Shannon & Weaver Model for Communication
Developed by Andrea Könnecke
Contents |
Abstract
Communication is an essential factor in project management and is defined as the intended or involuntary exchange of information. [1] Successful communication is affected when what is implied is perceived as intended. Communication within project management is seen as a foundation function that integrates the areas of scope, schedule and resources [2] Ineffective communication can therefore lead to misunderstandings and to a failure of a project. For that reason, an effective communication system and a fundamental understanding of the project, portfolio or programme manager to the communication maintenance during the life cycle of a project are mandatory for a successful project. [1] Thus, a solid understanding of communication and developed skills to communicate are necessary for project manager to ensure the potential for cooperation and an effective communication within the project team and with all project stakeholders.
The following article looks into the basic model of communication and its components which is known as the Shannon and Weaver Model for Communication. This model is often referred as the Mother of all Models as it was particularly important for the development of communication studies. [3] However, it was primarily designed to improve technical communication of radio and telephone. [4] Later, the model was used in order to understand and develop effective communication as it offers insights in the way in which communication is designed. Shannon and Weaver suggested three levels of problems and introduced some key concepts which are used in further communication research. A common application of the theory are general communication guidelines for project manager as well as project stakeholder communication and communications management plans.
Model Description
History
During the Second World War, Claude E. Shannon, a research mathematician and electrical engineer at Bell Telephone Laboratories developed a mathematical theory of communication providing the first systematic framework to improve the design of telephone systems. Shannon’s aim was to identify the quickest and most efficient way (channel) to get a message from one point to another. This was motivated by the goal to discover how communication messages could be converted into electronic signals most efficiently, and how those signals could be transmitted with a minimum of error. The theory gives an approach of how to maximise the amount of information in a given channel and how to measure the channel’s capacity. He presented his theory in an article “A Mathematical Theory of Communication” published in two parts in the July and October issues of the Bell System Technical Journey in 1948. [4] After this article was published, Warren Weaver recognised that Shannon’s information theory and model has a wider potential for the general communication theory. In 1964, “The Mathematical Theory of Communication” was published by the University of Illinois Press, Urbana, in 1964. [5], consisting of two papers. In the first part, W. Weaver gives an introduction and explanation of Shannon’s theory, accessible for non-scientist and more related to the human communication since the original work was designed under a technical aspect and was formulated as a binary mathematical model. Part two is a reprint of the article published in the Bell System Technical Journal in 1948 with some minor corrections. [5]
Eventually, it became the basic model for communication, known as the Shannon and Weaver Model for Communication. In John Fiske’s words, this model is ' widely accepted as one of the main seeds out of which communication Studies has grown. It is a clear example of the process school, seeing communication as the transmission of messages. ' [6]
Basic Elements
The Shannon and Weaver Model represents the communication process in a linear form which involves a one-way communication from a sender transmitting a message to a receiver. The basic model contains six basic elements which form the general communication system according to Shannon and Weaver. [5]
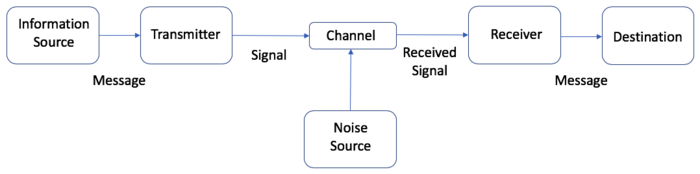
A desired message or a sequence of messages out of a set of possible messages is selected by the information Source, also called Sender. In order to send to message over the communication channel, a transmitter changes the messages into a signal. The receiver can be seen as an inverse transmitter which changes the signal back to a message and hands this message over to the destination. The noise, created by a noise source refers to any distortions or errors in the communication process which can occur during the transmission or at one of the terminals. [5]
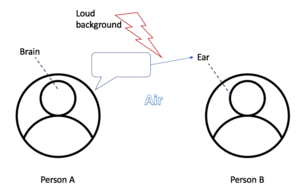
Example of Oral Communication
W. Weaver gives a simple example of human communication in order to understand the elements of the Communication Model. [5]
In this particular case of oral communication, Person A wants to share an idea with Person B. The brain (information source) of person A selects the desired idea (message) to transfer to person B. The voice mechanism (transmitter) of Person A transforms the thought into sound which is transferred through the air (channel). When the oral message arrives in the ear and its associated nerves of Person B, the sound can be reconstructed into the idea, so Person B received the idea. As Person A speaks to Person B in a loud surrounding (noise source), it might be that Person B can not fully receive the sound. Or, Person B got distracted by the loud background and thus, does not listen to the incoming sound of Person A. [5]
The Levels of Communication Problems
Shannon and Weaver identified and suggested three levels of problems in the area of communication. These levels show no clear boundaries, but rather an overlapping and interrelation with each other. [5]
Level A
The technical problem: How accurately can the symbol of communication be transmitted?
Level B
The semantic problem: How precisely do the transmitted symbols convey the desired meaning?
Level C
The effectiveness problem: How effectively does the received meaning affect conduct in the desired way?
