Using Learning Plans to Counter Project Uncertainty
Sourcing Gennemtjek abstract Annotated bibliography Definition på Learning Plan I starten i abstract
Contents |
Abstract
Innovation projects are fraught with uncertainty in their nature. However, oftentimes management approaches presume a high degree of knowns and plan clear pathways through development stages. Doing so can be a costly and time-wasting affair and is caused by not recognizing that project teams are proceeding based on assumptions instead of known facts. [1]
The learning plan offers a systematic and iterative learning approach that deals with the high uncertainties to reduce maturation time or the time needed to reach a decision to kill the project by as much as 50%.[2] Using the learning plan allows a team to manage the ongoing evaluation and redirection in innovation projects, where specific objectives most likely are unclear or where the final goal is clear, but the pathway is uncertain. This article describes what the learning plan is, how to implement it and highlights the benefits and limitation of the tool.
Introduction

When the uncertainties are high, project teams often need to proceed based on assumptions rather than known facts. For instance, this is the case when dealing with innovation projects where the final market is unclear, which products will gain market acceptance most quickly and fully are unknown. The significance and number of uncertainties make it difficult to define milestones and the pathways to achieving them. In such projects, it is more reasonable and useful to use the approach of the learning plan. The learning plan allows a project team to evaluate and redirect the project in a proactive way when objectives may be unclear or when the goal is clear, but the path is uncertain. There is no standardized version of the learning plan, however different versions typically consist of the following basic steps:[2]
- Identify and categorize uncertainties into market, technical, organizational and resource uncertainties
- Identify the critical uncertainties to be resolved first
- Develop assumption for each uncertainty
- Define approaches to test the assumptions and define success criteria to approve/disapprove the
- Conduct the tests and evaluate the learning
- Iterate
The template in figure 1 shows an approach that emerged from a seven year study by MIT Sloan School of Management, where twelve innovation projects in ten large technology firms from the USA were tracked.
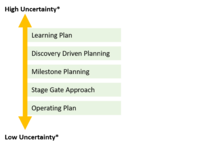
Figure 2 illustrates how the learning plan compares to alternative planning approaches in terms of dealing with uncertainty.
Measuring Progress by 'Learning Per Dollar Spent'
The progress in projects is measured by ‘Learning per dollar spent’, which gives management a metric to continually assess the value of cumulative learning compared to the costs incurred. Learning in this context is the extent to which an unknown has become a known. This is an effective way of measuring progress in high uncertainty projects because it acknowledges that the direction or goal of high uncertainty projects tend to change much more frequent compared to projects of low uncertainty. This gives managers a foundation to decide on an ongoing basis whether the cumulative learning is of sufficient value to warrant continuing the project. [2]
The Four Categories of Uncertainty Used in the Learning Plan
The learning plan categorizes uncertainties into four groups to be systemically examined as shown in figure 1: technical, market, organizational and resource uncertainties.
Technical uncertainties comprise those related to the completeness of scientific knowledge regarding the problem, technical specifications, which technologies to apply to to solve technical challenges, maintability and so forth.
Market uncertainties are related to the extend to which customers' needs, customer segments and competitors' products have been understood. Uncertainties in relation to revenue models andsales and distribution channels are also a part of market uncertaines. [2] The difficulty in understanding the customers’ needs and translating them into functional and symbolic characteristics of the product generates market uncertainty. [3]
Organizational uncertainties are associated with the dynamics of the organization. The time horizon for innovation projects are typically 10 years or more, which creates organizational uncertainties that should be taken into consideration. These include, organizational resistance, lack of persistence, inconsistencies in expections and metrics, changes in strategies, and changes in internal and external partners. Organizational uncertainties also comes into play when an innovation project transitions to an operating entity. [4]
Resource uncertainties include financial resources but also competencies. Project teams often lack one or more competencies critical to the success of pursuing opportunities. This may lead to project teams spending large amounts of time on acquiring the competencies needed. [5]
Implementation of the Learning Plan
The learning plan template in figure 1 consists of three phases each containing a number of steps, which the project team must go through. The three phases will be explained in the following in a practical way that allows for implementation: conducting a learning loop, evaluating the learning, and proceeding with the next learning loop.
1. Conduct Learning Loop
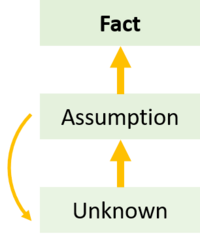
The first phase starts by defining what is known and unknown within the four categories of uncertainty. Next, the unknowns are assessed based on their criticality. The most critical unknowns are selected for the learning loop. Testing one set of critical assumptions is defined as a learning loop. The purpose of selecting unknowns it to increase the knowledge level on this specific set to an extend where they become facts instead of unknowns. This is done by developing assumptions based on the team’s current knowledge for each of the selected assumptions. The team then develops different approaches to test them to prove or disprove them. The idea of moving from unknown to fact is illustrated in figure 3.
