Basic estimation techniques
Contents |
Abstract
When managing a project, a manager has to achieve specific objects within time, resources and money. This can often be challenging, as there is a lot of uncertainty in doing so. How can the amount of time for each activity be calculated? How many resources are needed to complete every task? And how much will the project cost in the end? This article deals with answering all these questions and focuses on how to come up with educated guesses to these uncertainties.
In the first section, a definition of what an estimate is will be given. A variety of best practices used in the estimation process will then be presented. Some of these techniques are more complex than others and will therefore require a more detailed explanation. For every presented technique, advantages and disadvantages, as well as examples on how to apply these, will be given in order to give the reader an understanding of how the methods works and what they can be used for.
Lastly, the challenges and limitations of using these tools will be discussed, as these can variate in accuracy depending on the size and the type of the projects. The involved risks when estimating will also be covered here.
Definition and techniques
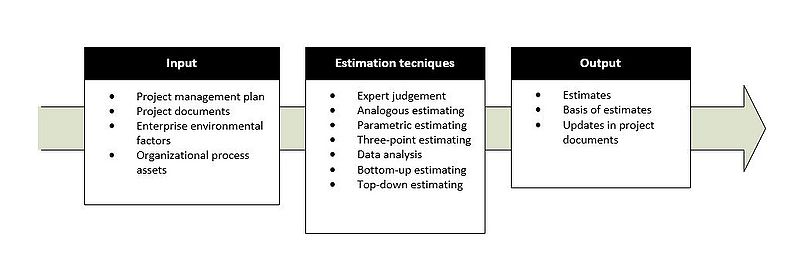
The process of estimating is a common practice within Project Management of finding an approximation to a specific value that is not known. An estimation can serve different purposes, for example give an indication of the duration for a specific activity, or the amount of resources that must be assigned to a task in order to complete in time. The process of estimating can be represented with model showed to the right.
Expert judgement
Analogous estimating
Parametric estimating
Three-point estimating
Data analysis
Decision making
Meetings
Learning curve
Simulation
Bottom-up and top-down estimating
Discussion on estimating
Bla bla bla
References
Bla bla bla