Value stream mapping in construction management
In this article, the introduction and implementation of VSM to the construction industry will be discussed. Initially a generic formulation of VSM is presented, follow by the introduction of VSM in the construction industry. The application of VSM in the construction industry will then shortly be discussed, based on case studies. Lastly the limitations associated with the use of VSM in the construction industry will be presented.
Contents |
The Big Idea
VSM generic formulation
Value stream mapping (VSM) originated in the manufacturing industry. It was developed by Toyota Motors Corporation, being a part of their Lean management tools. The Lean management philosophy is to identify and eliminate every activity in the design, production and supply chain management related processes that does not create value for a costumers point of view[2]. Generally it is characterized as a process-improving management philosophy, that seeks to minimize the waste without decreasing the productivity.
Let's first define what a "Value stream" is. The formal definition is as follows: "All the steps both value added and non-value added, required to take a product or service from row material to the waiting arms of the customer".
Value stream mapping (VSM) is used to both analyse and design the flow of material and information, that is required to bring a product or service to the end customer. It is a visual tool that provides a holistic view of the overall process, and thus a platform for strategically improvement and adding value to the costumers[3]. It has also been used to initiate a systemic implementation of the Lean production tools. The goal is to design an “ideal state”, also known as the “future state” by analyzing the “current state”. The current state presents how the process is at the time of making the VSM. This is very important due to the dynamic nature of VSM. An enormous amount of waste or in Japanese (Muda) is often present within the a work flow system. This waste is identified by reflecting the current state. The future state represents the state where the all the identified waste has been eliminated.
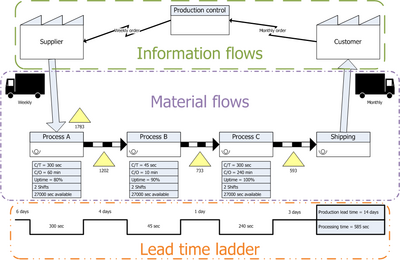
The general mapping of a current state is presented in Figure 1, showing the three key points:
- Information flow
- Material flow
- Lead time ladder
The overall lead time of the product or service is an important part of a VSM. Usually significant amount of non-value added activity or waste is found, and takes an enormous amount of time. Having identified the wastes, a future state can be designed where the wastes are eliminated, often applying additional Lean tools to achieve it. Standardized symbols are used when mapping a process state, to obtain a common language for communicating through the VSM[4].
VSM in the construction industry
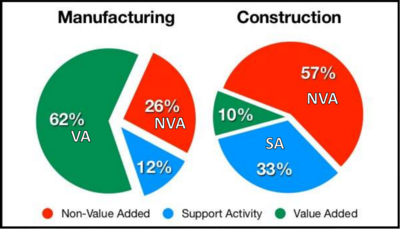
The construction industry in terms of productivity, quality and efficiency, is often characterized as a backward industry, that fails to innovate compared to other industries. The Lean Thinking philosophy way introduced to the construction industry in 1993, and some successful implementations has been achieved. The major difference between the manufacturing- and construction industry is uniqueness related to a building project. Unlike, for instance in the car industry, the assembly line has been used since it's first implementation in the early 20th century. This automation of a standardized product cannot directly be implemented in the building industry due to the unique nature of building projects. However increasing automation is seen in constituent parts of construction project, as in pre-fabrication of concrete elements. This has furthermore been shown reduce both energy consumption and cost. The Construction Industry Institute states that only 10% are value added inputs and striking 57% are waste. This is compared to the manufacturing industry where 62% is value added and 26% is waste[2]. The lack of performance in the construction industry compared to other industries, has been directly related to the low rate of innovation. Another issue is the competition for building project, mainly in the public projects, which is cost centered. The cheapest bid wins the project, and under these circumstances bidders invest very little amount of time, money and vitality in advance[3]. These statistics are a major motivation, for studying and identifying the wastage, which is frequently present in the industry. Consequently how to apply Lean tools and techniques to reduce the wastage. Examples of value adding activities are pouring concrete, erecting steel or installing the roof. Examples of waste are excessive material handling, design errors, conflict between contractors, ineffective supply chain and rework.
