The 6C Model
Contents |
Abstract
During a design process, knowledge is produced in many ways, especially in multidisciplinary teams where several approaches are implemented to drive innovation, sustainability, and functionality. Non-design fields are increasingly influencing the traditional deign methods, including sketching, prototyping, planning and development[1]. To facilitate a holistic approach, a designer must have an understanding of how knowledge is produced and combine/integrate diverse fields to ensure shared understanding.
To help expand the designer's understanding the 6C Model has been developed, which describes six types of knowledge production in a design process. The model is designed to help the team members actively observe and become aware of different approaches when designing. Together with a collection of co-creation cards, the method helps translating knowledge into practical approaches (Friis, S.A.K.)[2] [3].
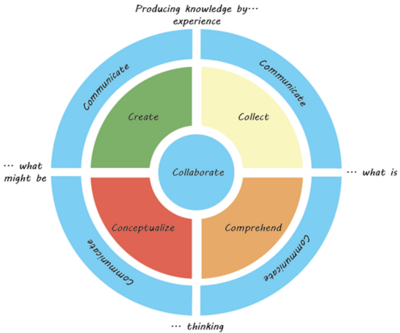
The model takes the design process through four stages: Collect, Comprehend, Conceptualize and Create, not necessarily in that order. This is held together using Collaboration tools and continuous Communication. The co-creation cards introduce specific step-by-step design methods within each of the six categories to promote continuous progress and help guide the project manager through the project.
The method introduces guidelines for creating project boundaries, which can be followed as a recipe in several projects to facilitate streamlined project baselines on a program level. The model makes it possible to map out the project stage, which is usually easy in well-structured project, but can be difficult in projects that follow an organic flow.
The term knowledge production refers to everything shared, used or implemented in the design process, which may contribute to a project. The method combines theory of cross-functional teamwork and understanding of the design process, similar to the 3 Cs[4] and the Double Diamond[5], respectively.
The 6C Model can be considered a management tool for mapping a project and choosing relevant design methods in open, complex problem solving. This article will explain the 6C Model and its comparison to similar models. Finally, benefits and limitations using this model will be discussed.
Introduction
Background
The 6C Model was originally developed by Friis and Gelting in 2016, with a focus on integrating co-creative design methods into everyday design practices. The model is a developed version of the 5C Model by the same creators[3]. It is a framework to facilitate the design process through observation, understanding and then conscious acting on diverse approaches of designing. The method aims to accommodate collaborations across different disciplines and cultures and expand design principles into new areas of application (Friis, S.A.K, Section 3.2).
The model is a product of the focus of enabling design thinking as an increasing role in organizational management, bringing innovation and adaptation to new circumstances of economic, social and cultural aspects (Buchanan, R.)[6].
Elements in the 6C Model
The 6C Model is a way of structuring the project work by planning and coordinating activities to ensure novel and innovative solutions. Traditional project management should be performed in parallel, while following the steps in the model. The model is structured around four stages of the design process: Collect, Comprehend, Conceptualize, and Create. Together with Collaborate and Communicate the model has six categories involving different types of knowledge production. A visualization of the 6C Model is shown in Figure 1.
The vertical axis in the model is a scale with opposite modes on each side: By experience or thinking, including some sort of subjective mental processing. The horizontal axis is relating to the orientation and focus of the production of knowledge, considering whether it is produced about an existing situation, so what is, or a future situation asking what might be (Friis, S.A.K, Section 3.2), similar to the transformation of an initial condition into a target condition (Züst, R., Section 1.2)[7].
How to use the 6C Model
The model has a circular shape, unlike the Double Diamond, which has a linear structure. In the beginning of a design process the team can intuitively start with collecting information and follow the steps in the circle clock-wise, but it does not have to be strictly followed. The idea with the model being circular is to allow for blurring the perception of a step being completely finished before the project finishes. This means that the step of e.g. collecting information will never completely end, which encourages the team to organically jump between steps in the design phase. The effect of this is to inspire a creative process by reducing boundaries and accept people thriving with fewer boundaries, as well as avoiding tunnel-vision and premature project decisions.
It is up to the project manager to decide whether the team should follow a structured or organic flow.
For each step the co-creation cards have specific suggestions of design methods they can follow. The project manager can use a card at any given point, and when used succesfully the team should have continuous project process
The Six Categories
The six categories are listed below with a brief description of the type of knowledge production, (Friis, S.A.K.) (Kjær, L.B., et. al.). For each category there are examples of co-creation cards, which work as design methods themselves. The cards will be explained further in the following section.
