Gantt chart and Scheduling techniques
Contents |
Abstract
The scheduling techniques that are going to be explained in this article are Gantt and CPM - hereby Network Diagram
- have they works
- have to use them in practice
- have they are connected and supplement each other
Goal: to simplify the different scheduling techniques, how to use them and connecting them to each other
Scheduling
A plan can only show the practicability of accomplishing its objectives when the actions and activities in the plan, are put together in a schedule that illustrates when each action or activity will be carried out.
Today there is many different methods and approaches to scheduling. It can either be by computer-based planning tools or done manually [1].
Tools like Gantt chart and Critical Path Method (CPM) are tools often used in the planning process of a project.
Gantt chart
What is a Gantt chart?
Gantt chart is the oldest form of a formal scheduling tool. The Gantt chart was developed in the 1910s by Henry Gantt, and today used widely as a scheduling tool in projects. [2]
Definition
"A graphic display of schedule-related information. In the typical bar chart, schedule activities or work breakdown structure components are listed down the left side of the chart, dates are shown across the top, and activity durations are shown as date-placed horizontal bars." [3]
When and why use Gantt chart?
Assess how long a plan should take, lay out the order in which tasks need to bed carried out Manage the dependencies between tasks See what should have been achieved at a certain point in the time See how remedial action may bring the plan back on course
How to create a Gantt chart?
Developing a Gantt chart takes some steps. In the scoping phase determines the level of details and the activities identifies in the project.[4] There are many ways to create a Gantt chart and in the end, it depends on the project and the working style. In the table below are some general steps to developing a Gantt chart described.
| Creating a Gantt chart step by step | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Step 1 - Creating the axes: Create a sheet with vertical and horizontal axes. The vertical axis represents the activities, and the horizontal axis represents the timescale. To make the Gantt chart more clear and get and an idea of the total time that needs for each activity, adding the calendar time in timescale is a good idea, see figure 1. [4]
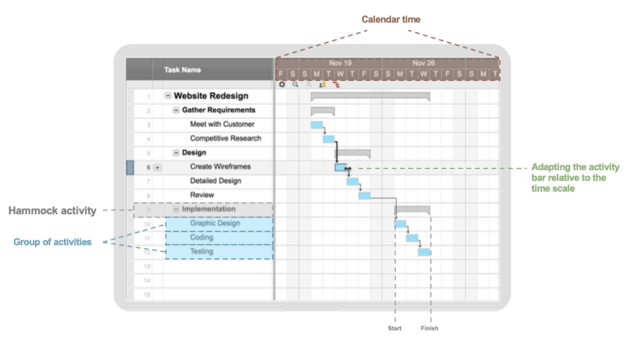 Figure 1: How to create a Gantt chart. Reproduced from: [4]
| |||||
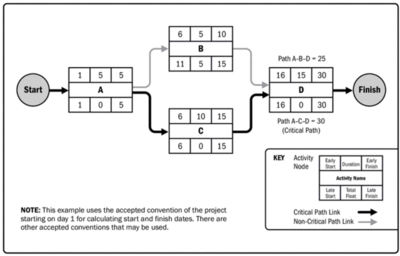
Critical path method (CPM)
What is the Critical path method
Develop in the 1950s by Morgan R. Walker and James E. Kelley. CPM is very similar to PERT(Program evaluation and review techniques), but represent information in a different way.
Definition
"A schedule network analysis technique used to determine the amount of scheduling flexibility (the amount of float) on various logical network paths in the project schedule network, and to determine the minimum total project duration. Early start and finish dates are calculated by means of a forward pass, using a specified start date. Late start and finish dates are calculated by means of a backward pass, starting from a specified completion date, which sometimes is the project early finish date determined during the forward pass calculation.” [5]
How to create the Critical path method
| Creating a Gantt chart step by step | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Step 1 - Specify each activity:
Step 4 - Estimate activity durations:
| |||||
Constructing a Network Diagram
| Checklist when creating a Network Diagram | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. 2. | |||||
The Importance of the Gantt Chart and the Critical Path for Project Management
How to connect Gantt chart and CPM
Pros and cons
| colspan="6" style="text-align: left; color: #699EB4;" Pros | colspan="6" style="text-align: left; color: #699EB4;" Cons
| |
|---|---|---|
| Gantt [6] |
|
|
| CPM [7] |
|
|
References
- ↑ Managing Successful Projects with PRINCE2. (2017). Managing Successful Projects With Prince2. The Stationery Office Ltd.
- ↑ DuBrin, A. J. (2011). Essentials of management. Cengage Learning.
- ↑ Guide, A., 2001. Project management body of knowledge (pmbok® guide). In Project Management Institute. (p. 436)
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Milosevic, D. Z., & Martinelli, R. J. (2016). Project management toolbox: tools and techniques for the practicing project manager. John Wiley & Sons. [[2]]
- ↑ Guide, A., 2001. Project management body of knowledge (pmbok® guide). In Project Management Institute. (p. 431)
- ↑ Craig Borysowich, Feb 2, 2008, Pros & Cons of Gantt Charts. [Available online]
- ↑ Craig Borysowich, Feb 2, 2008, Pros & Cons of PERT/CPM. [[3]Available online]