8 types of waste in the construction industry
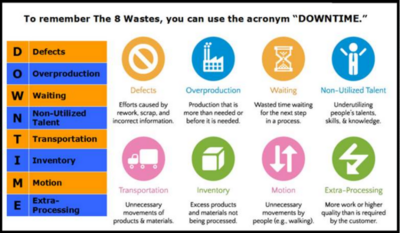
The following table list the 8 types of waste, typically found within the construction industry[5].
| Waste type | Definition/cause | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Inventory | Excess products and material not being processed. | Steel door frames delivered in bundles during steel erection. (Early delivering - just to be safe) |
| Motion | Unnecessary movements by people (e.g. walking). | Early delivery of the steel door frames got in the way of production operation and had to be moved. |
| Defects | Efforts caused by rework, scrap, and incorrect information. | In the process of moving the early delivered steel frame doors, some were damaged. |
| Extra-Processing | More work or higher quality than is required by the costumer. | Some of the damaged doors were repaired, and spending time ordering new doors. |
| Non-Utilized Talent | Under-utilizing peoples talents, skills and knowledge. | Carpenters moved the steel frames to the construction install area. |
| Transportation | Unnecessary movements of products and materials. | New doors has to be delivered on site. |
| Waiting | Wasted time waiting for the next step in a process. | Waiting for the new doors to be delivered. |
| Overproduction | Production that is more than needed or before it is needed. | Due to lack of doors to install, the carpenter began on other tasks too early. |
These 8 types of wastage can be recognized as "DOWNTIME", see Figure 3.
Application
Regarding the application of VSM in the construction industry, no unique guidelines has yet been made on how to implement it[3]. Unlike the manufacturing industry, all construction projects has unique design specifications, and there is very little repetition involved and too much variability. Due to the lack of generic guidelines, two case studies will be examined instead.
Case study - Precast concrete yard
A paper by (Nimesha Vilasini & J. R. Gamage, 2010)[2], presents a case study of the application of VSM at a precast concrete yard. The aim was to resolve quality issues and reduce the cycle time. Initially process information were gathered, and reflecting the current operation status, a current value stream map were created. The waste generating activities were identified, and by use of different analysis tools (Five whys and Cause and effect diagram), the root to the issues were found, and solved by a Kaizen approach. Subsequently a future state map was created to provide guidelines for future lean activities, and to monitor each Kaizen process.
The major steps involved in the mapping is summarized in following table:
| Steps | Description |
|---|---|
| Preparation stage | What product or project to study, and how it should be mapped. Additionally find a mapping team. |
| Current state map | Collection of data from each individual process, and connecting all the states of production to establish the flow information and material resources. |
| Future state map | Analyzing the current state map, and searching for areas where improvements could be performed, and possible solutions to there were discussed. |
| Planning and implementation | The future state map were completed for each identified issue, and an action plan were developed to visualize and share information about Kaizen projects. |
Case study - Brazilian building company - Masonry stage
A paper by (Fernanda Pasqualini & Paulo Antônio Zawislak)[6], aims to introduce the Lean production ideas to the construction industry in a more systematic way. Centered around the value flow, the paper presents modifications and application of VSM in a Brazilian construction company (contractor). Modifications of VSM were necessary due to the, already mentioned differences in the manufacture and construction environments. By applying VSM, it was possible to identify both wastes and solutions to improvement. This resulted in a more fluid production, and unification of the planned flow vs. the accomplished flow.
The application of VSM is describes through the following four sections. The case study is about the production process in an apartment building construction.
1. Selection of a construction stage
Since VSM were adapted to be used inside of an industrial plant, within the manufacturing process, the most obvious were to consider the process on the building site. The mapping should not be carried out for all products manufactured by the Brazilian company, but only a family of products. However a construction project consists of many long period, different stages or "sub-constructions", were different products are required and different processes are utilized. Thus, instead of selecting a single family of products to apply VSM on, a stage of the productive construction process were selected. In this case the masonry stage.
