Competitive tendering
This article is about competitive tendering which is the most commonly way for a client to procure construction services. Procurement is important because of the principal/agent problem where the client has to choose those who are appropriate, competent and trustworthy. This leads to the lemon problem which attends the problem regarding asymmetry of information.
Competitive tendering is a way to form the project coalition by making a set of codified documents that suppliers can make a bid on to offer their construction services. From the respond the client can then choose the most suitable contractor or supplier.
There are different things for the client to consider when making a tender. The first to consider is whether the selection criteria should be based on lowest price or best value. The second thing to consider is whether the bidding should be open to everyone, based on a tender list or based on a background of prequalification. The client can choose the option to make the tendering a two-stage tendering and/or if it should be a sealed bid action.
All these decisions and in overall the choice of competitive tendering as the procurement has both advantages and disadvantages.
The appropriate procurement is often based on a function of the two variables; the level of mission uncertainty and the phase in the project life cycle. The lower the levels of mission and dynamic uncertainty, the more appropriate the use of competitive tender becomes.
A big part of setting up the competitive tendering is the compliance with valid legislations within the area.
Contents |
Big idea
Competitive tendering is the most commonly used way for the clients to procure construction services.
The procuring phase is important to attend because of the principal/agent problem where the problem is asymmetry of information. The asymmetry togetaher with self interest for each partitioner of the contract, generates two main problems which are the moral hazard and the adverse selection. Here is the problem of the adverse selection, also called “the lemon problem”. The lemon problem for the client that wishes to procure construction services is that he/she maybe do not know everything about the supplier. In the procurement face the client dos maybe not know if the supplier supplies poor quality work. The lemon problem is engaged to insure that the client hires competent suppliers of construction services. When asymmetry in information is high the poor-quality goods will drive out the better-quality goods in the market. This is especially the case in construction due to the high levels of uncertainty and it is highest in the early stages of the project. Another purpose of competitive tendering is for the client to get a lower price and the competition in the building market is kept sharp and motivated to the project.
Alternatives to the competitive tendering in procuring construction services are mainly In-house capability, appointment and concours (competition).
Application
To form the project coalition by competitive tendering, the client first has to issue a codified set of documents which provide a detailed description of the construction service that has to be performed.
The presented documents allow the suppliers to calculate a price and proposal for supply of the services. On basis of the respond from the suppliers the client can then choose the most favorable.
Pre-qualification
Reducing the resource consumption in the procurement phase can be achieved by using a pre-qualification process. This process is often used in tendering of construction services and it reduces the amount of tenders that has to spend time and money to make a tender. Also it reduces the resources for the client to go through them all.
In connection to pre-qualification the incoming applications goes through a four step evaluation.
The first step is the exclusion which is made of a mandatory exclusion stated by the directives and the procurement act. This is e.g. if a tender is convicted of some criminal acts, has laundering money or made bribery. The other part is the voluntary exclusion where the client can make non-obligational execution of tenders. However the execution reasons must be equal for all tenders and can e.g. be based on bankruptcy or debt to the public services.
The second step is a suitability study where it is controlled if the tenders meet the minimum criteria for economy and technical capacity. This step also controls that it is the right documents that have been submitted.
The third step is a qualitative selection to obtain the most qualified tenders for the specific service.
If there are still too many tenders after the qualitative selection than needed, a quantitative selection can be made as the fourth step.
These selection criterias can be set as the client fits best, but it is important that the client has stated which criteria the tenders have been chosen by in the contract notice.
Tendering criteria
It is an option to only base the tendering criteria on lowest price though it might not be the best solution. This is because when the criteria is only based upon price it can lead to unrealistic low prices from the tenders which will then have an influence on the quality of the work. The contractors will also become more eager to engage in legal action to recover their losses. It is also more likely to result in a higher cost because of overrun in cost and time, and the end result will then have a higher maintenance and operation cost. In the long run this will result in higher cost for the project and no client is interested in that.
