Mapping stakeholders
It is the term used to describe the process of stakeholder analysis graphically, so that those involved can be understood from different points of view.
The stakeholder mapping is to facilitate the reading of the various analyses to be carried out, for better understanding and comprehension.
During investigations it is common to develop ways of presenting the data they have collected. The organization of data allows classifying and reviewing the information collection for valuable information.
The representation of the content allows comparing contrast with the known data collected, or simply allows others to absorb or understand the data more easily. In the world of construction projects, the most effective presentation of the data is graphical or pictorial. [1]
Contents |
Objectives[2]
- Develop a useful list of the Stakeholders.
- Evaluate the main characteristics of each participant.
- Present information in a way that helps the project team to implement effective stakeholder management initiatives.
- Replace Subjectivity with objective measures.
- Make de measure process easy to understand.
- Facilitate the review of the stakeholder’s analysis.
- Simplify the updating of the analysis during the construction phase.
Mapping methods
Below are mentioned the stakeholder mapping techniques better known and commonly used.[3]
Salience Model[4]
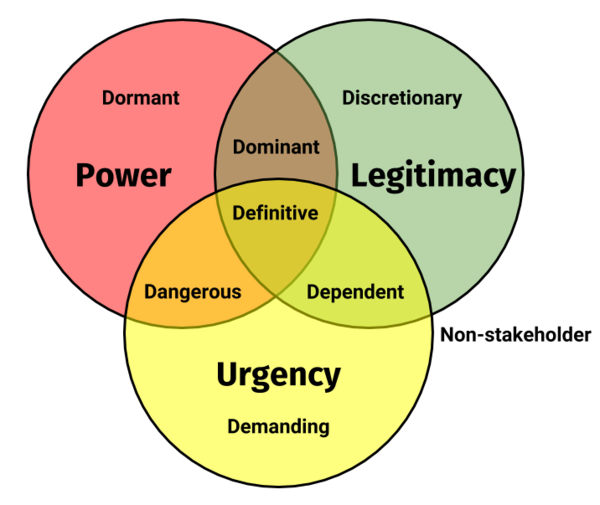
The Salience Model is used to help identify the needs of a stakeholder. Unlike other methods, this model uses three dimensions to classify the stakeholders: power, legitimacy and urgency, which are defined as:
- Power: is the ability of a social actor influence over another social actor to do something that would not have done otherwise, such a way that the results of a project or organization are affected. Some associate terms are:
- Legitimacy: Is the level of authority or having an actor involvement in socially constructed system of norms, values and beliefs system. E.g.: the authority of a stakeholder in a project.
- Urgency: The degree of attention stakeholders need, i.e. is the expected time to meet the expectations of the concerned.
- Salience: the degree to which managers or researchers prioritize the satisfaction of the needs of stakeholders.
This three-dimensional view of stakeholders, needs and expectations of a project may help researchers reduce key stakeholders.
Graphical representation
A Venn diagram represents it as you can see below.
Classification
Stakeholders are classified into 4 salience levels, High, Medium, Low and null. Likewise each combination between power, legitimacy and urgency, requires different attention.
Latent Stakeholders
It is only when you Dated an attribute (power, legitimacy or urgency) to the interested party. The relevance will be low as managers take only one of the attributes into account
- Dormant
Those who have power but no legitimacy and urgency in their requests
- Discretionary
It has legitimacy, but no power or urgency
- Demanding
Urgency but has no power or legitimacy
Expectant Stakeholders
The priority is medium as managers take two of the attributes into account. Is in between a passive and active level that requires certain attention to be satisfied.
- Dominant
Is the situation in which the parties are both powerful and legitimate time, but do not have the urgency. Should focus on your expectations, but provided there is no great urgency.
- Dependent
According to the model, these stakeholders have no actual power in the project. However, they need to be managed, as they can quite easily choose to side with other stakeholders and thereby influence the project.
- Dangerous
Named appropriately, these actors have the power and urgency, but without legitimacy, therefore they have demands on the project without actually being a part of it.
