(Re)Introducing Project Management in a SAFe world
This wiki focusses on (Re)Introducing Project, Program and Portfolio Management to firms that have introduced SAFe but do not have a functioning PMO. This article is intended for both SAFe practitioners and Project, Program and Portfolio Managers and the Executives that lead them.
By Ben Blackburn
Background
Traditionally Software development has utilized Project, Program and Portfolio Management to support delivery. With the creation of new and highly effective small scale software development approaches like Scrum (1986 Hirotaka Takeuchi and Ikujiro Nonaka / 1990's Jeff Sutherland, Ken Scwaber, John Scumniotales and Jeff McKenn), Extreme programming (1996 Kent Beck), the Agile manifesto (2001), DevOps (late 1990's crystalizing in Pätrick Debois 2008/9), and Design Thinking (Cross over into Software development from the late 1990's onwards) development organizations have been evolving fast.
As the small scale but highly effective practices gave significant advantage to the team using them they rapidly gained popularity and adoption. As enterprises saw the value in these practices the demand for deploying these approaches grew.
Methods such as and Large Scale Scum (LeSS) in 2005, Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe) in 2011, Disciplined Agile Delivery (DAD) were developed to meet this need for introducing scalable Agile Practices. From the mid 2010's these practices were regularly featured in popular business literature such as Forbes and Harvard Business Review.[1] [2]
Those companies that adopted these practices gained significant success with results such as "98% experiencing success with Agile practices" and "75% saying that more than half of their Agile projects were successful" [1] Competition created an imperative for most software organizations to change and adopt these practices.
The impact n Project management as a profession in Software development was profound. Early SAFe versions advocacy of a new organization with new roles took removed traditional project, program and portfolio manager responsibilities and moved them into the new SAFe's roles such as Product Owners, Scrum Masters, RTE, Epic and Business Owners. The impact on project management as a profession has been profound with the most popular Enterprise scale Agile model in the world [3] Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe), effectively advocating removing Project Managers from development organizations. This led many organizations to "throw out the baby with the bathwater" in relation to those project, program and portfolio management best practices that were not explicit in the scaled Agile models.
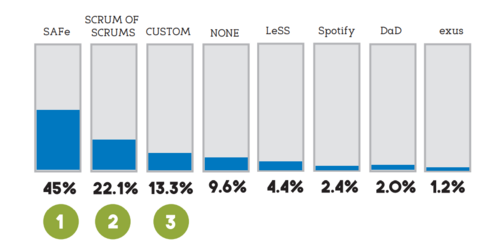
During the period 2011-2017 Project management as a separate formal practice within many software development Organizations literally had no place in those organizations that deployed SAFe as written. This is important because as of 2017 the SAFe methodology was used by 45% [3] of those firms using an Agile methodology at scale.
Many of these firms have had to contend with a number of issues that this caused up until the acceptance of Project Management through its "(Re)introduction" in the form of an Agile Project Management Office (APMO) in the 2017 release of SAFe version 4,5. This new version implicitly accepted the role PMO's (and by extension Project Managers) play in strategy formation, Project and Program execution as well as owning and disseminating best practices (in this case represented in the SAFe model by the "Lean Centre of Excellence").
In this article we look at the issues that have arisen in many firms during their SAFe implementations and how implementing an APMO solves these issues. The article is intended for practitioners who are working in or with organizations that have deployed early versions of SAFe as part of the support for establishing an APMO along the lines now advocated by SAFe. It is also relevant or those organizations that are implementing SAFe but have not had an effective PMO in place before
Note: Due to the relatively new and evolving nature of SAFe there is limited empirical data around specific “Implementation issues in Large Scale Agile transformations” [4]. As a consequence this article is more reliant more on Anecdotes, Personal Experience and other literature in this space.
Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe)
According to the extensive "Scaling Agile Report 2017" by C-Prime .[3] SAFe is the most popular Scaling Agile methodology by far. It is more than twice as popular as its nearest competitor Scrum of Scrums (or Scrum @ Scale) and more than 3 times as the 3rd most popular choice "Custom" (representing an in house patchwork of approaches)
What is SAFe?