The technical problem in Level A represents the main question for that the model was originally developed for. [6]
It focusses on the correct transference of sets of symbols, signals or pattern from the sender to the receiver. The accuracy depends on the technical efficacy of the medium or the channel.
Semantic problems compare the coverage of the intended meaning transmitted from the sender with the meaning interpreted by the receiver.
The effectiveness problem deals with the extent to which the meaning expressed by the sender and transmitted affect the conduct of the receiver in the desired way. [5]
Staples in Communication Research
Besides the suggested levels of problems in communication, the theory represents basic concepts which are used as staples in further communication research. [6]
Information
Within the scope of this particular communication theory, the word information is not related with meaning as it focuses on what is said rather than what could be said. It is defined as “a measure of one’s freedom of choice when one selects a message” where the concept of information is used to the situation as a whole and not to an individual message. The unit information states the extent of freedom of choosing a message. [5]
Entropy
The concept of entropy H describes the measure of uncertainty in a system. When the probability in choosing between two messages to send is completely free and unbiased, the entropy is large as the receiver can not predict the incoming message because of the uncertainty. In contrast, the entropy is very small when there is no choice of different messages for the transfer. [5]
Redundancy
A message is highly redundant when it contains a lot of items that add no new value. These parts of the messages are unnecessary, meaning that the sense of this message would be still complete even if this fraction of message would be missing. A general understanding of redundancy in communication is important because it helps combat noise in a communicating system e.g. in repeating a message. [5]
Channel Capacity
The capacity C of a channel is described as the ability of the system to transmit what is produced out of a source of given information. [5]
Strengths
Shannon and Weaver’s model for communication contains six elements connected with arrows indication the direction or influence. Advantages of this model are:
Limitations
There are some limitations of the Shannon-Weaver model highlighted by D. Chandler. [7] Some of the most relevant issues are related to the simplicity of the model as it enhances misinterpretation of the nature of human communication.
1. Linearity and lack of feedback
The transmission model consists of two separate elements, namely “sender” and “receiver”. In this system of communication, there is no simultaneous “sending” and “receiving” possible. Furthermore, the sender marks an active role who determines the meaning of the message while the sender is passive. This critique point also highlights a missing feedback loop, as the model is defined as one-way communication.
2. Content and meaning
The model originally describes a mathematical theory focusing on the pure transmission of information rather than their meaning. In this model, the content of a subject is framed as “the message” excluding feelings or similar influences. The process of decoding is treated as the inverse function of encoding, also excluding the receiver’s frames of interpretations. Shannon showed awareness of this limitation in his introduction stated as the following:
3. Influence of Context
Related to the pure transmission of information, D. Chandler critises that the model does not include the importance of context. Meaning and context such as situational, social, institutional, political, cultural and historical context are directly related and influences the interpretation of a message.
4. Influence of Relationships
The participants in the model are seen as isolated individuals without any influence of relationships (e.g. differences in power) and social roles.
5. Aspect of Time
The model does not include the aspect of time regarding a dynamic change and the circumstances of time which influences a different understanding of a message. It assumes that the elements sender and receiver remain separate in the same role over time.
6. Nature of the Medium
The medium (channel) of the communication model is assumed as neutral, having no effect on both the form and the content of a message in the process of communication.
Application in Project Management
Over the past years, the model of Shannon and Weaver has been highly influential in the area of communication and provided a basis for intense subsequent thinking in the way communications were analysed. This led to a further development of a wide range of other communication models. [3]
In general, the purpose of communication models is to facilitate communication. [8] Using the Shannon and Weaver Model of Communication simplifies the complexity of communication and emphasise the analysis. It aids to break down the communication process into steps which can be then diagnosed in order to investigated where barriers of communication are erected or where communication breakdowns take place. [9] Using the suggested three levels of problems can support the understanding of how the accuracy and efficiency of the communication process can be improved. [6] Furthermore, the model can be used in a predictively way as it supports the dismantling of barriers or compensates the decoding loss be anticipating and carefully encoding the message in order to achieve successful communication. [9]
Communication Guidelines based on Shannon & Weaver's key concepts
The development of the Shannon and Weaver Model of Communication has highlighted three interrelated aspects that can serve as communication guidelines within any project and for any manager. [10]
1. The importance of noise reduction
Supporting the assumption that a very accurate encoding is likely to lead to very effective decoding by reducing the semantic noise in particular. [10]
Semantic noise takes place when there is a misunderstanding of the message because both the sender and receiver have a different frame of reference. Therefore, a receiver does not assign the same meaning to a message which is intended to transmit by the sender or simply does not understand the message because of difficult vocabulary and unknown terminology. [11]
In respect of this assumption, semantic noise can be reduced when the project manager uses vocabulary and terminologies which are adapted to the person's understanding he or she is communicating to.
