Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs and Project Management
Developed by Osman Furkan Simsek
Contents |
Abstract
Maslow’s need of hierarchy is a theory about five stages of human needs. Project managers are directly in contact with their team as a leader or manager. Therefore, they need to know how human psychology works for managing and motivating their team through the project aims.
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
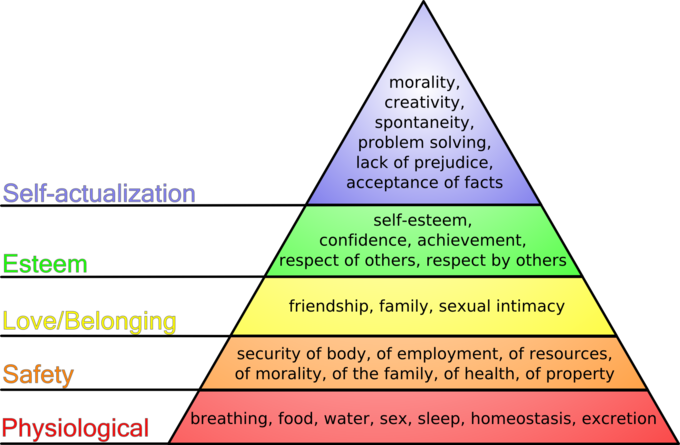
Inspired from Maslow hierarchy of needs DTU wiki article. " [1].Abraham Maslow wrote the “Hierarchy of Needs” theory. He studied human motivation and successful people’s life such as Albert Einstein, Jane Addams, Eleanor Roosevelt and Frederick Douglas. Maslow argued that humans are motivated with unsatisfied needs and more basic needs should be satisfied before more complex needs. There are 5 different types of needs in his pyramid, which are physiological, safety, love/belonging, esteem, self-actualization needs. [2]
People should fulfil these needs step by step. All our behaviours can be explained by our needs and human life is going through satisfying these needs. To explain this theory better, I examine the needs more detailly.
Physiological Needs
Physiological needs are survival for the human. Eating food, drinking water, breathing air, sleep, etc. can be given as examples. When these needs are not satisfied, people cannot think or be motivated about other topics.[3]
Safety Needs
After Physiological needs are gratified, human will start to think about his or her safety. Safety helps people to create stability and consistency in a chaotic world. Needs can be categories here as security, stability, dependency, freedom from fear, order, law, etc. [4] For example when a person does not have the salary or economic safety, we can not accept that this person will be motivated for a higher purpose than money. Because when someone does not trust that he will take his salary next month, he will not be motivated for his work. Or in unhappy marriages can be given as an example in this need. When you know that there is an abusive husband who is waiting for you at home, the wife will not think about other subjects than her safety at home.
Love/Belonging Needs
Love and Belongings are the needs coming after feeling safe in life. Humans are social animals. Therefore, in order to feel good, people need to be part of a group, love and being loved are necessary. Teenagers want to fan group of a rock band, football fans coming together and sing, lovers show their feelings to each other, etc. All these examples can be thought of this category. In my opinion, in the management perspective, one of the most important needs is belonging needs for the project teams.
Esteem Needs
Esteem needs include two different categories. First is self-esteem which is coming from competence or mastery of a task. Second is the attention and respect from other people. Maslow said that “All people in our society (with few pathological exceptions) have the need or desire for a stable, firmly based, usually high evaluation of themselves, for self-respect or self-esteem, and for the esteem of others. These needs may, therefore, be classified into two subsidiary sets. These are, first, the desire for strength, achievement, adequacy, mastery and competence, confidence in the face of the world, and independence and freedom. Second, we have what we may call the desire for reputation or prestige (defining it as respect or esteem from other people), status, fame, and glory, dominance, recognition, attention, importance, dignity, or appreciation.” [5] In other words, people need to see respect and recognition in life. When a scientist got a prize for his or her scientific study, he or she will see the respect of the scientific community and feel self-esteem. I think most of the white colour workers like engineers, doctors, lawyers are getting motivated when they see respect and recognition for their work.
Self-Actualization
Self-Actualization is the last step of the needs. The human can show all their potential when they reach this last point of the pyramid. Maslow thought that only a few people can achieve self-actualization, for instance, Albert Einstein had become one of the most famous scientists with his contribution to physic. This kind of people can seek knowledge, peace, esthetic experiences, self-fulfillment, etc. [6]
Project Team Needs
Before starting the chapter, there are 3 concepts that should be defined. In this chapter, the project management team’s needs are focused on.
- Project Management:The application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to project activities to meet the project requirements.
- Project Management Team:The members of the project team who are directly involved in project management activities.
- Project Manager: The person assigned by the performing organization to lead the team that is responsible for achieving the project objectives. [7]
Maslow wrote his theory for individual needs and the teams are consisting of many individuals working cooperatively. In order to motivate the team, project managers should know their needs. Especially the first four steps of the pyramid are directly related to project managers. In this chapter, the project team is evaluated as an individual. The purpose of the project team in the project management is achieving project on time, on budget with success.
References
[1] Maslow hierarchy of needs DTU Wiki Article. http://apppm.man.dtu.dk/index.php/Maslow_hierarchy_of_needs
[2]A. Sarma, A. Van Der Hoek, A. Einstein, J. Addams, and E. Roosevelt, “A Need Hierarchy for Teams 1 Introduction Maslow ’ s Need Hierarchy,” Exch. Organ. Behav. Teach. J., pp. 1–5, 2004.
[3]A. Sarma, A. Van Der Hoek, A. Einstein, J. Addams, and E. Roosevelt, “A Need Hierarchy for Teams, Physiological Needs Maslow ’ s Need Hierarchy,” Exch. Organ. Behav. Teach. J., pp. 1–5, 2004.
[4]A. Sarma, A. Van Der Hoek, A. Einstein, J. Addams, and E. Roosevelt, “A Need Hierarchy for Teams, Safety Needs Maslow ’ s Need Hierarchy,” Exch. Organ. Behav. Teach. J., pp. 1–5, 2004.
[5] Maslow, A,H., Motivation and Personality. 3rd edition 1987, HarperCollins Publishers, 293.
[6]A. Sarma, A. Van Der Hoek, A. Einstein, J. Addams, and E. Roosevelt, “A Need Hierarchy for Teams, Self-Actualization Maslow ’ s Need Hierarchy,” Exch. Organ. Behav. Teach. J., pp. 1–5, 2004.
Cite error:
<ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found