According to ScaledAgileFramework.com[5]:
Quoting Dean Leffingwell (the creator and chief methodologist of SAFe) [5]
“SAFe® for Lean Enterprises is a knowledge base of proven, integrated principles, practices, and competencies for achieving business agility using Lean, Agile, and DevOps.” “It “…is built around the Seven Core Competencies of the Lean Enterprise that are critical to achieving and sustaining a competitive advantage in an increasingly digital age”
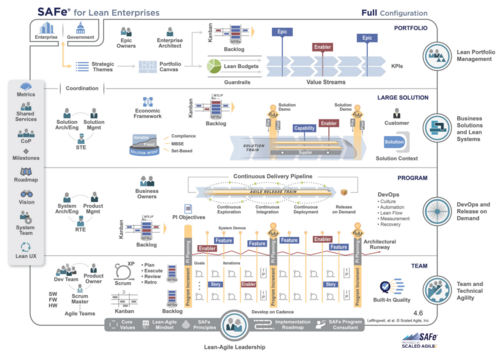
ScaledAgileFramework.com illustrates the overall framework below. It makes this framework and support material available to all along with an extensive library of resources that can be used for free to support implementing and running SAFe in practice
The seven core competencies:
From the Sacledagileframework.com[5]
"Lean-Agile Leadership – Advancing and applying Lean-Agile leadership skills that drive and sustain organizational change by empowering individuals and teams to reach their highest potential
Team and Technical Agility – Driving team Agile behaviors as well as sound technical practices including Built-in Quality, Behavior-Driven Development (BDD), Agile testing, Test-Driven Development (TDD), and more
Agile Product Delivery – Building high-performing teams-of-teams that use design thinking and customer-centricity to provide a continuous flow of valuable products using DevOps, the
Continuous Delivery Pipeline, and Release on Demand Enterprise Solution Delivery – Building and sustaining the world’s largest software applications, networks, and cyber-physical solutions
Lean Portfolio Management – Executing portfolio vision and strategy formulation, chartering portfolios, creating the Vision, Lean budgets and Guardrails, as well as portfolio prioritization, and road mapping
Organizational Agility – Aligning strategy and execution by applying Lean and systems thinking approaches to strategy and investment funding, Agile portfolio operations, and governance
Continuous Learning Culture – Continually increasing knowledge, competence, and performance by becoming a learning organization committed to relentless improvement and innovation"
Levels & Objectives
SAFe's model aims to create an optimized "continuous delivery pipeline" via one or many Agile Release Trains (ARTs). There are 4 levels of SAFe suggested - "Essential", "Large Solution", "Portfolio" and a "Full" SAFe. All of ARTs should deliver improvements in delivery efficiency but at the Portfolio and Full levels the suggested organization changes to focus organization around the delivery of value with a more strategic portfolio emphasis relevant to larger companies that may have significant numbers of people working in a wide range of different business areas or providing a wide range of services
Introduction of Project, Program and Portfolio management
From SAFe 4,5 onwards we start to see the introduction of formal portfolio management processes as historically defined . First with Lean Budgets and then more features in each version until SAFe V5.0 which effectively introduces full portfolio management and portfolio optimization capabilities in the traditional project management sense with Portfolio Kanbans and Backlogs, Lean Budgets and project & program budget "Guardrails". By also introducing an APMO working with the Lean Center of Excellence it seems the model has created P3O's definition of program or portfolio offices
Roles and responsibilities
Developer and tester roles remain very similarly defined to the past but have new practices such as daily stand-ups, regular demo's & retrospectives but the roles responsibilities remain broadly the same but SAFe defines new roles in its organizations such as Scrum Master, Product Owner, Product Manager, Release Train Engineer and Solution Train Engineer, System Engineer & Solution Architects. This means may of the higher level expert and managerial positions change change substantially - having different relationships, responsibilities and reporting lines than.
