The Cynefin Framework
This article will introduce the Cynefin framework and its underlying practices, which can be used for sense- and decision making in a complex and complicated world. [1] The framework is developed by David J. Snowden (born 1 April 1954)[2], and is used by leaders to determine operative context so they can make appropriate choices. The framework has been applied in multiple contexts, among them are strategy management, project management, research, policy making, leadership training, healthcare etc. [3]
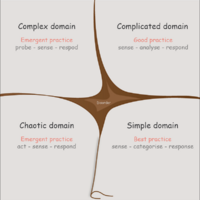
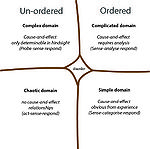
The Cynefin framework splits the issues that faces leaders into five contexts; simple, complicated, complex, chaotic and disorder. Each of which requires different approaches to leadership style. [1][4]
Reflekter på hvordan det passer ind i APPPM
Contents |
History
The Cynefin model
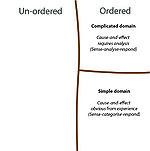
The Cynefin framework distinguieshes between order, unorder and disorder.[5] It describes five contexts that leaders can use for categorizing operating contexts for making appropriate choices. Each context requires different action.[1] The simple and complicated domains assume an ordered universe, where decisions can be based on facts, right answers can be determined and there is a direct link between cause-and-effect. Whereas the complex and chaotic domains are unordered and deals with uncertainty, there is no direct link between cause-and-effect, and decisions and right answers is searched for in emerging patterns. In the the final domain disorder is hard to determine when one is in it. different leaders have different opinions, and the way out is to break the situation down to smaller parts and assign the each one to one of the four domains. [1]
Order:1. Simple contexts (known knowns)
The domain of best practice, known-knowns, here we know exactly what we are doing and we have done it before, so we sense, categorize and responds (S-C-R)[1][4]
2. Complicated contexts (known unknowns)
The domain where we do not know what is going on, but we know that we can analyse what has happened and figure it out. We are sense, analyse and responds (S-A-R)[1][4]
3. Complex contexts (unknown unknowns)
In the complex domain we can not determine what will be the outcome, but we can run some experiments and see if they will move us in the right direction. We probe, sense and respond (P-S-R).
In this domain we can only understand what is happening in hindsight [1].
4. Chaotic contexts (unknowable unknowns)
In this domain, the domain of unknowables, it does not make sense to search for answers, no patterns exist - only turbulence. We act (do something), we sense where stability emerges and then we respond by working towards complexity (A-S-R)[1][4].
Disorder (not determined)
These are the situations where one are yet to break down and determine where the situation belongs in the framework.[1][5]
Guide on leadership
Framework for decision making in multiple contexts[4][1]
Snowden states, that if you want to become effective as a leader, you must learn to shift your leadership style to match the changing business environments. The four different domains call for different leadership styles and managerial responses.
| Characteristics of context | The leaders job | Danger signals | Response to danger signals | |
| Simple |
-Known-Knowns, |
-S-C-R: Sense, Categorise, Respond, |
-Comfort, |
-Don't assume that things are simple, |
| Complicated |
-Known-unknowns, |
-S-A-R: Sense, Analyse, Respond, |
-Experts overconfident in their solutions or in past solutions, |
-Encourage internal and external stakeholders to challenge expert opinions and thinking, |
| Complex |
-Unknown-unknowns, |
-P-B-R: Probe, Sense, Respond, |
-Temptation to look for facts rather than allowing patterns to emerge, |
-Be patient and allow time for reflection, |
| Chaotic |
-Unknowable-unknowns, |
-A-S-R: Act, Sense, Respond, |
-Applying a command-and-control approach longer than needed, |
-Try to move the situation towards the complex domain, |
Perspective on organisational theory and paradigms
Ontology and ideology
In most current management practices, the ideology that seem to exist assumes that there is an underlying relationship between cause and effect, and predicts that the future can be planned by discovering these underlying relationships. Examples are case studies and consultancy frameworks, that rely on transferring best practices across companies and industries[6].
It is assumed that there is a right answer to problems/situations, and that failure hereof is a failure in analysis on the underlying causal relationships[4].
This ideology belongs to the modernist paradigm of organisational theory, where managers base their decisions mainly on descriptive measures and statistics[7]. This ideology of decision making is represented in the right hand side of The Cynefin Framework (the domain of order: simple and complicated).
When introduced to complex situations, former practitioners have relied on reductionistic scientific methods, which assumes that complex systems is nothing but a sum of its parts[8]. Managers have therefore made decisions by breaking down the situations into sub-parts, analysed each part individually and then made their decisions. Implying that the answer to the complex problem could be found in the sum of cause-and-effect relationships. The method of reductionism is contradicting with the ideology of complexity, when reductionist thinking asserts that we proceed when certain. Complexity thinking enables us to proceed by probing that which always be uncertain.
