Stakeholder analysis
Contents |
Abstract
A stakeholder can be shortly described either as an individual, group or organisation who is likely to affect or to be affected by the output of a project. Stakeholders have an engagement in the achievement of the project and they can be inside or outside the organisation that is supporting the project. Companies have already initiated to focus the stakeholder identification in the early 1930's, whereas the first official definition is detected in 1963 and its owed to Stanford Research Institute (SRI). However, the original stakeholder definition and stakeholder model owe their origin to Freeman (1984). Stakeholder analysis is a critical step for the success of the project and it aims to identify all the relevant stakeholders categories, to categorise and prioritise them according to different criteria like their interest, influence and power, utilising alternative mapping techniques, to profile stakeholders and plan their engagement and, in conclusion, to decide on the stakeholder management processes.
Key words: Stakeholders, Stakeholders analysis, Project Management, Portfolio Management, Program Management
Stakeholders and stakeholder analysis
According to the classic definition of stakeholders from Project Management Institute(PMI) that is relevant for any project case “Stakeholders of a project are individuals, groups, or organisations that are affected or recognised to be affected either in a positive or negative way by a decision, action, or output of a project” [1]. Stakeholder analysis is referred as the systematic gathering and analysis of quantitative and qualitative data to decide whose interests should be taken into consideration throughout the project. The objective of performing a stakeholder analysis is to provide the project manager and project team an overview of the people who have interest in the project. It should be one of the first steps of each project. It aims to identify everyone with a concern who needs to be involved.
History
The term stakeholder in terms of definition, use and purpose constitutes a quite unclear concept in the literature and it tend to vary over the years. The first time the term ‘stakeholder’ appeared in the bibliography was in 1963 at the Stanford Research Institute (SRI) and originally included owners, employees, customers, supplier, lenders and society. However, it is truth that the business world was thinking and utilising the stakeholder idea many years before 1960s. According to Dodd (1932), GEC was identifying shareholders, employees, customers, and the general public as the main groups that they had to handle. Sapieca (1990) stated that Johnson & Johnson determined customers, employees, managers, and the general public in 1947. Igor Ansoff and Robert Steward developed further the term based on the SRI’s approach [2]. Freeman (1984) present the definition of stakeholders as “any group or individual who can affect or is affected by the achievement of the organisation objectives” in his book “Strategic Management: A Stakeholder Approach [3] .This is one of the most popular definitions as 20 out of 75 in total share this approach. In the figure below, the original stakeholder model developed from Freeman is presented.
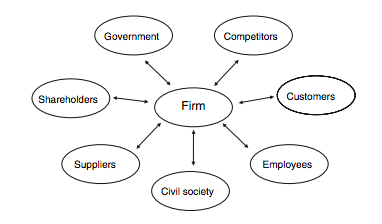
Stakeholder analysis process
There are several approaches regarding the stakeholder analysis process in the bibliography, but most of them have a common philosophy and can be summarised in four principal steps: Identifying, Prioritising, Profiling and Managing Stakeholders. In the initial stage, there is a need of recognising all the people who are affected or influenced by the project and have an interest in a successful or unsuccessful result. Stakeholders can be internal such as managers and employees or external like customers or suppliers. Stakeholders can also be characterised primary with a direct interest and stake to the project (employees, customer, suppliers) or secondary who do not engage in direct exchange but are affected by or can affect the project (business partners, competitors, regulatory authority). The next step is to asses and prioritise stakeholders according to their importance related to the project. Subsequently, stakeholder engagement follows, and the stakeholder analysis process finishes with stakeholder management process.
Identify stakeholders
The first key step in stakeholder analysis process is to identify all the people (individuals or groups) and organisations that are impacted by the project, and report all relevant information concerning their interests, engagement, influence and effect on project success. Possible project stakeholders may be people who are [1]:
- employed on the project
- sponsoring it or supporting it
- competitors
- contributing to the requirements or are determined to use the final product, process, service, or outcome of the project like regulatory agencies and potential customers
- involved in the marketing and advertising of the product or the service;
- responsible for the financial sustainability of the project;
- offering goods and services that are consumed by the project (suppliers)
- using the result of the project (customers)
There might be also other stakeholders indirectly involved like those contributing in recruitment activities, suppliers who contribute to the project by offering resources to the project, shareholders, those performing administrative and logistic tasks, the project management office that might perform various activities like governance, standardisation, project management trainings and so on. It is of crucial importance that the project team starts with identification of right (and legal) stakeholders, identifying their needs, demands, wishes, preferences dreams and priorities. It is important to take into consideration that stakeholder identification is not a stable activity that is done only in the initial days of the project, but it is a dynamic process that needs to be continuously updated as the project is in progress. Once the stakeholders are identified, they are listed in a stakeholder table or represented in a diagram.
