The Periodic Table of Project Management
Developed by Brynja Benediktsdóttir - Under construction
Contents |
Abstract
This article will discuss the field of project management and different ways used to divide the field into smaller parts in order to obtain good oversight in projects. The possibility to make a periodic table for project management to acquire oversight in projects will be explored and two different versions of tables for project management will be presented. The periodic table of project management competence elements developed by the international project management association (IPMA) and the periodic table of project elements developed by Dr. Mike Clayton. The most famous periodic table is the periodic table of chemical elements that have been used and developed for 150 years. The biggest reason for its success is that it is useful for both scientists and modern students as it helps to predict the types of chemical reactions for its elements. Only by looking at the table many characteristics of elements can be determined which is one of the key factors for its wide usage all over the world. [1] With this much success of one periodic table, it raises the question if this could be done for other fields to simplify the content and display it in a table where a glance would tell several characteristics of the content (elements). The article will first discuss project management and three different ways that are used to divide the field up in order to get an overview of a project. Next, the periodic table of chemical elements and the reasons for its wide distribution and usage across the globe will be explored and finally, will the two periodic tables of project management be examined.
Project Management
In order for projects to succeed a certain number of factors have to be fulfilled and depending on the project along with its requirements, the factors can vary between projects. The goal of project management is to meet project requirements by applying knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to project activities. [2]
The Six Vital Signs
The Seven PRINCE2 Themes
The Ten Knowledge Areas
The Periodic Table
The periodic table of chemical elements often referred to as the periodic table, is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements where the elements are organized in a way that it provides various information about the elements and their properties. The table is divided into groups (columns) and periods (rows) that contain elements with similar characteristics. [1] The periodic table of chemical elements was published in 1869 and has improved a great deal since then. The table had a number of gaps in as the elements had not all been discovered at the time. However, could the table predict the chemical and physical properties of the missing elements which have been added to the table through time and the latest update of the periodic table of chemical elements was made in December 2018 by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). [3]
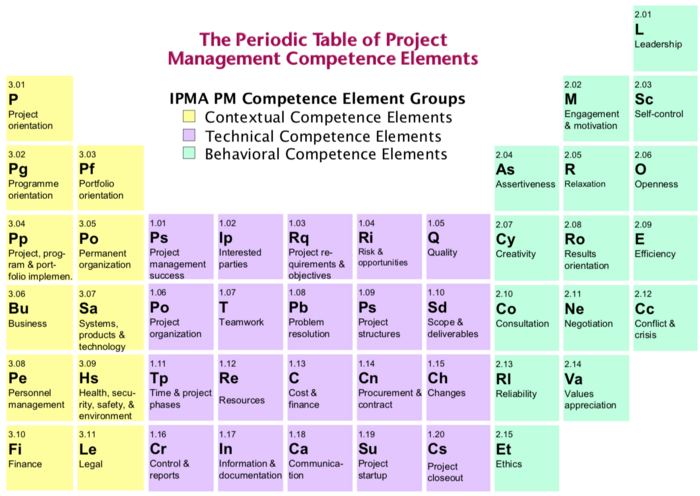
The Periodic Table of Project Management Competence Elements
In the periodic table of project management competence elements are 46 elements to illustrate the essential factors for project management. The elements are divided into 3 groups: contextual competence elements, technical competence elements, and behavioral competence elements.
The Role of Knowledge
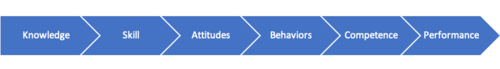
To seek the desired outcome in a project the performance competence needs to be at its best. The IPMA standard embraces performance competence by moving beyond knowledge. In order to achieve the desired performance in a project the knowledge must be used right and can be demonstrated in steps leading to the performance. With only knowledge, nothing is accomplished even though knowledge is an important foundation. As knowledge is applied, a skill develops, and something gets accomplished during this phase. Skill has a longer lifetime then knowledge and when demonstrated skill is rewarded and recognized the learning tends to move to the next step, attitudes. New learning tends to continue as attitudes are strengthen when rewarded and recognized. Combining attitudes with more soft skill, the behaviors and interpersonal skill, the individual develops along with other new technical skills. When an individual is not able to obtain these skills, it results in people not willing to work with the individual. Focusing only on one skill without combining it to relevant behavioral elements will lead to long term success. After acquiring the attitudes and behavioral skills the next step is competence. This skill is measurable in projects, as it is demonstrated by project managers how the combination of knowledge, skill, attitudes, behaviors, and experience has been mastered. Different situations call for different approaches and project managers show their competence by being flexible and adapt that combination accordingly to each project. All these steps are essential inputs for project management success however the ultimate results desired is the project performance which the steps lead to if done according to each project. Heimild: Diff context – stacy goff
The Periodic Table of Project Elements
Another periodic table inside the field of project management is the periodic table of project elements where components in project management are thought of as elements and put in a table.
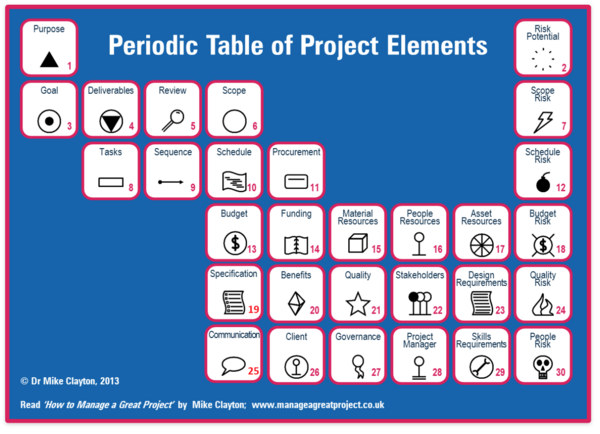
The table was made by Dr. Mike Clayton in order to advertise his book but compared to the periodic table of project management competence elements the table relates more to the function of the original periodic table of chemical elements. The columns (groups) are elements that correspond to each other and is seen very clearly in column 9 which would simply be called risks and contains various types of risks that can occur in the project process. Column 1 seems to be the fundamentals of a project where purpose and goal are grouped together. By going from column to column, a linkage can be found between elements along with an appropriate name. The rows (periods) seem to have been categorized in steps of a project. Where in the first step the tasks are to define the purpose of the project and estimate potential risks. The second step is to define the goal, identify the deliverables, review and scope the project and identify the scope risks. The steps then continue one by one.
Conclusion/Discussion
The purpose of a periodic table is to have all the elements easily accessible at one place where the arrangement of the table can describe the properties of the elements in the table as well as undiscovered elements that could be added in the future. For the field of project management, it is highly unlikely that many elements are left undiscovered as the amount of completed, complex projects in the world that did not have any precursor are extremely many. However, as the field is very wide and covers different areas it is possible that terms that are used today could be divided into more detailed elements which would help the understanding of the term. Further development on both of the project management related tables could be an app where further information could be gained by clicking on an element.
Annotated Bibliography
Refrences
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 https://www.thoughtco.com/why-is-the-periodic-table-important-608829 A.M. Helmensteine. Why Is the Periodic Table Important? Retrieved 09-02-2019.
- ↑ Project Management Institute. (2017). A guide to the project management body of knowledge (PMBOK® Guide). 6th ed. Pennsylvania: Project Management Institute, pp. SETJA INN.
- ↑ https://iupac.org/what-we-do/periodic-table-of-elements/
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedStacy - ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedMike