, Project Management - A Systems Approach to Planning, Scheduling and Controlling, 12th ed. Wiley, 2017.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 A. Hayes, “Trend Analysis,” Investopedia, Sep. 05, 2021. https://www.investopedia.com/terms/t/trendanalysis.asp (accessed Feb. 11, 2022).
- ↑ P. Patanakul, B. Iewwongcharoen, and D. Milosevic, “An empirical study on the use of project management tools and techniques across project life-cycle and their impact on project success,” 2010.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 R. J. Martinelli and D. Z. Milosevic, “Project Management Toolbox,” vol. 2nd. Wiley, 2016.
- ↑ J. A. Ward, “Productivity through project management,”,Information Systems Management, 10580530, Vol.11, Issue1, 1994.