Project Management in the Fuzzy Front End
In many organizations the pressure on the Product Development Process (PDP) has increased through the demand of greater product varieties and shorter lifecycles. Organizations aim for a structured way of speeding up the Product Development Process while not loosing effective scoping in the identification of market needs. Often they have succeeded using the Stage Gate Process - or a customized version of it. [1] Yet the application of the Stage Gate Process has shown that it enabled only a certain type of innovation to be handled with higher efficiency - incremental Innovations. [2] Radical Innovations demand a different and however still largely unpracticed handling in the initial stages. What is more, even though the execution of an incremental innovation in organizations has increased in efficiency the search and selection of the ideas in the "Fuzzy Front End" of the Product Development Process resembles great complications to the project management. This comes with no surprise since the "Fuzzy Front End" is typically characterized through a high degree of uncertainty and equivocality. [3] To answer these difficulties transferring knowledge from the Risk Management tools for decision making under uncertainty or forecasting can be applied to ease the Project Management in the Fuzzy Front End.
Contents |
The "Fuzzy Front End"
Definition

The Management of Innovation can be divided roughly into 4 stages:
- Search - Finding opportunities for innovations
- Select - Selecting the ideas to pursuit
- Implement - Development of the product and launching it on the market
- Capture - Capturing value from the innovation
On one hand most of the parameters for the later success or failure are set in the first two stages. On the other hand project managers are reluctant to make fast decisions because these stages are characterized with the highest risk and uncertainty levels of the whole process of innovation. The Search phase involves detecting signals in the environment like e.g. technological opportunities or changing requirements in the market. Here opportunities can be easily overseen. The Select phase the inputs from the Search phase are distilled and very few converted into an innovation concepts. Based on these concepts the whole organizational mechanism can now implement the innovation and capture value. [5] Hence in Innovation Management the Fuzzy Front End is considered the period between when an opportunity for a new product is first considered until the concept if the innovation enters the formal product development process.[3]
The Fuzzy Front End of incremental and radical Innovations
The Fuzzy Front End is an assortment of factors to control with difficulty, which create high uncertainty and risks for decision makers such as the project manager in charge: complex information processing, conflicting organizational pressures, market uncertainties, technology uncertainties, equivocality or reciprocal interdependencies to name a few. But it seems to get even more complicated: the Fuzzy Front End process seems not only to differ between firms but also between individual projects within the firms regarding e.g. individual activities, their sequencing, the overall duration and their degree of overlap. [3]
Innovation Managers distinguish between radical and incremental innovations. In general incremental innovations are characterized by minor changes in existing products which cumulatively improve its performance. They often take place in the context of facelifts of products or the concept of continuous improvement. The scope is to improve quality and/or the productivity of the product. However the underlying ideas in incremental innovations are not new but result often from the typical "learning curve" effect. Nevertheless most of the innovations take place in the incremental fashion and a successful project management can result in a stable ROI.[6]
As incremental innovations are many times a result of the continuous improvement within total quality management or the daily and planned facelifts of already launched products. Since they are often a product of the overall strategic planning process a high degree of certainty characterizes the Fuzzy Front End: an earlier version of the product is already on the market and risks like the technical feasibility or hence market adaption are not as high as with breakthrough innovations. Therefore a "gentle" screening of the overall strategic fit, the market attractiveness and the technical feasibility is sufficient to reach a level of certainty which is acceptable for the further execution. In terms of the project management, since the uncertainty is not as high as in breakthrough innovations, technical staff or employees from the marketing are gatekeepers for the project - not the senior management. At the same time most of the resources needed for the project can be assigned from the very beginning after the market and technical assessment. Most often it is also possible to forecast quite precisely the financial benefits of the product and the decision for the product is a result of it. The financial attractiveness routes in an already accepted earlier version of the product on the market. Sometimes incremental innovations arise not from the strategic planning process but e.g. from other creativity workshops or engaged employees. These unplanned ideas often need to "fight" more for their resources and for strategic acceptance. Sometimes companies create internal "seed-funding" for these ideas. When they are not provided with sufficient resources market acceptance and technical feasibility is often harder to predict and the management of the project in the Fuzzy Front End is characterized by more uncertainty. [7]
Radical Innovations, also breakthrough innovations or discontinuous innovation, completely change the nature of the product and bring hence a very high degree of novelty. These innovations often change the rules of their industry through opening up new opportunities but also challenging the existing players to reframe their operations. [6][8] But irrespective of the radical innovations the tendency of higher complexity and uncertainty in the innovation process is increasing. This emerges due to business, technological or regulatory changes, increasing need for speeding up the development
Challenges of Project Management
Based on the description of the Fuzzy Front End it is easy to comprehend the difficulties of organizational project management. Generally flexible project management skills are needed with a profound insight of the individual success factors of the firm and ability to adapt to changing conditions. For each project three types of constraints need to be discussed: should the idea screening be "gentle" or "harsh"? How formal should the Search and Select process be? How much uncertainty can be dealt with?
