Construction Contract Management Guidelines and Administration
Contract plays a vital role in project management, business strategies, and relationships. It is the foundation of value for the business. Organizations both in public and private are looking for efficient performance at a reduced cost. [1] They are now realizing the importance of contract management in delivering a successful project. Effective contract management can make or break organization's vision, strategy, and its reputation.
All over the world projects are losing billions of monies due to poor contract management. The factor affecting poor contract management can be attributed to many elements such as the lack of knowledge with regards to proper contract administration, the impact of globalization creating a thicker volume of the document, strict government rules and legislation, technological innovation like BIM, and speed of change in contracting norm.
The significant impact of contractual issues affecting the overall performance of an organization leads to a realization that proper contract management guidance and administration is necessary to ensure minimal contractual risk, claim dispute and eliminate the possibility of arbitration cases.
In this article, the approaches and guidelines for Contract Management and Administration for pre-award (tender stage) and post-award (project execution stage) activities will be elaborated and discussed. The article will be divided into two sections. Section 1 includes the contract management principles such as the definition of contract, the contract management and administration definition and value measurement, the benefits from good contract management, contract management lifecycle and its processes, this is to give the readers an overview of what is contract management. Section 2 is the contract management guidelines for pre-award and post-award used to successfully implement the contract.
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
SECTION I - CONTRACT MANAGEMENT PRINCIPLES
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
1.1 WHAT IS A CONTRACT?
A contract is a legal document stating the obligations between two or more parties. The contract documents usually outline the principles of offer, acceptance, and consideration, it also defines the terms of payment, the principles of negotiation, the scope of work and the expected level of service.
1.2 WHAT IS A CONTRACT MANAGEMENT AND ADMINISTRATION
Contract Management and Administration is the process of managing the contracts between the company and the vendors/partners. It involves decision-making and timely flow of information to achieve project goal in conformity with the contract documents. Moreover, effective contract management can be measured if;[2]
1 The arrangements for service delivery continue to be satisfactory to both customer and supplier;
2 Expected business benefits and value for money are being delivered;
3 The supplier is being cooperative and responsive;
4 All parties know their obligation in the contract;
5 There are no disputes;
6 There are no surprises;
7 The contract is fully compliant and satisfied both legislative and requirements.
1.3 CONTRACT MANAGEMENT PROCESSES
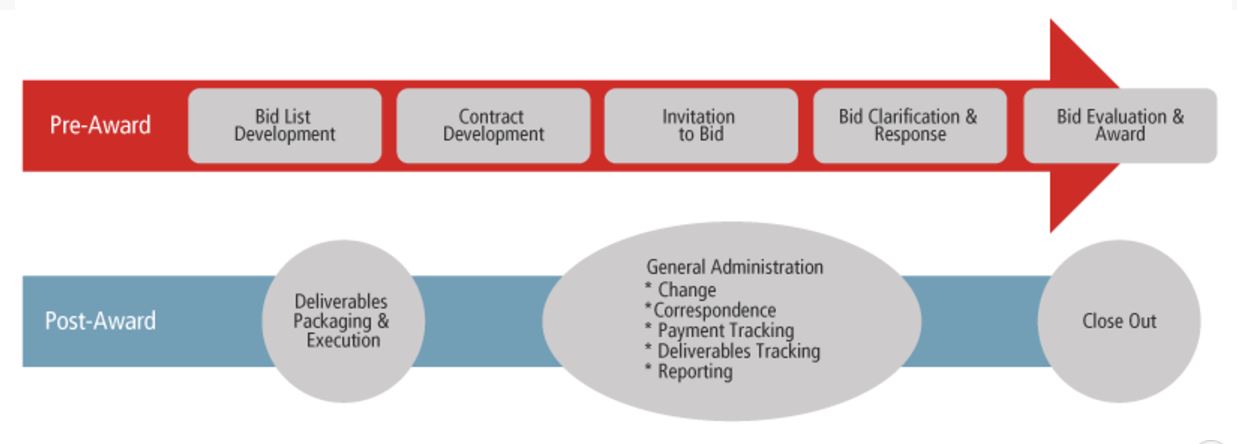
1.4 ORGANIZATIONAL REQUIREMENTS FOR EFFECTIVE CONTRACT MANAGEMENT
To ensure efficiency in contract management. It is important for the organization to consider people skills and competencies. The type and level of resources required for contract management will vary for different types of contracts. Different levels of skills and competencies will be required for different types of contracts. Some will require the establishment of a contract management team while others will be managed by a single person.[4]
To carry out the contract management activities efficiently. The contract managers and other commercial team members must have appropriate skills and competencies to understand the task at hand in connection with the types of contracts they are dealing with. In addition, senior management should also provide leadership to ensure commitment to improvement.
1.5 DIFFERENT TYPES OF FIDIC CONSTRUCTION CONTRACTS
Some of the most common types of construction contracts used in the construction industry are the following:[5]
1 Green Book - Short form of contract, First Edition 1999
- The Short Form of Contract is recommended for engineering and building work of relatively small capital value. The Guidance Notes for the Green Book recommended that generally it should not be used on projects with a contract value greater than US$500,000.It is a flexible document containing all the essential administrative and commercial arrangements. The contents of contract book: (a) Agreement (b) General Conditions (c) Rules for Adjudication (d) Notes for Guidance.
2 Red Book - Conditions of Contract for Construction For Building and Engineering works designed by the Employer First Edition 1999
- The Red Book provides conditions of contract for construction works where the design is carried out by the Employer. The Red Book is intended for use on projects where the employer carries out the design but it also allows for some elements of the project to be Contractor designed. Payments are normally determined by measurement and applying the rates and prices from the bill of quantities. There is an option for payment to be on the basis of a lump sum. The contents of contract book: (a) General Conditions (b) Guidance for the Preparation of the Particular Conditions (c) Forms of Tender and Contract Agreement (d) Dispute Adjudication Agreement.
3 Red Book Multilateral Development Bank (MDB) edition- Conditions of Contract for Construction For Building and Engineering works designed by the Employer (MDB Edition 2005)
- The FIDIC MDB edition of the Red Book simplifies the use of the FIDIC contract for the MDBs, their borrowers and others involved with project procurement, such as consulting engineers, contractors, and contract lawyers. As part of their standard bidding documents, the Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs) have for a number of years required their borrowers or aid recipients to adopt the FIDIC Conditions of Contract. The contents of the contract book: (a) General Conditions (b) Guidance for the Preparation of the Particular Conditions (c) Forms of Tender and Contract Agreement (d) Dispute Adjudication Agreement.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
REFERENCES:
1..2 https://www.cips.org/documents/CIPS_KI_Contract%20Management%20Guidev2.pdf
3 http://www.coreworx.com/effective-contract-management-in-engineering-and-construction-projects-pre-award-to-post-award/
4 https://www.scribd.com/document/196148989/Contract-Management-Guidelines
5 http://fidic.org/sites/default/files/FIDIC_Suite_of_Contracts_0.pdf
Cite error:
<ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found