Management and leadership differences
Abstract
Management and leadership are both critical in achieving the desired results in any project. The two concepts are sometimes misunderstood as being the same and are commonly confused for one another. It is understandable since they share several common characteristics, but in fact management and leadership are two separate concepts. Management focuses on ways to achieve project objectives. That includes planning, organizing and monitoring the work. On the other hand, leadership focuses on people and activities involved with the project team. That involves inspiring, guiding, listening and influencing team members. Excellent project managers possess a combination of both leadership and management skills. The balance may vary depending on the circumstances but combining qualities of both allows project managers to organize and monitor the undertaking project as well as motivating their teams to succeed [1].
This article will explain the differences between management and leadership in more detail, by defining the two concepts separately and comparing the differences and similarities. Furthermore, guidance will be provided on how to apply the concepts for project managers as well as pointing out limitations.
Contents |
Management
Definition
The simplest definition of management is "making things happen" [2]. More specific, management is the process of determining what has to be done and then completing it with the best possible use of available resources. It focuses on the actions managers take to put work into action. Bringing about, accomplishing, having charge of or responsibility for, and conducting anything are all definitions of managing. Management involves setting objectives and identifying the necessary resources such as people, finances, work systems, and technology. They furthermore assign the resources to scheduled actions and make sure that the planned actions happen as expected to accomplish predetermined objectives [3].
In the context of project management, PRINCE2 defines management as the planning, assigning tasks, monitoring and regulating every element of the project, motivating those who are involved, and meeting the project objectives within the projected performance metrics for factors such as time, cost, quality, scope, benefits and risk [4]. The definition of project management from PMBOK guide is applying knowledge, skills, tools, and procedures to project activities in order to achieve project requirements. Project management is the process of directing project work to produce the desired results. Project teams might use a variety of techniques to produce the desired results. Moreover, project manager is the individual chosen by the performing company to lead the project team and be in charge of attaining the project's goals [1].
Processes
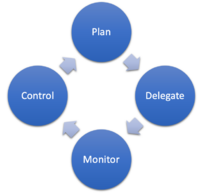
The processes of management to execute any project can be divided into a number of separate processes. However, the main management processes have been defined by PRINCE2 as the following four managerial elements: plan, delegate, monitor and control.
Plan: Write
Delegate: Write
Monitor: Write
Control: Write
Figure from PRINCE2
...
Competences
To achieve the above mentioned processes effectively, management requires a wide range of skills, behaviours and qualities. Managerial skills suggested to be needed ...
...
The managerial behaviours that will result in effective performance are achievement orientation, business awareness, communication, customer focus, developing others, flexibility, leadership, teamwork, problem-solving
From Handbook, p. 26-27
...
Management qualities is about doing the things right, including:
- Rational
- Consulting
- Persistent
- Problem solving
- Tough-minded
- Analytical
- Structured
- Deliberate
- Authoritative
- Stabilizing
- Position power
Subsection
Leadership
Definition
We are quite knowledgeable about management, but less so about leadership. Several specialists have tried to define this concept and there are more than 400 definitions of leadership. There are numerous perspectives on leadership as well as numerous interpretations of what it means. Simple definitions of leadership include "getting others to follow" and "getting people to do things voluntarily." Leadership can also be defined more narrowly, such as "the use of authority in decision-making." It might be used due to personal expertise or wisdom, or as a function of one's position. Leadership can be viewed as either a behavioural category or as a personality trait. Another way to look at it is from the perspective of the leaders and their capacity to influence others to perform effectively [2].
The following definition is from the Handbook of Management and Leadership by Michael Armstrong: “Leadership is about inspiring individuals to give of their best to achieve a desired result, gaining their commitment and motivating them to achieve defined goals.” [3].
According to PMBOK guide, leadership is one of the principles that a project manager should acquire to support the needs of the team and the individuals. Project success is facilitated by effective leadership. Better outcomes may result from a project environment that emphasizes vision, creativity, inspiration, enthusiasm, encouragement, and empathy. These characteristics are frequently connected to leadership. Leadership is the attitude, skill, character, and behaviours needed to influence those on the project team and outside it to achieve the desired results [1].
PRINCE2 states that it is not possible to define leadership in a method, despite being the utmost importance in project management. Leadership styles differ greatly, and what works in one circumstance may not be suitable in another. This is supported by how easy it is to think of examples of successful leaders who have used a variety of leadership styles, from authoritarian to collaborative [4].
Roles
Role and function of leadership and what is expected...
...
Competences
Leadership competences such as skills, behaviour and qualities is something that can be practised. Any team member in a project can grow leadership skill. It is something that can be learned and developed so that it helps the project and its stakeholders while also helping the individual's career. PMBOK provides four skills that are associated with leadership, which are establishing and maintaining vision, critical thinking, motivation and interpersonal skills [1].
- Establishing and Maintaining Vision: A purpose exists for each project. It is essential that the project team members understand that purpose for them to devote their time and energy in the proper direction toward reaching the project purpose. The purpose of the project is summarised in the project vision. The vision outlines an appealing but realistic view of the projected results in the future. The vision is not only a description of the desired future condition, but it also serves as a potent motivator. It is a method for inspiring passion and meaning for a project's intended objective. Having a shared vision keeps everyone moving in the same direction
- Critical Thinking: It is necessary across all the many project performance areas to recognize bias, determine the root cause of issues and take into account difficult problems like ambiguity, complexity, and so on. These tasks can be completed with the use of critical thinking. Disciplined, logical, and evidence-based reasoning are all components of critical thinking. It requires the capacity for objective analysis and an open mind. Conceptual imagination, insight, and intuition are possible components of critical thinking, particularly when it is used for discovery.