W. Dow and D. Taylor [12] state that general noise or interference can be a personal filter which influences the understanding and interpretation of a message. This personal communication filter is based on the personality, the background and the experiences of each individual. This can be essential when a project manager is communicating with a person from a different country or needs to handle different cultures such as Eastern and Western cultures. A project manager should be aware of potential personal bias and cultural differences leading to misunderstanding. This awareness should be used in order to individually adapt a message and increase the possibility of understanding the main idea. [12]
2. The relevance of redundancy
The use of redundancy is useful in order to prevent information loss when transferring a message in a noisy channel. Redundancy is presented by three types
- a) Conventional redundancy: Style of presenting a message
- b) Code redundancy: Ways of how the content of a message can be represented
- c) Content redundancy: Iteration/Repetition of the same message
- a) Conventional redundancy: Style of presenting a message
In order to draw attention to e.g. an important meeting date, a project manager can remind the project team by sending reminder e-mails.
3. The necessity of balancing redundancy and entropy
In order to achieve successful decoding, messages need to point out background knowledge or need to be congruent with the individual’s capacity to deal with them.
Overcoming the problem of a message which is transmitted completely unexpected, the redundancy of this entropic message can be increased. [13]
Therefore, a project manager should e.g give some keywords before introducing the main message. This person should be then able to frame the topic and scope and understand the main idea of the message. Another approach could be the use of different communication ways (face-to-face, presentation, phone call,.. ) tailored to the communication preferences of each project team member and stakeholder.
Communications Management Plan
It is essential for a project manager to understand the Shannon and Weaver Model for Communication to be familiar with the steps in a communication process. This understanding can assist to develop strategies in order to minimise the risk of a communication error or misunderstanding. A Communications Management Plan summarises the developed strategies and planned activities for an effective communication. It usually contains guidelines and templates to facilitate communication throughout the project. This is particularly important when communication is necessary between different countries, cultures, and languages. [8]
See also
Communication Management Strategy
Effective Communication in Project Management
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Project Management Institute. A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide). Sixth Edition; 2017
- ↑ Zulch, B. Communication: The Foundation of Project Management. Procedia Technology. 2014 Oct; 16: 1000-10009
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Stewart,R. Malayan, R. and Roberts, R. The evolution and use of communication theories. EUROCON'2001. International Conference on Trends in Communications. Technical Program, Proceedings (Cat. No.01EX439), Bratislava, Slovakia, 2001, pp. 251-254 vol.1. doi: 10.1109/EURCON.2001.937806
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. The Bell System Technical Journal. 27; 1948: (July and October): 379–423, 623–656
- ↑ 5.00 5.01 5.02 5.03 5.04 5.05 5.06 5.07 5.08 5.09 5.10 5.11 Shannon, C.E., Weaver, W. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Champaign, IL, US: University of Illinois Press. 1964
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 Fiske, J. Introduction to Communication Studies. Routledge. Second Edition. 1990
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Chandler, D. The Transmission Model of Communication. 1994 http://visual-memory.co.uk/daniel/Documents/short/trans.html [Access: 22.02.19]
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Project Management Institute. A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide). Fifth Edition; 2013
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Eunson, B. Communicating in the 21st Century. John Wiley & Sons, Australia. Fourth Edition; 2015
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Lin, N. The Study of Human Communication. Bobbs-Merrill. 1973
- ↑ Narula, U. Handbook of Communication: Models, Perspectives, Strategies. Atlantic Publisher & Distributors. 2006
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Dow, W., PMP, Taylor D. Project Management Communication Bible. Wiley Publishing, Inc. 2008
- ↑ Lowes, A.-K, Christensen, J. M. M., Jørgensen, T. Starting up a business - a communicative framework for defining and reaching a target audience. The Aarhus School of Business; 2004
Annotated bibliography
- A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide). Project Management Institute, Sixth Edition, 2017
Chapter 10 - The chapter Project Communication Management describes the process of the three steps in order to develop and implement a communication strategy that can be used to prepare a Communications Management Plan. Fundamental definitions and tools are also presented including the 5Cs of written communications and several communication methods to share information.
- Communicating in the 21st century. John Wiley & Sons, Australia, Fourth Edition, 2015
Chapter 1 - The chapter Communication today presents various communication models and their strengths and limitations. It also gives insights about successful communication and breakdowns of the communication process.
- Effective Communications for Project Management. Auerbach Publications Taylor & Francis Group, 2008
In the book, the essential elements of effective communication are presented. It contains tools for the Active and Effective Listening (Chapter 4), the development of a Communications Management Plan (Chapter 5) as well as key steps for successful meetings (Chapter 7) and effective Presentations (Chapter 8).
- Handbooks of Communication Science - Theory and Models of Communication. Cobley, P, Schulz, et al. De Gruyter M, 2013
The authors of this book give an overall and in-depth description of various communication models within different research areas as well as the components of communication based on the contemporary use and understanding of communication.
- Leadership Communication. Barrett, D. J. McGraw-Hill Education, Fourth Edition, 2013
This book provides guidelines for leaders in order to gain appropriate communication skills and to perform communication with high productivity and effectiveness. It also gives some insights into the theoretical aspects of leadership communication.