Generally stakeholders can be categorised in two different main groups: internal and external [1].
Internal Stakeholders are individuals or groups inside the organisation with a direct interest or influence to the project, for instance employees, owners, and managers. They have substantial interest in the success of the organisation and they are in most cases highly affected by the ongoing activities, decisions, and outcomes of a project.
External stakeholders are individuals, groups, and organisations that are outside the business area, and they are likely to affect or be affected in a positive or negative way by the outcome of the project. External stakeholder might, for instance, be suppliers, shareholders, regulatory authorities and competitors and undoubtedly the customers.
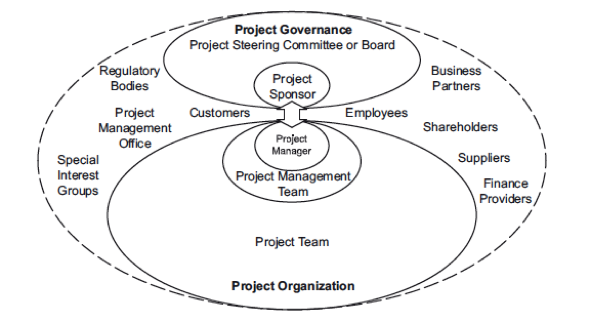
In order to better understand the different categories of stakeholders, a diagram from ISO 21500:2012, Guidance on Project Management, an international standard developed by the International Organisation for Standardisation, is used. It includes any person inside and outside the project as is represented in the figure below. It categorises the stakeholders in three main groups:
- Project organisation that includes the project team, the project management team and the project manager.
- Project Governance that may include the Project Steering Committee or Board and the Project Sponsor.
- Additional stakeholders like Employees, Customers, Suppliers, Shareholders, Business Partners, Finance providers, Regulatory Authorities, Project Management Office and stakeholders with special interest.
Prioritise stakeholders
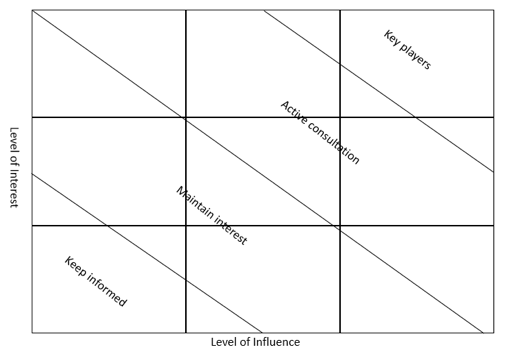
Once the stakeholders are identified, they are listed in a stakeholder table or represented in a diagram. The next step in the stakeholder analysis process is to prioritise the stakeholders and is commonly performed with the use of mapping techniques [6]. Some of the most commonly used mapping techniques constitute the power-interest grid, the power-influence grid, the influence-impact grid and the stakeholder tube and are further analysed below [7]:
Power/ Interest Grid: In the power-interest grid, also known as Power/Interest matrix, the stakeholders are placed on a two-dimensional graph. The horizontal axis represents the interest level whereas the vertical axis symbolises the power and the authority related to the project. For example, on the one hand, in the case that a stakeholder has both a high influence and interest in the project, it is considered as key stakeholder with a high importance in the project. On the other hand, if a stakeholder lacks influence in the project, then he is not likely to affect the project in a high level, even in the case that he has high interest. A typical Power/ Interest grid is presented below. The Power/ Interest Grid is the one of the most commonly methods for mapping and prioritising stakeholders.
Power/ Influence Grid: The Power/Interest grid model presents similar structure with the aforementioned model and plots the stakeholders in a two-dimensional graph. The axis Y represents the authority level whereas the axis X the capability to influence the decisions and the output of the project.
Influence/ Impact Grid: The Influence/Impact Grid plots the stakeholders in a two-dimensional graph, representing their capability to affect the project compared with their ability to cause changes in the project management and execution, and cons in the final outcome.
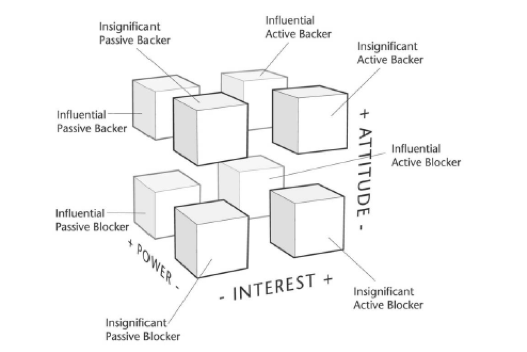
Stakeholder Cube: The Stakeholder Cube model maps out the stakeholders in a three-dimensional graphical representation of their interest (active or passive), power (influential or unsubstantial), and power (backer or blocker). A stakeholder cube is represented in the figure below to provide a clear overview and better understanding of the model [8].
