Financial appraisal of project proposals
Abstract
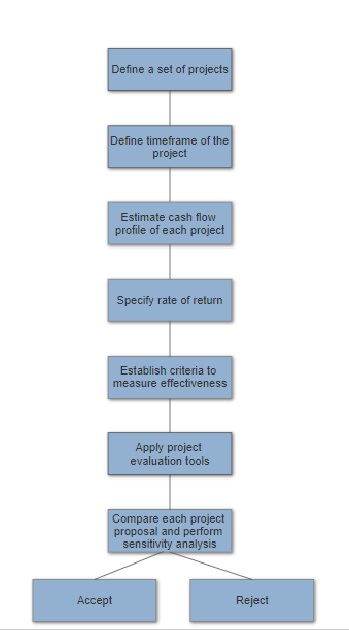
Generally, project managers have a difficulty in selecting the potential project proposals which give the best rewards for the company into their program or portfolio. One way to do this is to apply financial appraisal tools to evaluates the best investment decision based on predicted costs and revenues which have been determined from either ground-up or top-down costing. The evaluation also depends on the size of the project and the time span over which the costs and benefits are going to be spread[1]. Usually, project managers take responsibility for two types of decision which are investment and financial decision. The investment decision is the decision that focuses on the concept of what to do in order to gain the maximum value, financial decision, however, related on how the projects should get the money from in order to run.
The aim of this article is to present techniques to make an accept or reject decision on investing project which are payback analysis, discounted cash flow, and internal rate of return which based on the concept of the “Time value of money”, and application of these tools also their limitations.
Time Value of Money
$1 of today is worth more than $1 of tomorrow Time Value of Money (TVM) is the concept that money available today provide more benefit with the same amount than tomorrow. The reason is that on hand money today can be invested to generate more money in the future. To begin with, a basic knowledge of simple interest and compound interest must be manifested. The first interest perception is where the interest rate is calculated based on principal only and it is constant throughout the period, while compound interest is the other way round which calculated on the principal plus total amount of interest accumulated in the entire preceding period which makes the amount of interest increased over time. The example below is demonstrated to clarify the difference between these two interest.
Example: Given the rate of return of 10% per year and the principal of $100, what is the balance in the following four years.
Simple Interest: 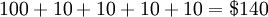 Compound Interest:
Compound Interest: 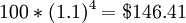
Some basic techniques to evaluate of TVM are;
Present worth(PW) Future worth(FW) Annual worth(AW)
References
- ↑ Harvey Maylor (2010) 'Project Management'. Bath, United Kingdom: Pearson Education Limited