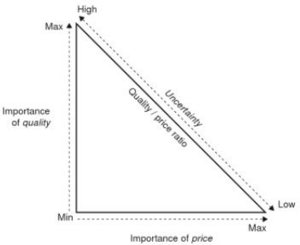
Another way to procure tenders are by the best value procurement. This is a combination of quality and price criteria. The quality is often assessed on a scoring principle which asses specific areas the client finds important. The criteria can e.g. be supplier track record, qualifications of key project personnel, reference and proposed approach to the problem. The score of the different criteria along with the price is then used to determine the value of the proposal. The quality to price ratio is important and varies with the level of uncertainty of the project. This is illustrated in Fig. 1.
For clients in the private sector an alternative is just to obtain prices from a number of contractors who are chosen by the client. Often the tendering is executed with a sealed bid auction to insure that every tender gives their best realistic bid and not just an offer that lies under the other contractors.
Two-stage tendering
If the client is pressed on schedule or the project requires early contractor involvement it could be an option to make a two-stage tendering. Two-stage tendering is first made of a competitive bidding for the supply of project management typically covering detail design and execution on site. This will typically fix the most important decisions such as services needed and costs. The chosen preferred contractor is then organizing a competing tendering for the second tier of suppliers. The second stage helps to reduce the uncertainty within the project. Some of the advantages of two-stage tendering are the speed of procurement and the early involvement of the contractor. A problem with the method is that even though the client is locked to the contractor after stage one the contractor is not locked to the client, who could walk away if the client is too tough in the second stage of contracting.
Appropriate procurement
It is important to know when to use competitive tendering rather than some of the other procurement methods.
The alternatives to competitive tendering are e.g. to maintain an in-house capability, appoint a supplier or launch a concours.
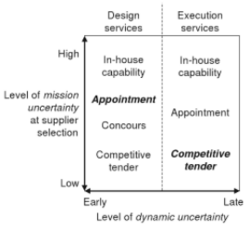
The base selection of a procurement form is a function of the level of uncertainty in the specification of the resource required at the time of selection. There are two main interaction dimensions to take into account when choosing procurement type. One is the level of mission uncertainty when the supplier is selected and the other is the phase in the project life cycle, where often the level of dynamic uncertainty has been reduced from the start of the project. The relationship between these two factors and the supplier selection method are illustrated in Fig. 2, the method in bold are the most commonly used method in each phase.
The lower the levels of mission and dynamic uncertainty, the more appropriate the use of competitive tender become, as seen in Fig. 2.
Where projects are very repetitive and mission uncertainty is low, particularly where multiple clients share the requirements for the project, the selection of external suppliers through competitive tenders may very well be more efficient than using in-house facilities.
Limitations
Advantages
• The price competition between suppliers will raise the production efficiency.
• The transparency of the selection criteria gives the client a better and faster decision on which tender to choose.
• The criteria minimize the risks of supplier cartels forming.
Disadvantages
• The high risk of the lemon problem, especially when tendering is open to all, because there are limitations in the knowledge of the competence of the suppliers. In competitive bidding in construction information is both asymmetrical and incomplete and no scheme of inducing suppliers to reveal their preferences will reduce that underlying uncertainty.
• A huge problem with competitive tendering is the high cost of search and select both for the client and the tenders. There have been cases where the resources to execute the tendering has way exceeded the benefits of the obtained result.
• When facing high-uncertainty projects the requirement of complete documents limits the use of competitive tendering. Typically the clients are not fully aware of their requirements for the facility at the termination of the project and contractors are not fully aware of the demands for the project life cycle.
Rules and laws
To insure that no corruption or discrimination is taking place the procurement rules have to be complied with.
Clients in the public sector have to follow a set of rules. When a bigger project exceeds a certain value the clients have to comply with the rules in the EU Directives. Here there is made a series of predefined processes that the clients must follow. The EU directives lay down some fundamental treaty principles of equal treatment, transparency and proportionality which always have to be followed by the public client.
In smaller projects the public client is subjected to the national procurement act which states a series of procedures to be followed.
Annotated bibliography
Books and articles
Professionel udvælgelse i byggeriet: Afdækning af mulighederne for at nedbringe ressourceforbruget i udvælgelsesprocessen – herunder gennemførelse af prækvalifikation, (S. Mortensen, 2012)
Effektiv prækvalifikation, (Værdiskabende Byggeproces, 2. edition, 2013)
The business case for lowest price tendering?, (Construction excellence, 2011)
Links
https://ec.europa.eu/growth/single-market/public-procurement/rules-implementation/thresholds_da