Risk Treatment in project management
Contents |
Abstract
In a project, a program, or a portfolio there will always be a number of activities. All these activities will involve risk to some degree – either as a threat or an opportunity. If risks are not managed in the project, program, or portfolio it will be difficult to accomplish success. Therefore, it is important for the project, program, or portfolio leader to manage these risks by identifying them, evaluate them and treat them. The latter will be the focus of this article. Risk Treatment, also referred to as Risk Control, is the discipline within Risk Management that takes place once a risk has been identified and assessed. Here, appropriate measures are put in place to mitigate and reduce all unacceptable risks and to steer them towards an acceptable target level. The identification of the treatment measures should be done from a cost benefit point of view, analysing the cost of treating the risk up against the potential benefits. Furthermore, as time and resource are often a limited factor, the identification and treatment should be focused on the most important risks identified from the preliminary evaluation phase. Risk Treatment is split into four main categories, namely risk avoidance, risk sharing, risk reduction and risk retention. Risk avoidance is the option where one simply avoids the underlying activity that causes the potential risk. Risk sharing is done by transferring either fully or parts of the risk to other stakeholders e.g., by insurance or by outsourcing the related activities externally. Risk reduction is done by removing sources of threats, reducing or removing the severity of vulnerabilities and by generally reducing the likelihood of threats. Lastly, risk retention is the category where the risk is accepted, due to either an acceptable threat level or a too costly treatment given the alternative options. [1]
Big Idea
To understand risk treatment, it is first necessary to understand what Risk Management is and where in the Risk Management process the treatment occurs.
In the ISO 31000 standard, Risk Management is defined as: “Coordinated activities to direct and control an organization with regard to risk” (DS_ISO 31000_2009, s. 2). This means that Risk Management controls several different activities that in combination with each other seeks to protect an organization towards risks. The purpose of risk management is to increase the probability of achieving the main goals and objectives of the project, program, or portfolio. This is done through the Risk Management Process as seen illustrated on figure XX.
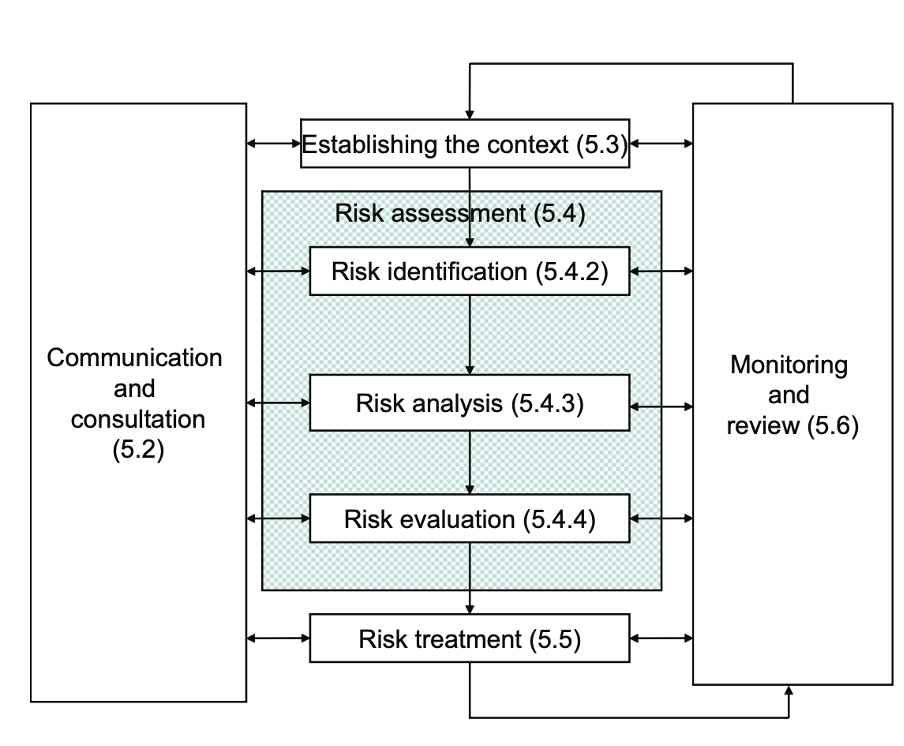
Kilde: DS_ISO 31000_2009. Figur: Risk management process.
