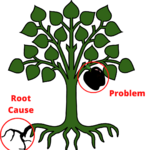
Root cause analysis (RCA)
Abstract
While managing programs or projects we face many challenges which affect the schedule or quality of the project. For the elimination of such similar future challenges, it is important to identify from where the problem has started (Root Cause). Root cause analysis is a method to identify the source of the problem and to know how it has happened and how to prevent such problems in future. Multiple industries like Construction, manufacturing, pharmaceutical, Information technology uses this method for successful identification of causes for the problem. RCA also gives the scope to identify the gaps in the existing process, reduce the cost of production or increase production. In this article, we will learn about What is root cause analysis and its importance, when and how RCA has to be done and methods of doing root cause analysis.
Introduction
Root cause analysis (RCA) is an important aspect of a broad problem-solving process and continuous improvement. A root cause is a part that contributed to a failure and should be removed completely using process improvement.The root cause is the most fundamental problem—the most fundamental reason—that puts in motion the a whole cause-and-effect that leads to the problem. Root cause analysis alone would not give any results, it has to be used as part of a bigger problem-solving effort aimed at improving quality. Organization uses continuous improvement method to remove that problem completely .
Root cause analysis refers to a variety of methodologies, tools, and procedures used to identify the root causes of issues. Some RCA approaches are more focused toward finding actual root causes than others, while others are more broad problem-solving procedures, but others simply provide support for the root cause analysis core activity.[1]
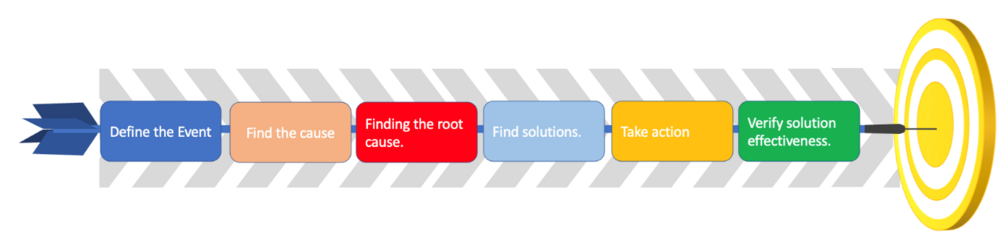
Process of Root cause Analysis
Below table shows purpose, output ,Success factors and tools that has to be used in each step.
| Step | Purpose | Output | Success Factors | Tools |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Define the Event | Know the Problem | Problem statement | Being Specific and objective | Interview |
| Come up with the starting point | RCA Team | No assumptions on what created the problem | Gantt Chart | |
| Create a RCA team | Project plan | Team balance | Survey | |
| Design a project plan | Planning the Schedule considers goals and time. | |||
| Find cause | Know the Problem better | List potential causes for the problem | No filtering or prioritizing the Potential causes | Flowchart |
| Bigger picture on the possible causes | Creative thinking | High-Level Mapping | ||
| Make sure that everyone in the team knows whats happening about the problem | Deep dive into the data and evidence of the problem | Brainstorming | ||
| Fishbone diagram | ||||
| Find the root cause | Detect the real root cause for the problem | Interpretation of the Root Cause | Having a calm and logical mindset | Cause and event tree |
|
|
Don’t conclude with the root cause too quickly | Five Whys | ||
|
|
Histogram | |||
|
|
Pareto analysis | |||
| Find solutions | Plan a feasible solution to eliminate the root cause | Explanation of solutions | Including those with idea with possible solutions | Flowchart |
| Including those who will be impacted with possible solutions | Brainstorming | |||
|
|
Ownership for the needed changes | The "Why Not" Principles | ||
|
|
Survey/Interviews | |||
| Take Action | Executing the solutions | Applied solutions | Able to push beyond | Force Field Analysis |
| Focusing on long term changes | Including those who will have to modify the work structure | Impact effort matrix | ||
| Measure and assess | Evaluate the change results | Confirming the right solutions to the problem | Stay critical in the evaluating the solutions | Pilot study |
| Evaluate the future change requirement | Report | Don’t be in hurry to complete the project and submit the report | ||
| Complete the RCA project |