Managing Group Development using the Johari Window
The Johari Window is a psychological model for effective group development and self-awareness, and plants its roots in the human behavioral phenomenon. Failing to manage group development can result in ineffective group communication, and hence be the source of various downfalls of a project, streaming from prevention of information sharing to decreased performance and unproductiveness. In order to prevent these circumstances the Johari Window will be discussed as a means to embrace self-awareness, enable dynamics, increase communication and create effective group development and draws upon psychological and managerial theories to enrich the model.
This article will start out with outlining the background history and purpose of the Johari Window, and give a thoroughly elaboration and description of the four quadrants. Additionally, the Shannon-Weaver model of communication and Tuckman's stages of group development will briefly be touched upon sideways with the importance of feedback to stress the necessity of managing group development, and simultaneously create a link between the models. Later in this article the application of the Johari Model will be discussed in which the how, when, to whom and where it is applicable will be examined, and finally limitations and benefits will be outlined.
Contents |
History
The Johari was propounded by American psychologists Joseph Luft (1916-2014) and Harrington Ingham (1916-1995) in 1955 [1] from whom the name Johari was derived combining both of the psychologists names. It was initially a psychological tool to enhance self-awareness but continued to expand towards being a communication tool, inter-group development- and intra-group development tool, with the common purpose to enhance self-awareness, increase effective group development and demolish communication barriers. (...)
The Johari Window and its purpose

The Johari window contains four quadrants, the open/free area, blind area, hidden area and the unknown area, each with similar sizes that can further be changed based on the particular group member. The quadrants make up the window and is the foundation of the model.
The 4 Quadrants
The Johari window contains four quadrants, the open/free area, blind area, hidden area and the unknown area, each with similar sizes that can further be changed based on the particular group member. The quadrants make up the window and is the foundation of the model. The four quadrants are represented in the following section.
The Open/Free Area Quadrant
When a group is developed the open/free area is small due to the lack of shared knowledge, however as the group development evolves the open/free area maximizes due to shared awareness taking place. This is particularly seen when new group members enter an already established group. This quadrant contains e.g. the behaviour, feelings, emotions, experience, skills, knowledge that is known by the individual group member and the other group members. Furthermore, it is the quadrant where group communication, collaboration, cooperation, individual effectiveness and individual productivity mostly takes place and mistrust, miscommunication, conflicts and confusion is downsized or barely existing.
The Blind Area Quadrant
When an individual is located in the blind area the information about oneself is unknown but known for the rest of the group members. This area is often referred to as the bad breath describing how other feel the smell but the individual does not (REF). It is tainted with unproductiveness and decreased effectiveness. The initial jump from this area is to reduce it and increase the open/free area through increasing self-awareness within the group. Another aspect of this area is that other group members purposely withholds information towards other group members and hence continuing the group development and/or group projects with individuals lacking information and consequently decreased motivation.
The Hidden Area Quadrant
This area represents an individual’s private information that is hidden from the rest of the group. Private information contains e.g. fears, secrets, hurt, bad intentions and motives, work related information that the individual does not want exposed and thus does not deliberately reveal. This area typically hinders performance due to the extent of hidden information that could relatively be an important factor for both group development and further a group’s effectiveness. That is not to say that all private and personal information should be exposed, it is thus the project manager’s role to steer a project group towards revealing information according to relevance and necessity. The aim in this area is to reduce the hidden area and hence demolish e.g. ineffective group communication, confusion, mistrust and misunderstanding and increase the open/free area through moving relevant information into it to increase effectiveness, productive and a mutual understanding.
The Unknown Area Quadrant
This area represents an individual’s behaviour, information, feelings, experiences, attitudes, capabilities and skills that are unknown to oneself and to the group. Relatively common unknown factors have been identified as being the following (REF):
- An ability or skill that is under-estimated due to the lack of opportunity, encouragement, confidence or training.
- A natural ability or skill that an individual does not realise they possess.
- A fear or subconscious feelings that an individual does not know they have.
- A conditioned behaviour or attitudes from an individual’s childhood.
The unknown factors can- if known- be used to great advantage within a group both to enhance competitive advantage and increase group effectiveness and efficiency.
Group Development
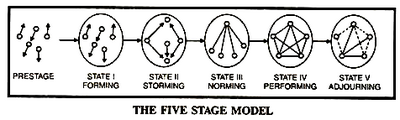
Described previously, the Johari Window can be used in group development especially when individuals become part of one unity striving towards common goals. Each individual is different and to try to unite a group can be both time consuming, and if not managed correctly, it can lead to decreased effectiveness and efficiency. The Johari Window explains the necessity to enlarge the open/free area to enhance knowledge sharing and self-awareness in order to enable e.g. effective group communication, collaboration, and productivity and hence create a smoother group development process. In order to explore what happens when individuals become a unity, psychologist Bruce Tuckman developed the five stages of group development, see Figure 2, and is perceived as being inevitable for every group to undergo regardless of the particular environment.
Stage 1. Forming
The first stage appears when a group is newly formed and on one side can consist of positivity and politeness [2] as individuals are being introduced and starting to know each other, and on the other site can contain individuals who are distance and testing the water. As anxiety and uncertainty can set in the Johari Window can play an important role to gather the individuals, enable shared knowledge, create clear objectives and task responsibilities.
Stage 2. Storming
When a group has overcome the forming stage, it moves into the storming stage where individuals start to push against the boundaries created in the previous stage. The storming stage is typically caused by the difference in working styles, resistance to change and to a delegated task, conflicts, individuals might feel overwhelmed and stressed [2]. Nevertheless, this stage is the most critical one, and can be termed the “win or break stage”. It is important for the project manager to resolve any storming factor to successfully move to the next stage. The Johari Window can work as a means to tear down individual walls towards the rest of the group members, and ease up the atmosphere through e.g. revealing what might be hidden and simultaneously communicating differences concerning the working style.