What are the benefits of SAFE?
As advertised on ScaleAgileFramewrok.com:
20 – 50% increase in productivity
25 – 75% improvements in quality
30 – 75% faster time-to-market
10 – 50% increase in employee engagement and job satisfaction
Results like these sound very impressive. While Quality improvements and Employee engagement and satisfaction can be pretty straightforward to report and compare, productivity and time to market are much harder to compare directly before and after an agile transformation. Increases in productivity are often very difficult to quantify when the basis changes (I.e from hours to stories) how do you compare these apples and oranges? Likewise with Time to market - if estimation comparisons are flawed so is time to market.
That said - and working back from quality metrics with some basic assumption (like the bugs that didn't need fixing after release are now available for new development) INSERT IBM COST OF BUGS TO FIX it seems logical that organizations gain significant efficiency improvements through SAFe
My personal experience at a Mid Sized software firm was introducing basic Agile practices such as cross functional team Scrum to a traditionally Waterfall organization raised productivity from 70-80% of estimated scope per to circa 104% within 12 months. In the case I mention we had the rare situation of 3 Agile teams having the old waterfall estimation process running throughout the period as the main development organizations processes still required the provision of hourly estimates. Therefore the figures are not subject to comparison errors as is usual during an agile transformation. This experience would seem to support the kind of figures SAFe advertise.
Issues raised with SAFe
General issues raised with SAFe
Epic (Program) Roles and Responsibilities Epics are usually defined as larger packages of work that cross Value stream/ART and spanning multiople PI’s. The role is typically delivered by either A) The ART or Value stream Product Manager B) an empowered individual who sits alongside the formal ART structures. Where the individual sits in Product Management there is a need to have standard prioritization and escalation paths in place to ensure delivery of dependencies in other ARTs. Without this being a strong and mature process with shared measures of value across the different Value streams/Business lines – in practice this is very difficult as Value streams are relatively large organizations and they may have very different working practices (estimation, value assessment etc) as encouraged by SAFe. They may also have different cadences for integration and delivery. Especially where Value streams are aligned with different products in the market. Competition amongst. Epic Owners that also work as Product Managers can also find it hard to manage the additional workload of dealing with other teams as well as their own product organization and customer responsibilities Where the individual sits outside of the ART / Value Stream structure they are not part of any larger organization such as a PMO. As their responsibilities are temporary the ART’s and Value streams they require work from may not prioritize their requirements. In the absence of formal PMO’s they also potentially have weaker escalation paths and less access to Peers that can support them as well as access to Best Practices. Should differences exist between the Product Owners in the various teams and the Epic Owner the conflicts are more difficult to manage as there are weaker formal relations at play than when a PO disagrees with their more senior Product Manager in the ART. There can also be conflicts between the Epic Owners requirements and the requirements the ART want to build – for example an Epic Owner wants to build and limit cost to a single interface but the ART mandates and demands more budget to deliver a flexible interface as that’s is what the team traditionally does.
Dealing with big tings
SAFe’s approach to delivery does not manage the largest deliveries well. By focusing on pikes to understand parts of the delivery and making assumptions about estimates likely based on very infrequent events SAFe de-emphasizes the advantages of more thorough analysis upfront. If initiatives have strict deadlines (regulation) or penalty clauses (contracts) SAFe’s approach can add significant risk as organizations may be unable to respond in time should effort to completeb´grow. As the Portfolio is generally fed from the Values streams below impacts on other teams and the organization as whole may not be adressed at the right time. For example an epic sits on a backlog insufficiently understood and then its true size emerges too late to be easily absorbed in normal operations
Dependency Management
Management of Dependencies between teams/ART’s and Value Streams is weak. Without shared concepts of value and agreed prioritization criteria it is hard to get dependencies resolved
Interfaces outside of the SAFe Organization
Interfaces with the rest of the organization, Management of customer contracts and 3rd party suppliers etc is very unclear in the model. SAFe pretty much ignores that this may require substantial effort and assumes it can easily be absorbed into other roles. SAFe does not open up to roles that may be needed as part of managing these interfaces
Not optimized for delivery of business to business development SAFe’s is rooted in Scrum which in turn made its biggest successes in Business to Consumer product development and when used inside firms IT teams to make them more responsive to their internal customers. This means it is optimized to delivery of small packets of work that create value at the end of each sprint. This works very well for delivery to customers of a new app that get a cool new feature or a trading desk that wants their developers to give then a new feature. But it does not necessarily support delivery of large complex packages of work that are tied into formal contracts. In particular there is a conflict between MVP for a client and an easy to use bug free product that has bells and whistles to make the customer happy. Agile usually suggests not doing these deals or only signing partnership deals that share risks and costs. This is a great idea but can be very difficult to deliver in practice as the majority of contracts that still work on fixed prices and penalties.