The Cynefin Framework breaks with traditional modernistic managerial-, decision- and sense-making, by introducing sense- and decision making approaches in systems that does not have underlying causality (complexity and chaos)[1] and is therefore belonging in the post-modern paradigm.
Examples of contexts
- Examples of simple contexts
- Examples of complicated contexts
- Examples of Complex contexts
- Examples of Chaotic contexts
- Examples of Disorder
Examples of uses
Cynefin used in projects
The Cynefin framework can be used in projects as a sense-making tool and as a common language for dealing with complexity[1][9]. When using the framework in project management, Snowden emphasizes using the framework as a collective sense-making method that allows specific patterns to emerge in the understanding of the project [9].
Snowden's idea with sense-making in projects is to provide a common understanding of language depending on the environment. Snowden claims that experts' language is too restricted and abstract for managing complexity in project work, and remains about the problem but still far above it[9]. Snowden therefore emphasizes the role of language in sense-making about complexity in projects and especially as a communicator to create meaningfull messages that are informative, comprehensive and not oversimplified [4][9].
- Cynefin used in Ergonomics
Criticism
- Critical reviews of the Cynefin Framework
- Risk of oversimplifying the problems
Additional reading
- Article: Harvard business review: Snowden, David J., and Mary E. Boone. "A leader's framework for decision making." [1]
- Article: Snowden, Dave. "Strategy in the context of uncertainty." Handbook of Business strategy 6.1 (2005): 47-54. [4]
- Article: Hasan, Helen, and Alanah Kazlauskas. "The Cynefin framework: putting complexity into perspective." (2014): 55. [5]
- Article: Jarrar, Yasar F., and Mohamed Zairi. "Best practice transfer for future competitiveness: a study of best practices." Total Quality Management 11.4-6 (2000): 734-740. [6]
- Article: Browning, Larry, and Thierry Boudès. "The use of narrative to understand and respond to complexity: A comparative analysis of the Cynefin and Weickian models." E: CO 7.3-4 (2005): 32-39. [9]
- Article: Van Beurden, Eric K., et al. "Making sense in a complex landscape: how the Cynefin Framework from Complex Adaptive Systems Theory can inform health promotion practice." Health promotion international (2011): dar089. [3]
- Book: Hatch, Mary Jo. Organization theory: modern, symbolic and postmodern perspectives. Oxford university press, 2012. [7]
- About Dave J. Snowden: http://web.up.ac.za/default.asp?ipkCategoryID=5667[2]
- Cynefin 101, an article by Greg Brougham http://www.infoq.com/articles/cynefin-introduction
- The new dynamics of strategy: sense-making in a complex and complicated world http://alumni.media.mit.edu/~brooks/storybiz/kurtz.pdf
- Video: (Youtube): The Cynefin Framework http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=N7oz366X0-8
- Article archive: cognitive-edge.com http://cognitive-edge.com/library/more/articles/
- Article: 'Cynefin Centre: Life after IBM' 2005, KM World, 14, 7, pp. 1-26, Business Source Premier, EBSCOhost, viewed 14 November 2014.
- Article: Elford, W. (2012). A multi-ontology view of ergonomics: applying the Cynefin Framework to improve theory and practice. Work, 41, 812.
- Definition of reductionism: Interdisciplinary Encyclopedia of Religion and Science ISSN: 2037-2329 [8]
Bibliography
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 Snowden, David J., and Mary E. Boone. "A leader's framework for decision making." harvard business review 85.11 (2007): 68.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 University of Van Pretoria, 2014
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Van Beurden, Eric K., et al. "Making sense in a complex landscape: how the Cynefin Framework from Complex Adaptive Systems Theory can inform health promotion practice." Health promotion international (2011): dar089.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 Snowden, Dave. "Strategy in the context of uncertainty." Handbook of Business strategy 6.1 (2005): 47-54.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Hasan, Helen, and Alanah Kazlauskas. "The Cynefin framework: putting complexity into perspective." (2014): 55.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Jarrar, Yasar F., and Mohamed Zairi. "Best practice transfer for future competitiveness: a study of best practices." Total Quality Management 11.4-6 (2000): 734-740.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Hatch, Mary Jo. Organization theory: modern, symbolic and postmodern perspectives. Oxford university press, 2012.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Interdisciplinary Encyclopedia of Religion and Science ISSN: 2037-2329
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 Browning, Larry, and Thierry Boudès. "The use of narrative to understand and respond to complexity: A comparative analysis of the Cynefin and Weickian models." E: CO 7.3-4 (2005): 32-39.