Such stakeholders should be kept satisfied by ensuring an adequate participation.
Definitive Stakeholders
They need to be providing of focused attention, as their requirements are related to the three attributes (power, legitimacy and urgency). Its priority level is high.
Non Stakeholders
Their priority level is null. These people are not interested in the project. Investing time and effort in this type of people do not help you get the results of the project in anyway.
The Power/Interest Grid[5]
identifies the expectations and power of stakeholders, and helps in the understanding of political priorities. The importance of two issues were highlighted:
- How interested each stakeholder is to show their expectations about the purposes and the choice of specific strategies of the organization.
- Whether that stakeholders have the power to do it.
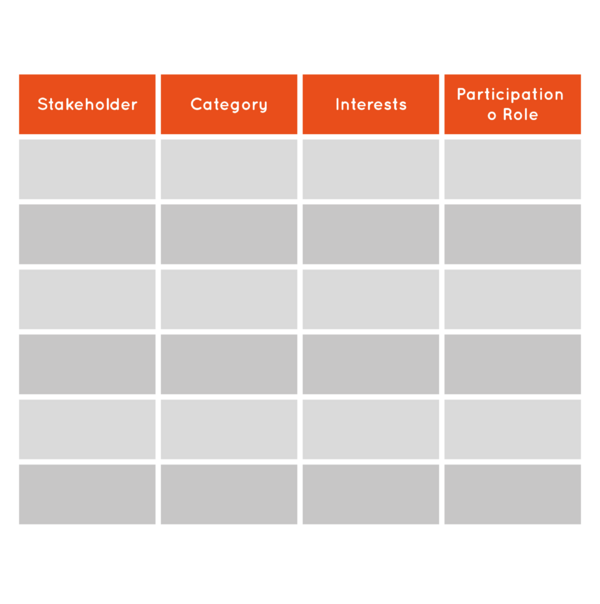
Stakeholder Assessment[6]
The main objective of the tool is to help map stakeholders and their interest in the project. It can be used to analyze and evaluate the importance of the project or organization, and assess the environment.
Each stakeholder might have several roles in the evaluation. These can be listed using the following table format:
Usage mode
- Once already identified stakeholders must be located in the left column.
- Identify which category each stakeholder. These can be founders, employees, managers or members of the organization. It must adapt categories of stakeholders under the project or organization. You can also indicate whether a stakeholder:
- It is a fundamental part of the organization
- Interested and committed to the organization
- Knows the organization but is not committed to the project
- Has a vested interest in destroying the organization, e.g.: competitors.
- Indicate the interests of stakeholders in self-assessment mode if each interested party will use the results to:
- Planning.
- Organizational support.
- Design of new programs.
- Creating new strategies.
- Implement changes.
- Identify the possible involvement or role of each actor in the self, ie, if the stakeholder ca:
- Be a data or information provider
- Make a decision on the results of self-assessment
- Benefit of change that arises from the evaluation.
- Any other benefit
Notes
- ↑ Chinyio, E., & Olomolaiye, P. (Eds.). (2009). Construction stakeholder management. John Wiley & Sons.
- ↑ Chinyio, E., & Olomolaiye, P. (Eds.). (2009). Construction stakeholder management. John Wiley & Sons.
- ↑ Chinyio, E., & Olomolaiye, P. (Eds.). (2009). Construction stakeholder management. John Wiley & Sons.
- ↑ Mitchell, R. K., Agle, B. R., & Wood, D. J. (1997). Toward a theory of stakeholder identification and salience: Defining the principle of who and what really counts. Academy of management review, 22(4), 853-886.
- ↑ Johnson, G., Scholes, K., & Whittington, R. (2008). Exploring corporate strategy: text & cases. Pearson Education.
- ↑ Lusthaus, C., Adrien, M. H., Anderson, G., & Carden, F. (1999). Enhancing Organisational performance. A toolbox for self assessment, IDRC.