Stage 3. Norming
The third stage appears gradually as group members starts to form common norms, bypassing differences and provides constructive feedback to each other. Individual becomes a unity and knowledge, goals and expectations are shared. This stage is marked by a stronger commitment, productivity, and respect to one another [2]. However, re-laps to the storming stage are not prohibited and can occur at any given time during this stage, thus it is necessary to continue bonding, giving feedback and communicating. This stage can be seen as the open/free area in the Johari Window, but as described earlier the area can shrink which is what happens when a re-laps occurs.
Stage 4. Performing
During this stage effectiveness and efficiency are increased and the common shared goal is worked towards with the support and commitment from each group member. Productivity is at its peak and results are visual. Referring to the Johari Window, the open/free area is large and communication, trust, and information sharing takes place at a great level.
Stage 5. Adjourning
The Adjourning stage was later added as a final stage in the Group Development process [2]. It initiates that eventually a group will detach e.g. project teams, which can cause uncertainty and be difficult to each individual who already have formed strong bonds with each group member. This stage can be inevitable and is natural to undergo to join a new group and hence start the process again.
Communication and the Johari Window
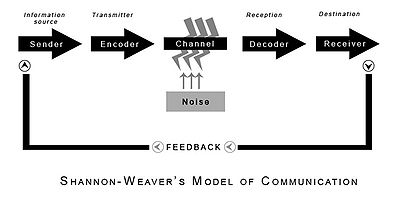
Communication is an inevitable factor of effective group development not only does miscommunication affect the information sharing, but can also affect the attainment of the project goal. The Johari Window touch upon the understanding of each group member’s way of communicating with other group members and how information is transferred from the sender to the receiver. The Shannon-Weaver model of communication, see Figure 3, describes the process from the sender i.e. the one who creates the message, chooses the channel and sends the message, to the encoder i.e. the transmitter who uses a machine e.g. a phone to convert the message into waves of binary data [3], moving on to the channel it is the medium that is used to send the message and is where noise can float in and intervene with the message being transferred. In other words, if noise intervenes it can be looked at as the bottleneck of an effective communication process and hence misunderstandings and miscommunication are factors that can occur. Nevertheless, the message continues towards the decoder, which is when the binary data is converted into a message [3]. Finally, the receiver is reached when the message arrives in turn the receiver provides feedback according to the message [3]. Linking this to the Johari Window, the model of communication can act as a tool to increase the flow of giving and receiving information in a group. As an essential part of the Johari Window and the model of communication, although not heavily in the latter, feedback is perceived as being an important part of effectiveness. Feedback from group members and the project manager can contribute to personal learning and realization of personal issues that can further be resolved and move the individual to the open/free are and hence increase communication effectiveness.
Application
The Johari Window have been used in various situations but its core principle of encouraging individuals to open up and move towards the open/free area has remained the same. This section will start out with looking into the theoretical way of applying the Johari Window. Later, two cases with two different setting, in which the Johari window has been applied, will be examined.
The theoretical recipé for using the Johari Window
A theoretical way of applying the model has been defined by the creators, Joseph and Harrington. The theory implies that an individual’s actions are guided by the mind [4] and thus the framework i.e. the mind is described to be like a square-shaped window with, as described earlier, with four areas the Open/free self, the Hidden self, the Blind self and the Unknown self. When groups are developed the core challenge is to expand the size of the open/free area, which on one hand, can be done horizontally into the blind area through the process of feedback solicitation i.e. actively listening to feedback from group other members and on the other hand, vertically into the hidden area through revealing e.g. information, feelings and concerns to the group and group members, likewise group members can speed up the process by questioning other group members about themselves [5]. As a project manager it is important to take part in the feedback both giving- and receiving feedback to manage the process. Furthermore, it is also the project manager’s responsibility to promote and encourage e.g. an open, honest, positive, helpful culture and knowledge sharing.
In order for a group member to move out of the blind area and hence into the open/free area, it is crucial for a project manager to promote non-judgemental feedback, and group response to what is revealed by the individual, to reduce fear [5]. Furthermore, the hidden area can be reduced by creating a shared organisational culture and working atmosphere, to limit the fear of judgement and vulnerability. Lastly, the unknown area can be reduced by self/collective/mutual-discovery or observations, to discover e.g. hidden talents i.e. skills, abilities. An effective way for a manager to contribute to the discovery of a group member’s hidden talent is to enable the opportunity to try new things, with no pressure to succeed [5]. Each area can be given a title, and hence each individual in the group can be given a title according to which area they are in, see Figure 4) i.e. if an individual is in the open/free area the personality title given is an Open person, The Questioner is given in the blind area, The Teller is given in the hidden area and the title The Clam is given in the area unknown.
Limitations
(.....)
Annotated Bibliography
References
- ↑ Wikipedia. Johari Window. Retrieved 10 September 2016.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Mindtools editorial team. Mindtool. (2016). Forming, Storming, Norming, and Performing. Retrieved 12 September 2016.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Mishra, Sneha. Businesstopia. Shannon and Weaver Model Of Communication. (2016). Shannon and Weaver Model Of Communication. Retrieved 12 September 2016.
- ↑ Prodcons Group. Johari Window. (2011). Johari Window. Retrieved 13 September 2016.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Chapman, Alan. Businessballs. (2016). Johari Window. Retrieved 13 September 2016.