2. Map of the Current State
Mapping of the current state should represent the exact value flow at the time of making it, and collecting information had to be directly at shop floor. Since processes within construction usually last a while, the data was impossible to collect in a single day. To achieve a high level of exactness, practically the whole masonry process had to be observed. Analyzing the collected data, adaptations from the original "manufacturing way", had to be made. The adaptation were related to the calculation of the Takt time, which were obtained by dividing the effectively available work time for each stage, by the amount of square meters to be executed for the same stage. As a result, the Takt time now represents the time in which a square meter should be executed. Secondly the cycle time (T/C) were modified to represent the average time it takes to finish a square meter of masonry.
3. Analysis of the map of the Current State
Analyzing the current state map, the goal were to identify wastes and improvements. The usual propositions of VSM were used, where adaptions consisted in interpretation of the propositions according to the characteristics of an construction environment.
4. Map of the Future State
Based on the current state map and resulting improvement proposals, the future state map could be drawn. Changes were proposed, regarding the individual relationship of each client with the constructor. Increase their internal communication, by arranging meeting more often, mainly before steps that involve personalization of the apartments. The goal of this change were to minimize non-compliance of already established deadlines, and reduce potential rework. The general schedule as well as the weekly program spreadsheets, remain in the map. Additionally a "mini-plant" were proposed, with the main objective to get all persons involved in the process, and in this way to make the production flow more continuously, eliminating stop times etc. Furthermore the "master of workmanship" could spend more time on increasing the quality by analyzing problems, rather than to give daily instructions to each employee, since it was already shown what to be done.
In the future state map, the weekly meeting day coincides with the day of ordering materials. In this way they ensured, that there were the sufficient amount of materials for the weekly activities at the site. Neither too much nor too little.
Regarding the material supply on the current state map, this was replaced by the adoption of the supermarket idea, in the future state map. The aim were to reduce the supply of raw materials, and increase control.
These process improving implementations, resulted in a large increase of productivity in all the masonry processes. The total lead time of the masonry execution went from 115 workdays, down to 88 workdays, i.e. a reduction of approximately 27 workdays, which is more than a month. The final deadline of the apartments were reduced consequently.
Additional application
A thesis by YAXU LI[3], states that based on literature search, the application of VSM in the construction industry can be divided into three themes: construction process, macro-process, and construction support processes.
Limitations
Value stream mapping as a generic Lean tool, cannot be directly applied in the construction industry. It has a huge potential, but modifications and redesign are required for the tool to be applicable in the industry. Relevant customization to the tool must be carried out to shown a significant effect. The limitations are centered around the fact that it was originally adopted in a manufacturing environment. [2][3][6] .
Annotated Bibliography
- Bygherreforeningen, Hvidbog om bæredygtighed i byggeriet: Et overblik over eksisterende viden og nye initativer, 2013, https://www.innobyg.dk/media/36207/hvidbog_om_baeredygtigt_byggeri_final_web.pdf
- The report gives an overview of existing knowledge and new initiatives in sustainable construction.
Implementing Value Stream Mapping Tool in the Construction Industry[2]
VALUE STREAM MAPPING (VSM) IN CONSTRUCTION AND
MANUFACTURING INDUSTRY˖A STRUCTURED LITERATURE REVIEW AND
COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS[3]
Value Stream Mapping in Construction: A Case Study in a Brazilian Construction Company[6]
References
- ↑ Value stream mapping https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Value_stream_mapping (19-06-2017)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Nimesha Vilasini & J. R. Gamage (2010) https://www.researchgate.net/publication/282156168_Implementing_Value_Stream_Mapping_Tool_in_the_Construction_Industry (19-06-2017)
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 YAXU LI, Master thesis (2015) http://oaktrust.library.tamu.edu/bitstream/handle/1969.1/156276/LI-THESIS-2015.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (19-06-2017)
- ↑ Strategosinc - symbols (rev. 2017) http://www.strategosinc.com/vsm_symbols.htm (19-06-2017)
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Robert Warcup, PhD (2016) http://c.ymcdn.com/sites/www.nasfa.net/resource/resmgr/Learning_Series/Intro_to_Lean_Construction_&.pdf (19-06-2017)
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Fernanda Pasqualini & Paulo Antônio Zawislak, (2005) http://iglc.net/Papers/Details/356 (20-06-2017)