First, the context of the project, program or portfolio needs to be established. This is done by articulating objectives, defining the parameters that needs to be considered, both internally and externally, and setting the overall scope of the project, program or portfolio. Secondly, the Risk Assessment phase should be initiated. This phase consists of three steps. First step is the Risk Identification phase. Here, a comprehensive list of risks related to the project, program or portfolio is made which creates the foundation for the risk analysis. In the risk analysis, all risks from the identification phase are understood by considering their causes and sources, their potential consequences, and the likelihood of occurrence. The risks are then evaluated based on the analysis. This creates a benchmark for the decision making where risks are to be prioritized, leading the risk management process into the final phase, Risk Treatment. This topic will be expanded further in the following section.
Risk Treatment
As previously described, Risk Treatment is the last activity in the Risk Management process. Risk Treatment both adresses the positive and negatives risks, accordingly also referred to as opportunities and threats. Opportunities are the risks that have the potential to create a positive impact on the project, program or portfolio while threats are the kind of risk that are likely to have a negative impact on the project, program or portfolio. The latter is often the type of risk that people think of when hearing the word risk. Options that can be used to treat risks with a potential positive outcome (Opportunities) include but are not limited to [2]:
- Beginning or continuing the activity that has been assed to cause a positive impact
- Manipulate possible positive consequences to maximize estimated gains
- Increase the likelihood of the risk to elevate positive outcomes
- Share the risk with other stakeholders that could either increase the likelihood of the risk happening or benefit from the risk happening themselves, increasing their motivation to provoke the risk
Also, options that can be used to treat risks with a potential negative outcome (Threats) are very similar to the ones above although they have the direct opposite meaning and interpretation. These options include but are not limited to [2]
- To simply avoid the risk by stopping, cancelling, postponing or diverting related activities
- To share the risk with other stakeholders
- ASDasd
- ASdasd
Management options for risks having negative outcomes look similar to those for risks with positive ones, although their interpretation and implications are completely different. Such options or alternatives might be:
to avoid the risk by deciding to stop, postpone, cancel, divert or continue with an activity that may be the cause for that risk; to modify the likelihood of the risk trying to reduce or eliminate the likelihood of the negative outcomes; to try modifying the consequences in a way that will reduce losses; to share the risk with other parties facing the same risk (insurance arrangements and organizational structures such as partnerships and joint ventures can be used to spread responsibility and liability); (of course one should always keep in mind that if a risk is shared in whole or in part, the organization is acquiring a new risk, i.e. the risk that the organization to which the initial risk has been transferred may not manage this risk effectively.) to retain the risk or its residual risks;
Application
Provide guidance on how to use the tool, concept or theory and when it is applicable. As mentioned in the Risk Treatment Process, the following steps should be taken before the treatment can occur:
1) Identify the risks 2) Asses the risks) 3) Plan on what you do as treatments on the risks
Insert 4 phases.
- Very useful in programs and portfolios, where risks and treatments can be discovered along the way -
Treatment plans
proposed actions, priorities or time plans, resource requirements, roles and responsibilities of all parties involved in the proposed actions, performance measures, reporting and monitoring requirements.
Development of Treatment plans
Approval of Treatment plans
Implementation of Treatment plans
Limitations
critically reflect on the tool/concept/theory. When possible, substantiate your claims with literature
- Impossible to first of all identify all risks in a project, secondly to create treatments for them - Risks are often identified through historical data/events. Certain things has happened previously in a project or similar cases, and have therefore been identified and documented as a risk. However, this can be difficult to predict/find data on in a time limited project where a lot of things are new. - Development of treatment plans can take time and not be useful in shorter projects. - More ideal for programs and portfolios, where data can be added to already existing data and where the treatment continuously can be developed over time. - Difficult to quantify the responses and they will therefore often be based on a persons opinion. [4]
Annotated bibliography
Provide key references (3-10), where a reader can find additional information on the subject.
References
- ↑ International Organization for Standardization (2018), DS/ISO 31000:2018, Risk management - Guidelines, Retrieved from https://sd.ds.dk/Viewer?ProjectNr=M296412&Status=60.60&Inline=true&Page=1&VariantID=41
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 ENISA, European Union Agency for Cybersecurity. Threat and risk management, Risk Treatment. Retrieved from: https://www.enisa.europa.eu/topics/threat-risk-management/risk-management/current-risk/risk-management-inventory/rm-process/risk-treatment
- ↑ Project Management Institute, Inc. (PMI). (2019). Standard for Risk Management in Portfolios, Programs, and Projects. Project Management Institute, Inc. (PMI). Retrieved from https://app.knovel.com/hotlink/toc/id:kpSRMPPP01/standard-risk-management/standard-risk-management
- ↑ International Organization for Standardization (2020), DS/ISO 21502:2020, Project-, programme and portfolio management - Guidance on project management, Retrieved from https://sd.ds.dk/Viewer?ProjectNr=M351700&Status=60.60&Inline=true&Page=1&VariantID=