Stewardship of Value Historical versions of SAFe moved many traditional project manager responsibilities to Product Owners. PO's might be given scope and therefore de-facto budget responsibility for delivery. Profitability for deals can easily be eroded where product owners manage scope and client satisfaction without regard to the bigger picture. This problem is particularly pronounced at the Epic level when multiple teams and ART’s are involved. Each team and ART aims to do the best job they can and the potential for additional work to gold plate and futureproof solutions can lead to new unnecessary scope/costs. SAFe did not emphasize that process are needed to ensure that value is achieved and budgets managed – on both large and small scale projects within and ART/Value stream as well as on Epics and across the portfolio. The processes to do this need to be overseen and managed or they will not operate. This is especially true in the business to business space
Prescriptive organizational model and practices SAFe structures Agile making delivery of large initiatives more complex. Smaller scale Agile would suggest organizing around these deliverables But SAFe would assign an Epic Owner to potentially manage delivery from multiple teams across multiple ART’s or value streams who may have different ways of self organizing, prioritizing and picking their own work, at different Planning, integration and release cadences with different ideas of value, definitions of done etc etc. SAFe is more prescriptive and aligned with large companies existing modes of operation The whole PI planning and sprints may not align with the workload of certain teams. For example many maintenance teams use Kanban to manage their workload as the most appropriate approach.
Politics The SAFe Model presupposes a certain culture where politics plays less of a part that is easier to implement top to bottom in small organizations. SAFe underestimates or ignore the role and influence politics has on implementing and maintaining the momentum for the models evolution in an organization. Power and authority are significant influences in large companies. Standardizing or accepting other peoples proposals for best practices (regardless of the idea that “best ideas win”) do not always align with individuals incentives. Finding ways to facilitate others success may not always have the right recognition and reward processes to support it. These kind of issues become more and more relevant the larger the organization. Politics is a particular concern for EPIC delivery where ART & Value stream Management have greater power and authority than external epic owners.
General criticisms of SAFe
I practice most organizations find work arounds to solve these issues as they mature, but as common problems experienced during implementation and early adoption they could be either incorporated more explicitly into the model or resolved by addressing them formally as part of the implementation.
Delegated Authority & Budgets
Dependency management In the absence of standards for prioritization and value agreed across Teams and ART’s deliveries - in particular larger "Epics" - can have issues synchronizing work. Even in teams with standards for agreeing value and having shared estimation basis, it is common that one team 1s blocking issue is not prioritized by team 2 due to higher value work in their backlog or the imperative to stick to their own sprints commitments. This can lead to delays and lost productivity that a traditional project manager would have resolved Dependency management processes across teams and ART’s need to be very advanced and flexible to optimize delivery. This is hard to do in practice. Otherwise delegated authority to make these decisions needs to be delegated sufficiently to optimize for whole deliverable performance.
- Hard to prioritize large and difficult things
SAFe implementations introduce lots of new working practices such as Business Kanbans
(Re) Introducing a SAFe APMO
Motivation for (Re)Introducing an (A)PMO
Formal Portfolio Management is a best practice in successful Agile companies
Market Research from CA Technologies suggests that "Agility Masters" (defined as the top 18% of respondents in terms of maturity of Agile and DevOps practices) are:
1) 3,2 times more likely to strongly agree that portfolio management has a key role to play in organizations
2) 4.1 times more likely to agree the company has the right Vision and strategy [6].