- Collaborate
- This category puts emphasis on the team members and dynamics, mapping out what expertise, skills, perspectives and values are present in the team. The collaboration category is respecting the relationships within the team roles and creates a set of ground rules. Successful collaboration utilizes sharing knowledge and learning from each other.
- From a stakeholder and company point of view the collaboration field puts emphasis having conversations and making observations. Knowledge is shared so everyone knows the process flow, strategy, and vision within the organization.
- Examples of co-creation cards are Personal Pictures, Check-In and Check-Out, Walk & Talk and Expectations.
- This category gives value to team familiarities which may seem irrelevant to the project, but clarifies that projects are driven by people, and personalities are inevitably affecting the project.
- Collect
- The design phase collect is about wondering, research and exploring, to thereby gain experience on the topic of the problem. This phase can be considered being on the objective side of the spectrum, by observing what the existing situation and context is. Knowledge is produced by physical engagement with the world, including interviewing people, going to the physical site of which the project is going to take place, and searching for information online.
- Understanding comes from experience and helps supporting the design process. In an organizational approach this can be done by collecting information on stakeholders and perform Stakeholder mapping. This is also where opportunities and challenges of the future are identified.
- The Co-creation cards supporting this topic are for example Experience Mapping, Photo & Collect Boards, Questionnaires, Visual Experiencing and Experiments.
- Comprehend
- Comprehending is knowledge about the existing situation and can be produces by processing information mentally as well as analyzing, sorting and organizing the collected data. The phase process introduces analytical thinking that opens up for new insights and descriptions of opportunities and challenges. Methods include Desktop Research, Challenge Framing, Clustering and Personas.
- Conzeptualize
- In this phase the design process moves into a potential solution space. The focus is on generating ideas and developing concepts for drafting possible solutions. Questions of what might be is produced by collectively sharing subjective visions and possibilities. This phase cannot be considered to be either converging or diverging but can go through the entire framework of the Double Diamond.
- Knowledge production is derived from intuitive thinking, innovative conceptualizing and selection of most promising ideas. For organizational projects this stage includes drafting, prototyping and testing for identifying whether a concept is useful and beneficial. Methods include Show & Tell, Inverse Brainstorm, Direct Inspiration and 5 Senses.
- Create
- In this stage, the focus is on physically producing and/or trying out new possibilities towards a final product that fits the problem scope and project objectives. Creative tools such as collages, models and sketching are used for sharing the concept with and present solutions to relevant stakeholders. An understanding of the result is derived from evaluation, active engagement with the concept, and reflection. Co-creation cards in this stage are Creative Constraints, Zen Walk, and Sketching Together. De-creation or inverse solution is helpful to support decisions on why certain solutions are made/not made, and can be carried out using the cards Take a Different Path, Let Go and The Other Hand.
- Communicate
- Communication, together with collaboration, is not a project phase but a requirement throughout the entire process. Within all phases of the design process knowledge about content and process is shared by articulating opinions either verbally or through models, sketches, text, logbooks, emotionally etc. It is important to stress that verbal communication should be a fraction of the communication, and visual and written communication is equally as important. Communication and interaction serve the understanding and dialogue between team members, the team, and stakeholders in all or the four project phases. Continuous communication creates more viable, desirable and implementable design results, and is guided using the cards Storytelling, Data Wall, Elevator Speech and Behind the Scenes.
Co-creation Cards
As an extra toolbox the Model includes a collection of 89 co-creation cards (developed from the traditional 62 cards included in the 5C Model[1]), which are designed to help translating understanding and knowledge into complex problem solving and design progress. The cards help the team investigating the situation and provides a shared language.
Physically the cards can be accessed through a PDF document or printed as physical playing cards. Each card has a title of the method, e.g. Personal Pictures, a short explanation of the method with an example, the why and how the card is used in practise. An example of a card is illustrated in Figure 2.
The cards are considered a tool and can be interpreted and followed more organically rather than considered a strict rule book. Oftentimes in team work many of the cards are followed without the team knowing, since methods included are following traditional procedures within design thinking and processes. The cards are simply framing the methods to give the team a pinpoint to where in the 6C circle they are located. In a creative process it is not uncommon that the team is in a stage of overlapping phases.
The cards are related to the 6Cs, but the cards themselves can also be put into categories that are not necessarily phase specific. The categories are
- Data - Designed to help team members collect and organize data.
- Insights - Designed to help the team share knowledge, analyze, and interpret data.
- Concepts - Helps the team generate ideas, develop concepts, and prototype.
- Evaluation - Gives an overview of the project and solution, which is then related to success of the design process.
.
