Decision Tree
Decision Tree
Contents |
Introduction
Background
Decision Making
Decision making in project management is a problem-solving process. The project manager makes decisions to face and solve the problems and challenges. The logic of this process is quite simple. After the identification of the problem, a decision needs to be made only if there are different alternatives or different solutions. If there is also one solution, the project manager tries to consider all the implications that will occur from this solution. If there are more than one different alternatives, the project managers try to make the decision that will lead the project and the company into prosperity. Moreover, these decisions must be made in timely fashion.
Decision Tree
Purpose
Structure
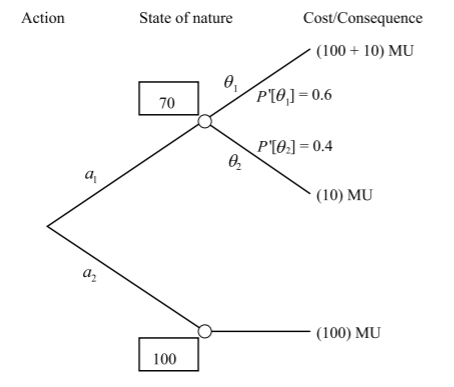
Decision trees are quantitative diagrams with nodes and branches representing different possible decision paths and chance events. [1] The decision tree is read from left to right. More specifically, a decision tree consists of the following elements
- Root node: It is the leftmost node of the decision tree
- Decision node: It is represented by a small square.
- Decision tree branches: These branches which emanate from the right side of the decision nodes, compose the set of alternative decisions – solutions, which can be pursued. The project manager can select and put into application, one and only of these branches.
- Chance node: Chance nodes are represented by small circles in the decision tree, indicate that a chance event is expected at that point. The number, which can be seen on the branch of each of these nodes, presents the probability of the decision on each branch to occur in the chance node.
- Endpoint: The right end of each path of the decision tree is named as endpoint. Every endpoint in the decision tree shows the final outcome of following this particular path from the root node to this particular point.
Construction of decision tree
For an accurate construction of a decision tree, a project manager needs to conduct the following steps
- Construction of a logic tree, usually from left to right, including the decision and chance nodes
- Addition of the probabilities of the different states on the branches of the tree. The logic tree is, therefore, transformed into a probability tree. Caluclation of the probabilities in the endpoints. The sum in the probabilities in the endpoints must be equal to one.
- Addition of the conditional outcomes. The construction of decision tree is completed.
Decision Tree Analyis
Limitations of Desicion Tree Analysis
Decision Tree Analysis has some inherent limitations in its application, as
- Inadequacy in applying regression and predicting continuous values
- Possibility of false relationships
Considerations
References
- ↑ Kerzner, H., Ph.D., (2006), ""Project Management: A systems approach to planning, scheduling and controlling"". Ninth edition
Annotated bibliography
- 1. Winch, G. M. (2010), "Managing Construction projects". Second edition
- Summary: The book presents a holistic approach of construction management. The basic principles of construction project management are presented along with different tools and techniques that aims to enhance construction performance and provide innovative techniques. The use of information and communication technologies is also a point of interest in the book.
- 2. Kerzner, H., Ph.D., (2006), "Project Management: A systems approach to planning, scheduling and controlling". Ninth edition
- Summary: The book illustrates the basic principles of project management. The book is targeting for enhancing the project skills of not only students, but also executives, pointing out that project management can be related to every profession apart from engineeering, including information systems and business.
- 3. Maylor, H. (2010), "Project Management". Fourth Edition
- Summary: This book cover all the topics of project management, focusing in the theory, as well as in the application and usage of the ideas discussed in it. The book points great emphasis into the 4D-model of the project.
- 4. Flyvbjerg, B. (2008) "Curbing Optimism Bias and Strategic Misrepresentation in Planning": Reference Class Forecasting in Practice, European Planning Studies Vol. 16, No. 1
- Summary: This paper presents the method and illustrates the first instance of reference class forecasting. The paper targets in the inaccuracy of the financial appraisal in planning in construction, explains them in terms of optimism bias and strategic representation and present a method of eliminating this inaccuracy.