- Motivation: Understanding what motivates project team members to perform is the first step in motivating project team members. The second is working with project team members in a way that keeps them dedicated to the project and its goals. Motivation might come from within (intrinsic) or from outside (extrinsic). Intrinsic motivation derives from within the person or is connected to their work. It is related to enjoying the task itself rather than concentrating on the benefits. Extrinsic motivation is the practice of putting in the effort for an external benefit, such as a bonus. Although there are many different things that can motivate a person, most people have a dominating motivator. Knowing each team member's strong motivation might help to motivate them effectively. To achieve the best results from each individual and project team member, motivating techniques should be tailored based on personal preferences.
- Interpersonal skills: Emotional intelligence, decision making and resolving conflict are a few interpersonal skills that are regularly used in projects. Awareness of own emotions, empathy for those of others, and the capability to behave in a way that is suitable for the situation are the foundations of good communication, teamwork, and leadership.
...
Leadership qualities is about doing the right things, including:
- Visionary
- Passionate
- Creative
- Flexible
- Inspiring
- Innovative
- Courageous
- Imaginative
- Experimental
- Initiates change
- Personal power
....
The behaviour of a leader
Approaches
There are various distinct approaches of leadership due to its complex and varied nature. A framework for the study of leadership is provided by Mullins which includes the following approaches [2]:
- Qualities or traits approach
- The functional or group approach
- Leadership as a behavioural category
- Styles of leadership
- The situational approach and contingency models
- Transformational leadership
- Inspirational leadership
Comparison
Both management and leadership require influencing others, collaborating with others, and working toward shared objectives. The two concepts overlap, but despite their similarities they differ from one another. [5]. Leadership can moreover be viewed as a subset of management, and both are crucial for facilitating organizational performance [6]. Managers must be leaders and leaders are typically (but not always) managers. However, management and leadership can be distinguished from one another and the difference is crucial. In rough terms, management consists of controlling work while leadership focuses on leading people [3].
Management involves planning, budgeting, controlling, and structuring in order to obtain the desired results. On the contrary, leadership is referred to as the process of guiding, inspiring, motivating, coordinating, and enabling the growth of people. In addition, leadership is also described as a method of influencing others to help the organization achieve its long-term objectives [6].
Leaders will utilize their energy to inspire others to be innovative in problem solving, but managers will ensure that the organization's day-to-day operations are carried out, which may require ordering employees what to do if necessary. A leader has soul, passion, and creativity, whereas a manager has mind, logic, and determination. A leader is flexible, innovative, inspirational, brave and independent and at the same time a manager is consultative, analytical, cautious, authoritative and stable. The literature, however, differs on the basic competencies of leadership and management. Some studies have adopted a more extreme view, claiming that management and leadership are almost diametrically opposed tasks [6].
Being a good manager is not enough, you also must be a good leader. It has been stated that "Managers do the things right, leaders do the right things" [3]. A person can be a great leader, a great manager, or both, each one demands slightly different abilities and characteristics. The following table gives a comparison of leadership and management [6].
| Management | Leadership | |
|---|---|---|
| Involves | Planning and Budgeting | Establishing Direction |
| Establishing agendas | Creating a vision | |
| Organizing and Staffing | Aligning People | |
| Establishing rules and procedure | Building teams and coalitions | |
| Controlling and Problem Solving | Motivating and Inspiring | |
| Generating creative solutions | Empowering subordinates | |
| Characteristics | Rational | Visionary |
| Persistent | Creative | |
| Consulting | Passionate | |
| Analytical | Innovative | |
| Structured | Courageous | |
| Authoritative | Experimental | |
| Stabilizing | Independent | |
| Mind | Soul | |
| Problem solving | Flexible | |
| Tough minded | Inspiring | |
| Aspect | Focus on system and structure | Focus on people |
| Minimize risks | Takes risk | |
| Maintains | Develops | |
| Subordinates | Colleagues | |
| Controls | Empowers |
Practical approach for project managers
Instructions will be provided on how project managers can use the concept and when it is relevant.
For project managers it is necessary to be able to distinguish between the two separate concepts if one wishes to perform well or develop their management or leadership skills. The PMBOK guide provides a list of principles for project management which are meant to guide the behaviour of project participants. One of the principles listed is to demonstrate leadership behaviour. Each project team member can develop leadership behaviour. It is therefore important for the project manager as well as the project team members to grow leadership qualities to fulfil the needs of both individuals and the team [1].
For project managers the first step in developing essential leadership qualities is motivating and inspiring teams. Additional leadership qualities, including communicating, listening, influencing, and team building, are equally crucial, particularly in terms of boosting team performance [7].
Limitations
Here, the concept and its application will be critically reflected upon, using key resources and literature. For example, under what circumstances it can not be used and what it can not do.
The problem with the leadership concept (from Armstrongs Handbook)
Annotated bibliography
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK ® Guide) – 7th Edition and The Standard for Project Management.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Management & Organizational Behaviour, by Laurie J. Mullins, 7th edition
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 A Handbook of Management and Leadership: A Guide to Managing for Results, By Michael Armstrong and Tina Stephens
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Managing Successful Projects with PRINCE2®, 2017 Edition.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Are Leadership and Management Different? A Review, by Dr. Ali Algahtani.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 A theoretical perspective on the difference between leadership and management, http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
- ↑ Essential leadership skills for project managers https://www.pmi.org/learning/library/essential-leadership-skills-project-managers-6699#.