Example of use in a project
In the following a case study is presented. The model is developed in the recent past by design researchers from Deign School Kolding and the Royal Academy, which means that the case study presented is limited to design students. Further examples of use outside of university and preferrably on a manager level is therefore essential to evaluate on the succes of the method.
During a 4-week course on Design School Kolding teams of 4-5 students were created to solve a task for a client, a official tourist organization. The teams were multi-disciplinary and with people of different genders. In the course the 6C Model was introduced and should be followed throughout the course to identify the problem and make solution proposals. The objective was to learn to apply design research methods to investigate a complex situation, and acquire an understanding of the significance of diversity in a creative teamwork. Consciousness and reflection was key for learning from each team member. One team had an exchange of persons at some point, where the person who left the team would later return. During this challenge the co-creation cards assisted and made a smooth transition and integration of the new team member. It was important for the team to establish professional as well as personal connections to acquire team "equality".
Later, the students from all teams reviewed the method and the design process and shared positive opinions such as:
- Getting outside one's comfortzone
- Learning much about themselves
- Acquiring new understanding of how other specialists think and gives new perspective
- Visual communication in complex problem-solving
Some negative aspects:
- A lot of time is spent talking/communicating in stead of delegating work and start producing
- Some expereinced feeling demotivated, lost, and stuck in the team
- Less succesful teamwork could cause less benefits and outcomes
It should be mentioned that the section is based on the report (Friis, S.A.K.) written by the author of the model, and there will naturally occur a bias towards the positive student aspects.
Discussion
Limitations
While the 6C model offers a useful framework for understanding knowledge production in a creative design process, there are a few limitations of the use of the model. Some limitations listed by the students using the framework shared that they spent too much time within the team where a lot was spent talking, and wanted more individual work before coming together for a "show and tell". The frustration of not producing and talking too much can reult in a point where som members simply deactivates and feels demotivated and stuck in the team (Friis, S.A.K.).
Like other frameworks with a focus on design thinking it is a benefit to keep teams at a maximum of 8 members. Even though the case study included a group member exchange the method encourage the group to strengthen relations and trust in the multi-disciplinary team, and even though there are co-cards which can be used for integrating new members, it is useful if the team defined in the beginning is mostly intact throughout the project. Furthermore, the model does not account sufficiently for complex social and cultural contexts in which the design takes place.
As explained the method includes investigating both problem and solution area, and if a project already has a well-defined goal and direction, the intention with the method is lost. The method encourages the team itself to set the goals and is suited for open problems free from previous opinions or ideas to expand the creative process[8].
The method does not extend after creating the solution, and does not introduce strategies for launching the solution. The lack of including the business aspect will require introducing other management models.
Comparison with similar design methods
As mentioned it will be interesting to study the use of the method in a leadership management case study, however the model does follow structures similar to classic design methods which are often used in management. While the 6C Model has a unique approach to understanding knowledge production in a design process for concious acting, there are many methods that are overlapping in the process. As listed previously the Co-creation Cards include traditional design methods such as Brainstorm, Questionnaires and Experiments, and the model will therefore be compared with other frameworks rather than single methods.
The comparisons will be with the Double Diamond and 3 Cs[4]. Further similarities can be found within Design Thinking, which shares the focus on empathy and boosting creativity with the 6C Model, and Lean Startup Methodology[9], that aims to shorten product development cycles to test the prototype through an agile procedure, which challenges the time-consumation of the team work using the 6C Model. These comparisons will not be covered in this article. The comparisons should help highlight strengts and weaknesses of each approach and help identify potential overlapping and possible integration.
The classic Double Diamond has become "the heart of the Framework for Innovation". In the wiki-article the design method is decribed as "the framework which dictates the plan and coordination of activities" in a project much like the 6C Model. The double diamond focuses on first discovering and defining the problem, and then developing and delivering the solution. This focus on understanding the problem and solution is sought in the 6C Model as well. Two steps are focusing on collecting and comprehending, which relates to seeking knowledge about what is, hence the problem. The other two in the middle circle has a solution oriented approach to what might be and explores concepts and creating the solution proposal. The circular approach, unlike the double diamond, blurs the understanding of finishing and moving on to next step, as described previously. The purpose of both is to shape the project within both planning, management and execution.
The 6C Model has an extra focus on the communication and coordination of the team and acknowledge the pressure that designers expereince while being in limbo for long stretches rather than producing a product. These extra Cs supports teams to be able to consciously contain and endure uncertainty in the complex work (Friis, S.A.K, Section 7.2).
