Sustainability in Project and Portfolio Management
Contents |
Abstract
In the past, there was not desire to know the ecological impact of products, since environmental disasters were rather rare. Contrarily, today several companies have adopted sustainable strategies as long term value in their business model, in order to face environmental problems as population growth, climate change and divergent living standards.
Sustainability integrated with portfolio management implies many changes in the operations, focusing on material issues, engaging with diverse stakeholders, managing climate and resource related risks, creating new sustainability driven opportunities, and reporting transparently on actions and performance.
The vision of sustainable value offers a compelling challenge to business. Companies that choose to start the “sustainability journey” have to go through different stages: [1]
- Exposure : includes energy savings, building efficiency and compliance projects.
- Integration : more holistic approach, starts including LCA. Better understanding of the positive relation between sustainability and business strategy.
- Transformation : the peak of the organizational change, when sustainability becomes part of the core strategic vision of the company, being part of all the decision, processes and metrics for success.
Organizational culture is defined as: “The values and behaviours that contribute to the unique social and psychological environment of an organization.” The way the culture is expressed by the leaders and the employees impacts relationship with external and internal stakeholders and the company efficiency in general. It is important to understand, how a shared vision and a common culture of sustainability is necessary to be created and promoted, to facilitate organizational understanding of core values and to help project mangers better understanding and leading a good alignment between goals and outcomes.
Driving sustainable strategy into an organization requires senior management to communicate the vision clearly. Sustainability gives to the organization a big competitive advantage, increasing expectations by stakeholders, obtaining radical transparency and contributing to support declining resources.
What is Sustainability?
The most quoted definition of Sustainability, in terms of Sustainable Development, tracks back to the Brundtland Commission of the United Nations on March 20, 1987 development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. [2] .This concept of thinking in the long term is becoming broaden in the business philosophy. Also if, as the famous economist John Maynard Keynes said, “in the long run we are all dead”[3] , this means that any long term policy is going to fail if the company is not able to survive in short therm business condition. Shifting from a daily profit-making company into a sustainable company requires a change in perspective, from the short to the long term.
The story said that many companies tried to become environmental friendly; for example, in 1975 the US company 3M set up the Pollution Prevention Pays (3P) programme, aiming to reduce costs by preventing waste and emission, a very entrepreneurial sustainable project at that time. Furthermore, the company found out that was reducing costs in maintenance, raw materials, accidents, clean-up operations and insurance, and many companies discovered those benefits. The inventor of the 3P programme was Joseph Ling, who affirmed that the environmental challenge for the next millennium "is to move from pollution prevention toward sustainable development and design for environment " [4].
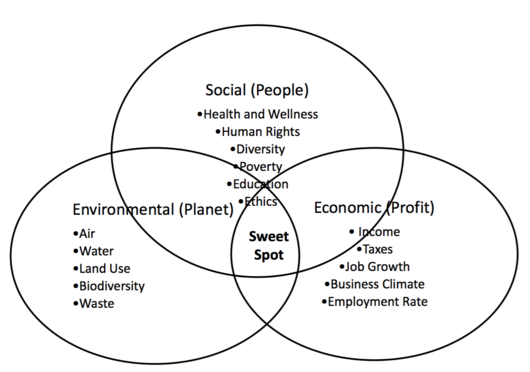
Then, producing without pollution is not enough, it is necessary that products, and the whole system is reviewed and redesigned in order to fulfil the costumer and the organization needs in a sustainable manner. In more detail, having a holistic concept of sustainability, in terms of Corporate Business, a three-pronged approach takes place: the Triple Bottom Line (TBL), introduced by John Elkington in 1994, where economic, environmental and social goals are aligned and impact on the decision and actions of the organization. [5]
.
This concept is present in the UN World Business Council for Economic Development (WBCSD), formed by 150 international companies worldwide, where leader involve the TBL in their business case, in order to address global challenges such as poverty, gender inequality, resource depletion, etc.
The WBCSD recommends to the companies to follow the SDGs Sustainable Development Goals as opportunity for business opportunity and influence in the society.
Developing a business case following the values and preposition of a sustainable development it is a entrepreneurial step, in the life cycle of a company, providing competitive advantages and new opportunities.
Global Compact
Business Case of Sustainable Development
Developing a business case following the values and preposition of a sustainable development it is an entrepreneurial challenge. Matching sustainability strategy within managerial aspects involves different factors, as involving many stakeholders, in order to have more informations about the opportunities and threats that impact the long-term health and viability of their organization.
The challenge of the Sustainable Business Development is matching the People,Planet and Profit Pillars (TBL) into the activities of the company, in the ordinary planning cycle of the company, in the business planning, operations and control cycle.
Managing Risk
References
- ↑ Kristina Kohl , Becoming a Sustainable Organization: A Project and Portfolio Management Approach, © 2016 by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sustainability
- ↑ Sustainability Development and the company: why, what and how?
- ↑ P.Sorenson, ‘Pollution Prevention Pioneer’ Inventing Tomorrow,1999
- ↑ Kristina Kohl , Becoming a Sustainable Organization: A Project and Portfolio Management Approach, © 2016 by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC