Lean 6 Sigma in project management
A rigorous management control of portfolios aim to control the risk and focus in investing in the most important projects in accordance with the overall strategy of the organization.
On the other hand, the Lean Six Sigma is a methodology that combines the lean philosophy and the Six Sigma methodology in order to increase the value of resulting products at a lower the cost. This combined methodology helps to gain in knowledge in how business processes are developed.
The Lean Six Sigma in portfolio management may help to conduct business processes into more efficient and effective ways. In this article it will be described how the waste reduction and high quality control can be implemented in each business operation of the entire portfolio project in order to maximize the profit.
Contents |
Background
In today's world, the strategies in companies are commonly seeking competitive advantages while gaining in profitability and quality. Miscalculation in delivery times or budgets can affect this competitiveness and cause sever risk for the ROI (Return Of Investment) of a firm. The main advantage doing a correct portfolio management is to optimize the overall program/project evaluating individual projects. In traditional portfolio management the progress of each project is tracked against tasks and not value created. This may lead to ineffectiveness that Lean Six Sigma may help to avoid.
Introduction
Lean Six Sigma in project portfolio management is a methodology that combines the philosophy and tools from Lean project management and Six Sigma management. In lean portfolio management the main objective is to minimize costs and maximize the use of the resource available. An entire project/program is decomposed in small projects and resources are distributed through an analysis of priority. Small projects enhance the flexibility of the people who are working in those projects. The prioritization is done after an approach to stakeholders and clients to identify features that can increase the ROI of an organization. The estimation of this priorities is done in small cycles since business conditions may change all time. Thus, the priority of different tasks may change as well.
As a complement to the lean philosophy, Six Sigma offers the possibility to improve the quality of processes and products. In Six Sigma portfolio management, procedures are standardized at the operational level of a company and focus in delimited goals always addressing to the highest ROI. It is a methodology that has to be implemented in the entire organization, from the strategic level to the operational level. A strong point that Six Sigma can offers is its capability to align the projects with the strategies followed by the companies. As in lean methodology, Six Sigma project are commonly for the short term. Both concepts can be applied in a common framework:
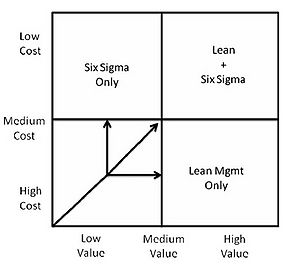
Applying both concepts together, lean six sigma is able to:
- Reduce the complexity of business processes.
- Optimize processes.
- Develop culture aiming to enhance the performance of operational teams.
Implementation
In order to develop a Lean Six Sigma methodology in portfolio management, several aspects have to be taken into account. For instance there has to be at least four categories of certified belt employees as in Six Sigma:
- Champions: They take responsibility of the implementation of Lean Six Sigma across the entire organization.
- Master Black belts: They have coach responsibility and spend all their time in Six Sigma evaluation, from the statistical analysis data to assure consistency of Six Sigma across function and departments
- Black Belts: They are focused in specific projects to apply Six Sigma and they dedicate full time for Six Sigma implementation.
- Green Belts: They are the employees who implement Six Sigma in their jobs responsabilities
Another concept applied from Six Sigma is the DMAIC framework:
-Define: In this first step, it is defined the opportunities the company have for different projects. It is the most important phase since it targets the limited sources of a company.
-Measure: In this phase, the business processes is documented. It is also validated the measurement techniques and the historical Sis Sigma is assessed.
-Analyse: The data collected in the previous step is analysed and the performance of different project is evaluated evaluating the roots of multiple problems.
-Improve: The teams in projects are able to eliminate the top case sufficiently to achieve the overall objectives of a project.
-Control: The company has been able to establish mechanism of control on possible causes of problems for the long run.
Tools
The tools used for the Lean Six Sigma portfolio management are a combination of the tools of both methodologies:
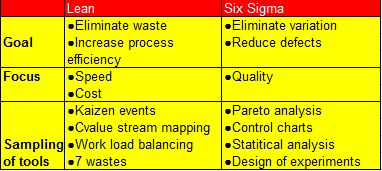
From the Lean methodology is commonly used:
-Kaizen Events:
-Value stream mapping:
-Work load balancing:
-7 wastes:
From the Six Sigma methodology:
-Pareto analysis:
-Control charts:
-Statistical analysis:
-Design of experiments:
Example: The multi-objective case.
An example of application of the Lean Six Sigma portfolio management can be found in the literature. In that case it is considered the problems of identifying the projects to implement Lean Six Sigma concepts. As the number of projects increase in a company, the risk of misusing resources of a company increase as well. The successful implementation of Six Sigma in a company involve a management involvement, training, communication and changes in the organization.
Consider the case where multiple projects are proposed in a company. The correct Lean Six Sigma implementation would deal with maximizing the benefits and minimizing costs:
Where ci are the costs, xi is a binary number which tells if the project is selected, B is the benefits, wj is the weight and sij is the normalized performance score:
To the previous mathematical model 3 kind of constraints are added: Resource constraints, Diversity constraints and Management limit constraint. The resource constraint equation tries to include the limitations a company has to implement Lean Six Sigma in every project selected as there is a limited number of certified belt employees who are able to process with those implementations. The Diversity constraint takes into account that in the application of Six Sigma involves all actors in a project. Decision makers not always want to involve all stake holders in Lean Six Sigma. Finally, the Management constraints equation tries to englobe the limits of projects a management group is able to handle. This analysis was done for a conductor company where 51 proposal project were evaluated. The potential benefit index:
ends with the following analysis:
Each of the point of the figure shows different optimal for project portfolio. The correct choose of the order in which projects are selected and execute depends on the necessities of a company. In this example, the Pareto frontier tells that for a total selection of projects with a portfolio cost e.g 1 million $ the portfolio benefit index should never be higher than around -470(the lower the better) in order to implement Lean Six Sigma.
Drawbacks
The implementation of Lean Six Sigma can often lead to loose simplicity of projects. The common pitfalls found are:
-So much attention in belt certification: Coming from the Six Sigma methodology, a proper Lean Six Sigma implementation requires green and black belt certifications. This characteristic may led employees to complete the belt certification with more enthusiasm than pursue real value for a business process.
-Unbalanced resources: When there are many belt candidates focused in belt certification it could happened a high demand on subject matter experts who are not able to attend to everything.
-Collect too much information or do not evaluate it properly: Six Sigma is a methodology data driven. It is observed in some companies a tendency to collect much more data that required and with poor data quality. Prejudices of people can also provoke not to read data gathered in a proper way.
- Rigid program implementation: As mentioned in previous chapter Lean Six Sigma take advantage of lean implementation in order to enhance speed and flexibility on projects. When the organization focus so much in the methodology tools the company may end up in inflexible procedures where many templates shall be filled out and all this advantages may be lost.
- Not following properly the DMAIC method: Another common mistake in the business world is to go directly for the implementation phase without considering to gather and analyse sufficient data.
- Assume that belt candidates have managerial skills/background: A Lean Six Sigma portfolio management has to include green and black belts employees with sufficient managerial skills and background. It usually happens that the selection of the candidates for this belts certificates have not been done considering that field.
-Assume there is a best way and not better ways: Lean Six Sigma philosophy is a continuous improvement methodology where there is not just a best way to manage projects but there is always better ways for improvement.