The 3Cs is a guiding tool for cross-functional teamwork for more efficient work, avoid problems, and for better decision-making using Collaboration, Communication and Coordination. While the mid-circle in the 6C Model is a framework for project structure, these 3Cs mapping out processes and find connections in how you work with others[4], like the inner and outer circle in Figure 1. Coordination is something the 6C structure does not include, which could be beneficial to implement if used cross-functionally for process tracking and synchronization.
Future Application
The role of collaboration and emphasis on multi-disciplinary team work are key aspects in the model, and it would be useful and interesting to further explore ways in which collaboration is integrated in the model to support a virtual or remote team in an increasingly digital world.
As the design field is continuously expandig and growing it will be important and necessary to consider how the 6C Model will adapt, expand and evolve to meet the changing needs and challenges. Since the model is still rather new and is developed in Scandinavia (Friis, S.A.K.), it is developed to fit into a context that is common for that specific geographical area. It will be interesting to investigate how the model fits into a broader context and accounts for culturally and socially responsible design practices.
Finally, the 6C Model should be explored and tested further as a tool for organizational management, and while it seems like a playfull trial-and-error approach it is valuable in project and program management for open problem solving in a complex context. As described by Kolko “Leaders need to create a culture that allows people to take chances and move forward without a complete, logical understanding of a problem” (Kolko 2015)[10]. The idea is to create a structured framework for reducing the enduring uncertainty and pressure that designers face during a project and assist in understanding the knowledge produced and hence the progress in the team (Friis, S.A.K, Section 7.2).
Annotated Bibliography
Books:
Kjær, L.B. & Eskholm, L. &, Tøstesen, T. & Lagoni, T., Gain Power - An empowering tool kit for designers to understand Business & Organisational Context [11]. First edition, first printing 2017, Published by Design School Kolding, ISBN: 978-87-93416-22-2
- The booklet describes the 6C Model related to Design Thinking and Sustainability
Articles and Web-pages:
Friis, S.A.K. (2016), The 6C Model: The Contribution of Design to Open, Complex, Problem Solving [2]. The International Journal of Design in Society; Rome Vol. 10, Iss. 3, 13-30. DOI:10.18848/2325-1328/CGP/v10i03/13-30.
- This paper describes the 6C Model and its use in complex problem solving. This article is interesting in describing the model and its benefits and weaknesses through a case study from the perspective of the model creator.
Buchanan, R. (2015), Worlds in the Making: Design, Management, and the Reform of Organizational Culture [6]. She Ji: The Journal of Design, Economics, and Innovation; Volume 1, Issue 1, Pages 5-21, ISSN 2405-8726. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sheji.2015.09.003.
- The article introduces design as a part of organizational management. Buchanan explains how there is a "principle that distinguishes design as a practice of management from other schools of management", and how companies can benefit from introducing design thinking in their organizational structure, as an addition to traditional management, by including different perspectives on management, innovation and entrepreneurship.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 [https://adk.elsevierpure.com/en/publications/the-5c-model] The 5C Model, Last visited 12-02-2023
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Friis, S.A.K. (2016). The 6C Model: The Contribution of Design to Open, Complex, Problem Solving, Available Online
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 [https://www.designskolenkolding.dk/sites/default/files/publication/download/gainpower_booklet._ex.cover_print_a3_bothsides.pdf] Gain Power - An empowering tool kit for designers to understand Business & Organisational Context, Last visited 12-02-2023
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 [https://www.intercom.com/blog/the-3-cs-of-cross-functional-teamwork] Communication, collaboration, coordination: The 3 Cs guiding successful cross-functional teams, Last visited 12-02-2023
- ↑ [https://www.teknologisk.dk/design-thinking/metoder-og-vaerktoejer/37321,3] Design Thinking - Metoder og værktøjer, Last visited 12-02-2023
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Buchanan, R. (2015). Worlds in the Making: Design, Management, and the Reform of Organizational Culture, Available Online
- ↑ Züst, R. (2006). No More Muddling Through : Mastering Complex Projects in Engineering and Management, Available Online
- ↑ Carlgren, L., Elmquist, M., & Rauth, I. (2016). The Challenges of Using Design Thinking in Industry – Experiences from Five Large Firms. Creativity and Innovation Management, 25(3), 344–362, Available Online
- ↑ Rasmussen, E.S. & Tanev, S., (2020), Start-Up Creation (Second Edition), Chapter 3, Pages 41-58, Woodhead Publishing, Available Online
- ↑ Kolko, J. (2015). Design Thinking Comes of Age., Available Online
- ↑ Kjær, L.B. & Eskholm, L. &, Tøstesen, T. & Lagoni, T. (2017). Gain Power - An empowering tool kit for designers to understand Business & Organisational Context, Available Online