Changing conversations based on the Stacey matrix
The Stacey matrix model was proposed by Ralph D. Stacey. It gives the possibility to distinguish management decisions and deal with complexity and uncertainty in organization platform. The result is brought out by usage of the two dimension Stacey matrix. It allows to compare the level of agreement with the degree of certainty. The decision can fall into the following areas of the matrix for further analysis: Simple, Complicated, Political, Chaotic.
The strategic choice theory
Ralph Stacey defined management and organization dynamics in frame of the theory of strategic choice. In this view the organization changes over time in a direction chosen by the most powerful individual or small group of managers. The theory of strategic choice displays its theoretical origin in two main pillars; cybernetic system theory and cognitivist psychology. Cybernetic theory is highly focused on control and regulation of a system which helps to guide and return into the state of stabile equilibrium and reach the desired destination. the cognitivist psychology describes the nature of human behavior in this context.
In the aspect and understanding of strategic choice, an important parameter is to consider the cause and effect of uncertainty and conflict.
Outline of the Stacey matrix
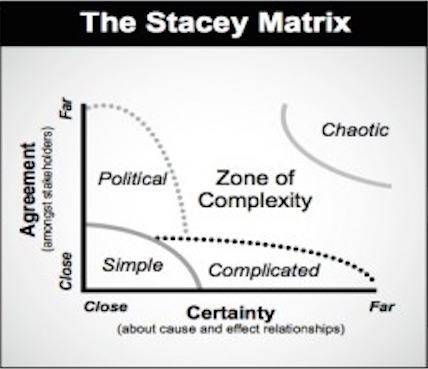
The Stacey matrix model introduces the phenomenon of strategic choice in the organization management by taking uncertainty and management agreement into account.
As an antecedent representative, Thompson and Tuden (1959) have already related to the effect of uncertainty on decision-making mode in a similar manner. They defined that uncertainty originate in the lack of clarity and the lack of agreement over objectives. Managers are mentioned as objectives. This alines with the theory of Ralph Stacey.
If the causal connections are clear meaning a high or far certainty is faced beside having shared objectives in agreement, this provides the conditions for the managers for a simple decision-making case. In Figure 1, it is showed by the area called Simple. In this situation, the management take the decisions in a rational, logical way. When the aimed direction, destination and circumstances are clear at a company, this can be the case of certain decisions. Although, as they move away from this field, the application of rational logic will be impossible and they need to use different approaches.
Cite error:
<ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found