The selected test approaches should be the most efficient in terms of learning per dollar spent. Success criteria for proving or disproving the assumptions are made, and tasks are defined along with a timetable for the learning loop. Testing one set of critical assumptions is defined as a learning loop. Finally, the team conducts the tests.[2]
2. Evaluate Learning
The second phase focuses on evaluating what has been learned. When a learning loop has been completed, an evaluation occurs involving the project team and an oversight board. The purpose of the oversight board is to act as a quality control and help assess the learning produced by learning loops. It typically consists of managers experienced in dealing with high uncertainty projects. The learning from a learning loop can be discovering unexpected insights coming from testing an assumption, which sets the project back. In this case, the project can either be redirected based on the new information or closed if the issue is a showstopper. The learning of the learning loop is reviewed, new identified uncertainties are prioritized, a new set of critical assumptions are clarified, and next tests are identified. It is important that the team and the oversight board agree on the assumptions to be tested and how they should be tested in the next learning loop.[2]
3. Proceed With Next Learning Loop
In the third phase, the project team proceeds with the next learning loop.[2]
Benefits and limitations
The following section lists key benefits and limitations of the learning plan as a planning approach.
Benefits
The learning plan is highly beneficial from a cost perspective if used correctly. Its way of reducing uncertainty systematically reduces maturation time or the time needed to reach a decision to kill the project by as much as 50%. The learning plan provides a step-by-step process which makes it easy to implement. Secondly, it encourages the project team to identify and act on the full spectrum of uncertainties to be resolved to succeed with a project. Furthermore, it helps to get an overview of what is known and unknown, which uncertainties to prioritize, suggest different assumptions about an uncertainty to be tested, and to find ways to test these assumptions as fast and inexpensive as possible.[2]
Limitations
Project teams tend to prioritize the uncertainties with which the team is more comfortable and to ignore those who are difficult to test. This is a pitfall for teams composed of specialists from the same professional backgrounds, who generally prefer to focus on challenges they can see a way through. Failing to recognize uncertainties of other categories increases the likelihood that one of these uncertainties will turn out to be a project killer. To counteract such tendencies, it is important for oversight boards to be staffed with veterans of high-uncertainty projects. It can be difficult to define the right success criteria based on which the results of an assumption test will be approved or disapproved. If the success criteria are slightly off, they may be measuring another parameter than the intended. Thus, it is important for the project team to discuss its plan for testing assumptions and defining success criteria with the overview board before executing tests. [2]
Glossary
- Learning loop: Testing one set of critical assumptions in the first phase of the learning plan. [2]
- Learning per dollar spent: The metric used for selecting approaches to test assumptions and for management to measure the progress of projects. [2]
- Learning plan template: No standardized template exists, however, the template shown in figure 1 has been developed by MIT Sloan School of Management, and provides a step-by-step process to implement the Learning plan. [2]
- Oversight board: A board consisting of managers that acts as quality control and help assess the learning produced by learning loops.[2]
References
- ↑ Cooper, R.G, Stage-Gate Systems: A New Tool for Managing New Products, Business Horizons 33, no. 3, 1990: 44-54
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 2.14 Rice, M. P., O’Connor, G. C., Pierantozzi, R., 2008. Counter Project Uncertainty, MIT Sloan Management Review, Winter, 54-62.
- ↑ Biazzo, S., 2009. Flexibility, structuration, and simultaneity in new product development, Journal of Product Innovation Management, 26, 336-353.
- ↑ Lechler, T. G., Edington, B. H., Gao, T., 2012. Challenging Classic Project Management: Turning Project Uncertainties Into Business Opportunities, Project Management Journal, 43, 59-69.
- ↑ Ray, H., 1987. Living with Uncertainty in Resource Management, North American Journal of Fisheries Management, 43, 59-69.
1. 2. See Z. Block and I. MacMillan, “Milestones for Successful Venture Planning,” Harvard Business Review 63 (September-October 1985): 184-196. 3. See R.G. McGrath and I. MacMillan, “Discovery-Driven Planning,” Harvard Business Review 73 (July-August 1995): 44-54. [1] 4. Rice, M. P., O’Connor, G. C., Pierantozzi, R., 2008. Counter Project Uncertainty. MIT Sloan Management Review, Winter, 54-62. 5. Biazzo, S., 2009. Flexibility, structuration, and simultaneity in new product development. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 26, 336-353.
Annotated bibliography
Mark P. Rice is the Frederic C. Hamilton Professor for Free Enterprise at Babson College. Gina Colarelli O’Connor is associate professor and Academic Director of the Radical Innovation Research Program at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute. Ronald Pierantozzi is CEO of PPT Research Inc., a materials technology company in Allentown, Pennsylvania, and the former director of business development at Air Products and Chemicals Inc.
G.C. O’Connor and M.P. Rice, “A Comprehensive Model of Uncertainty Associated with Radical Innovation,” 2007. This article explains about the uncertainty matrix, which is a useful tool for the project team when prioritizing uncertainties during the first phase of the learning plan.
Cite error:
<ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found