PMO's address many of the problems raised with SAFe
In the study "Recurring Concerns and Best Practices of Agile Coaches and Scrum Masters" [7] Analyzes the issues raised by Scrum Masters and Agile coaches. As the Agile coach operates at all levels of the organization the issues raised can be seen as general issues rather than specific to any one role. The issues are analyzed and specific best practices within Agile suggested to resolve them. The conclusion of the study is that the majority of issues in SAFe implementations can be addressed with the mediating actions below. (1) PUBLISH GOOD PRACTICES (2) SUPERVISION (3) GLOBAL IMPEDIMENT PROCESS (4) GLOBAL IMPEDIMENT BOARD (5) DON’T USE SCALING AGILE FRAMEWORKS AS A RECIPE
When modified to apply to fits very well with many activities performed by a formal PMO along the lines of the those recommended by Axelos or the PMI (through its P3O methodology). Points 3 & 4 relating to Global Boards very explicitly states that Companies should have higher level bodies to help manage issues across teams conflicts incorporate best practices regardless of its inclusion in the SAFe model formally or not.
Dean Leffingwell says so...
As Dean Leffingwell (the creator and chief methodologist at SAFe) advocates havng an APMO from Version 4,5 the most up to date versions of the model suggest having one optimal for organizational performance. As the monitoring and control of value is managed out of the APMO it may also be advantageous to as Dean Leffingwell says himself in his 2010 book "Agile Software Requirements"[8] "Project Managers should be re-tasked as Agile Project Managers." Both then and now Dean Leffingwell appears to be recognizing the value of all of the parts of project management that were not passed explicitly into the scrum teams themselves such as contract and relationship management and communication interfaces with suppliers, customers and other parts of the enterprise.
The introduction of the APMO into SAFe suggest an active role for a PMO to both support execution and to act as a Center of Excellence(CoE). Many would recognize this as two of the key aspects of a Portfolio planinng function in line with P3O best practice.
This leads to the conclusion that larger companies benefit the most from Implementing SAFe with a strong PMO supporting strategy formation and execution regardless of any specific direction or lack of direction about this from SAFe.
How to (Re)Introduce a (A)PMO
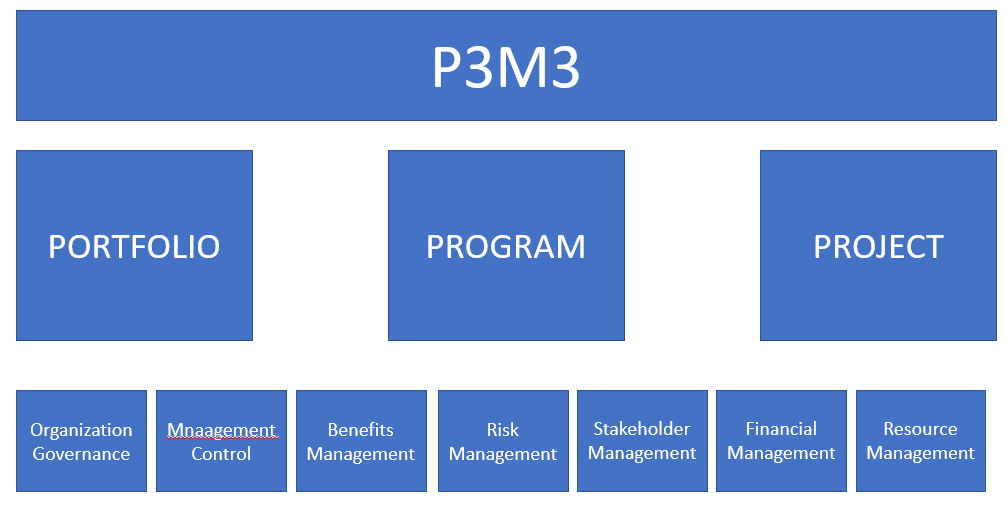
Best practice would suggest implementing a P3M3 maturity assessment to identify the state of the organization prior to identifying at what stage of maturity the organization is as well as to identify the organizations aspiration for the function and best practice implementation approach. It would be advisable for any Assessment to be run by someone who is also used to the SAFe model to ensure alignment of language and full awareness of the practices that already exist in the SAFe organization that mitigate many concerns that could otherwise be raised.