Profile stakeholders
Next step in stakeholder analysis process is to profile the stakeholders and plan the stakeholder engagement. The main object of this step is to develop approaches to include project stakeholders in regards with their needs, anticipations, interests, and potential influence on the project. The substantial advantage that stakeholder engagement provides is that constitutes an actionable plan to interact efficiently with stakeholders. This process is executed regularly throughout the project according to the project management needs and the most common method is constructing a stakeholder engagement table. [1].
Stakeholder Management Processes
Identification, prioritisation and engagement of the stakeholders are the main principles that the stakeholder management strategy is based on. According to PMI, one of the most well-known project management techniques for stakeholder management is the communication plan.
The communication plan is an initial and critical step in the stakeholder management process. The objective of this plan is to communicate the project to all the relevant stakeholders and to prioritise issues when forming the communication strategy. There are different channels and strategies for a communication plan. Communicating channels can be in general categorised into written and oral means. Written channels can be emails, hard copies, tweets and blogs, whereas the most typical oral means are face to face communication, telephone and video conferencing. Both oral and written channels have advantages and the selection depends on the circumstances and the need for communication [O’Reilly and Pondy 1979] [9] . For instance, oral communication seems to be more effective when there is a need for feedback, different opinions and justifications. On the other hand, oral means tend to be effective when different vocabularies are used between people as they offer the opportunity to study and better understand the message. Except for the benefits of different channels, there are also external limitations in a business unit that lead in the final selection in terms of cost and time. Face to face communication may be more effective in terms of sharing opinions and collaboration. However, it needs time, cost and energy, whereas an email is an efficient, instant and “cheap” channel, but less effective than personal contact.
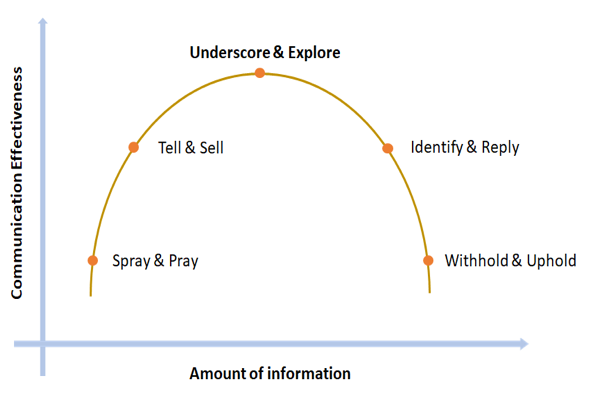
Except for different channels for a communication plan, there are also various communication strategies that can be used depending on the willingness of the top management members to share information and details with the employees regarding their content and directionality. Five different communication strategies can be found in the bibliography [Clampitt et al. 2000] [9]:
- Spray and Pray
- Tell and sell
- Underscore and explore
- Identify and reply
- Withhold and uphold
The communication strategies' graph depicts the effectiveness in the communication regarding the different communication strategies. As is evident the most effective method is the underscore and explore that balances the optimum ratio of transmitted information and effectiveness.
Auditing the effectiveness of the communication strategy is vital for the success of a project and this can be achieved by using the “regular auditing of communication”, as Hargie and Tourish (2000) recommended. A clear overview of the communication objectives is required answering in questions like: “Who is communicating with whom?”, “What issues are they talking about?”, “Do people understand and use the information they receive?” etc. This discussion aims to clarify ‘what, when, who and how’ [Hayes 2018]. Moreover, it is also worth pointing out that the communication change should not be based only in the aforementioned questions, especially if it is considered that there are not ready answers to these questions. Ergo, change managers should also focus on how they understand, interpret and finally use the information provided by other people according to the specific circumstances.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Project Management Institute. (2010) A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide), Project Management Institute. ISBN: 9781930699458, 193069945X
- ↑ Fontaine C, Haarman A., Schmid S. (2006), The Stakeholder Theory.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Freeman, R.E. (1984) Strategic Management: A Stakeholder Approach.
- ↑ Guidance on Project Management, ISO 21500:2012.
- ↑ The Stationery Office(TSO) (2011), Managing Successful Programmes
- ↑ Polonsky M. (1996), Stakeholder management and the stakeholder matrix: Potential strategic marketing tools.
- ↑ Sanguera P. (2018), Managing the Stakeholders.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Bourne L. (2005), Stakeholder Relationship Management
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Hayes, J. (2018), “The Theory and Practice of Change Management