In the Searching phase the screening for opportunities in as many different ways as possible is key to success. However the organization should get rid of the bad ideas as quickly as possible in order to save costs of failed development. On the other hand a quick and "harsh" rejection can also sort out good ideas. Sometimes a "gentle" treatment of ideas is of advantage because they flourish through informal discussions in the company and then gain momentum. The next individual balance to be found regards freedom and formality. On one hand a high degree of formality can reduce risks create transparency and predictability. On the other hand a too high degree of formality can decrease innovation and flexibility. The project management needs to find an individual balance suitable for the project in all three constraints. Since the Fuzzy Front End differs to a very high degree between industries, companies and projects it is key success factor that the project manager is aware of the type of development project. The two types to be distinguished are incremental and radical innovations. Based on the type he can create the frame regarding the aforementioned constraints. [3]
Relevance of Project Management
Project management is a management task divided into project definition, project implementation and project completion. The aim is that projects are properly planned and controlled so that the risks are limited, seized opportunities and project goals high, on time and be accomplished within budget. It is defined as a set of management tasks, organization, techniques and materials for the development of a project. [9] In terms of product development the project management structure is strongly correlated with the success of the developed products. Contrary to the project management the purely functional structure has shown the lowest success rate. However managing a product development project needs to fulfill all the demands regarding quality, costs and time as any other project. [10] Typical for product development projects is that in the very initial stages the resource commitment is still low, while there is a very high degree of uncertainties. Throughout the project the uncertaities decrease but the resource commitment increases strongly. In many cases high resource commitment can create a "lock-in" effect and leads organizations into pursuing projects which will fail in the end hoping, since they have invested heavily already, for a high return on invest. (technology, market, internal etc.). [1] To avoid costly "lock-in" effects project management is highly relevant not only for the successful execution of the goal set within the quality, costs and time aimed for, but also regarding the correct setting of the goal. In terms of the project management in the field of product development this means to choose the "right" ideas to implement and launch as innovations on the market.
Project Management of Innovations in the Fuzzy Front End
The Stage Gate Process
A Method to structure the Product Development Process
Since the innovation process of incremental innovations is relatively predictable many organizations succeeded in structuring the project execution. The most typical way to orchestrate the innovation process is through the Stage Gate Process - or an individualized version of it. It resembles a structured process with milestones - the "Gates" - which force the team to make stop/go decisions at each of them. Along with the "go" decisions comes an increased resource commitment. The further the project develops, and the higher the resource commitment gets, the more seniority will have the staff to make the stop/go decisions.
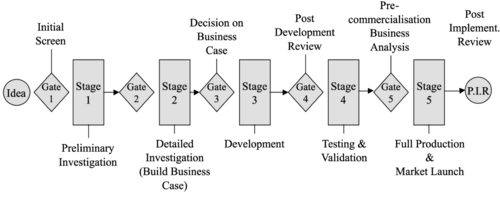
The original Stage Gate Process was developed by Cooper in 1993 and included the following five stages:
- Preliminary investigation - a fast examination and scoping of the project
- Detailed investigation - detained analysis which results in a business case, a project definition and project plan
- Development - design and development of the actual product
- Testing and Validation - trials on the marketplace and laboratory to test the market and technical feasibility to reach a product validation
- Full Production and Market Launch - commercialization, full production, marketing and sales
It can be noted that Cooper sees the idea generation as the pre-phase of the Stage-Gate-Model. [12] Nowadays many companies have changed the nature of their innovation process from a linear process to a model of feedback systems between the individual stages - creating "learning loops" and adjustments. [13]
With respect to the Fuzzy Front End the first two Stages - Preliminary Investigation and Detailed investigation - are of interest since they set the scope for the following development project. BLA BLA
Limitations of the Stage Gate Process
Decision Making under Uncertainty
Forecasting Innovations
Risk Assessment and Decision Making
Limitations of the Project Management in the Fuzzy Front End of radical Innovations
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Tidd, J. & Bessant, J. (2013). Managing Innovation - Integrating Technological, Market and Organizational Change, John Wiley & Sons Ltd, 5th Edition, p.405-412, UK, ISBN 978118360637
- ↑ Herstatt, C., Verworn, B. (2001). The "Fuzzy Front End" of Innovations, Technical University of Hamburg, Retrieved 12.09.2016, Available Online
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Florén, H. & Frishammar, J. (2012). From Preliminary Ideas to Corroborated Product Definitions: Managing the front-end of new product development, California Management Review, 54 (4), p.20-43
- ↑ Wikipedia. Fuzzy Front End. Retrieved 11.09.2016
- ↑ Tidd, J. & Bessant, J. (2013). Managing Innovation - Integrating Technological, Market and Organizational Change, John Wiley & Sons Ltd, 5th Edition, p.88-96, UK, ISBN 978118360637
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Dogson, M., Gann, D., Salter, A. (2008). Management of Technological Innovation, Oxford University Press, p.54-60, UK, ISBN: 9780199208524
- ↑ Koen, P.A. (2004). The Fuzzy Front End for Incremental, Platform and Breakthrough Products and Services, PDMA Handbook, 2nd Edition, Retrieved 11.09.2016, Available Online
- ↑ Tidd, J. & Bessant, J. (2013). Managing Innovation - Integrating Technological, Market and Organizational Change, John Wiley & Sons Ltd, 5th Edition, p.23-35, UK, ISBN 978118360637
- ↑ Gabler Wirtschaftslexikon. Projektmanagement, Retrieved 11.09.2016, Available Online
- ↑ Tidd, J. & Bessant, J. (2013). Managing Innovation - Integrating Technological, Market and Organizational Change, John Wiley & Sons Ltd, 5th Edition, p.405-412, UK, ISBN 978118360637
- ↑ Wikipedia. Stage Gate Process.,Retrieved 12.09.2016 Available Online
- ↑ Dogson, M., Gann, D., Salter, A. (2008). Management of Technological Innovation, Oxford University Press, p.220-223, UK, ISBN: 9780199208524
- ↑ Dogson, M., Gann, D., Salter, A. (2008). Management of Technological Innovation, Oxford University Press, p.60-65, UK, ISBN: 9780199208524