Best practice would suggest use of a formal change management model such as ADKAR to guide the introduction of these changes.
As many SAFe organizations have spent considerable time and energy rejecting past practices they may resist the introduction of what might be considered old fashioned practices. So aligning it to the latest models of SAFe, the framing of the reasons to change and language used in the initiative is likely to be vey important to its success
Addressing the culture issue
Beyond SAF'e V5.0's APMO
Current SAFe model 4.5 addresses many issues by providing a flexible new function - the APMO but it does not address all of the issues raised in XXXX.
For instance: By not clarifying the scope of the manate of the new LACE/APMO it does not clarify as the scope necessarily have a mandate to address issues with Communities of practice not rolling out best practices efficiently
Annotated Bibliography
Broadcom https://docs.broadcom.com/doc/how-agile-and-devops-enable-digital-readiness-and-transformation
Research on the state of Adoption of Agile principles, DevOps and interestingly on the impacts of Agile practices on the wider organization. Agility and business performance opinions and statistics.
Researchgate has several useful (but small scale) studies on issues with Large Scale Agile implementations. One of the most relevant was this one. It Investigates the types of issues experienced by Practitioners of large scale agile frameworks and provides the best practice options to resolve them. Including most importantly the finding not to treat the frameworks as gospel.
VersionOne State of Agile Annual reports. https://stateofagile.com/#. Background to Agile adoption and key trends in Agile by one of the larger dedicated Agile Systems vendors. Circa 1500 respondents across industries and at varying organizational sizes. Covers everything from motivations to adopting Agile through to to perceptions of success and specific techniques used. Solid general background to Agile in practice
Quotes
Article on Medium.com - On of the 15 reasons to choose SAFe over waterfall was give as "2. Enhancing the Role of Project and Program Managers". [9]
Suggestions for further reading
Scaledagileframework https://www.scaledagileframework.com/
The Agile Manifesto: https://agilemanifesto.org/
Agile Alliance: https://www.agilealliance.org/resources
Disciplined Agile https://www.pmi.org/disciplined-agile/start-here
HotPMO: https://www.hotpmo.com/
© SAFe and Scaled Agile Framework are registered trademarks of Scaled Agile, Inc
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 https://hbr.org/2016/05/embracing-agile , https://hbr.org/2018/05/agile-at-scale, May 2018
- ↑ 'https://www.forbes.com/sites/lbsbusinessstrategyreview/2020/03/28/the-new-boardroom-imperative-from-agility-to-resilience/?sh=66e52fbc3867, Forbes March 2029'.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 C-Prime, https://www.cprime.com/wp-content/uploads/woocommerce_uploads/2017/09/cPrime-Scaling-Agile-Survey-17-Digital.pdf, (NC-Prime, 2017), p14.
- ↑ '[Dikert et al. 2016; Alsaqaf et al. 2019;Uludag et al. 2018].
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 https://www.scaledagileframework.com/about/
- ↑ https://docs.broadcom.com/doc/how-agile-and-devops-enable-digital-readiness-and-transformation /Page 12
- ↑ Recurring_Concerns_and_Best_Practices_of_Agile_Coaches_and_Scrum_Masters, Oct 2019
- ↑ Dean Leffingwell, Agile Software Requirements, (Wesley, 2010),
- ↑ https://medium.com/scaled-agile-framework/15-reasons-why-safe-is-essential-for-agile-teams-494ddd264518