Waste management on construction sites
Group: The Minions
Members: Signe Ebsen Olling (s154194), Janak Raja (s192757), Samarth Shivanand Karseri (s192743), Kathrine Butler (s153360) Amalie Hammershøy (s152985), Arsalan Aman (s190218)
Contents |
Abstract
Xxx
Introduction
MT Højgaard is one of the leading construction companies in the Nordic countries. The companies sustainability department is working towards a more sustainable future in the building industry and a part of this is looking at the waste management on the construction side. By collecting more waste for reuse on the construction side the buildingside does not only become more sustainable. The right waste management is also beneficial in in terms of certified buildings (DGNB), the economics of a building project and the selling argument for choosing MT Højgaard over another company. From this project we will find solution for how to make sure that the waste is mannaged correctly by the use of project management tools. A part of this is looking and the behavior of the craftsmen and how to change this and looking into the economics of the case. The project is dividend as described in the overview.
Overview
People oriented: 1. Fish Bone Diagram, 2. Motivation Theories and 3. Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs.
Process oriented: 1. Business Canvas Model, 2. Star Model, 3. The Iron Triangle, 4. Gantt Chart, 5. SWOT, 6. Efficiency and Effectiveness Matrix, 7. Value Propositions Canvas, 8. Problem Tree and 9. Stakeholder Analysis.
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
Xxx
Definition
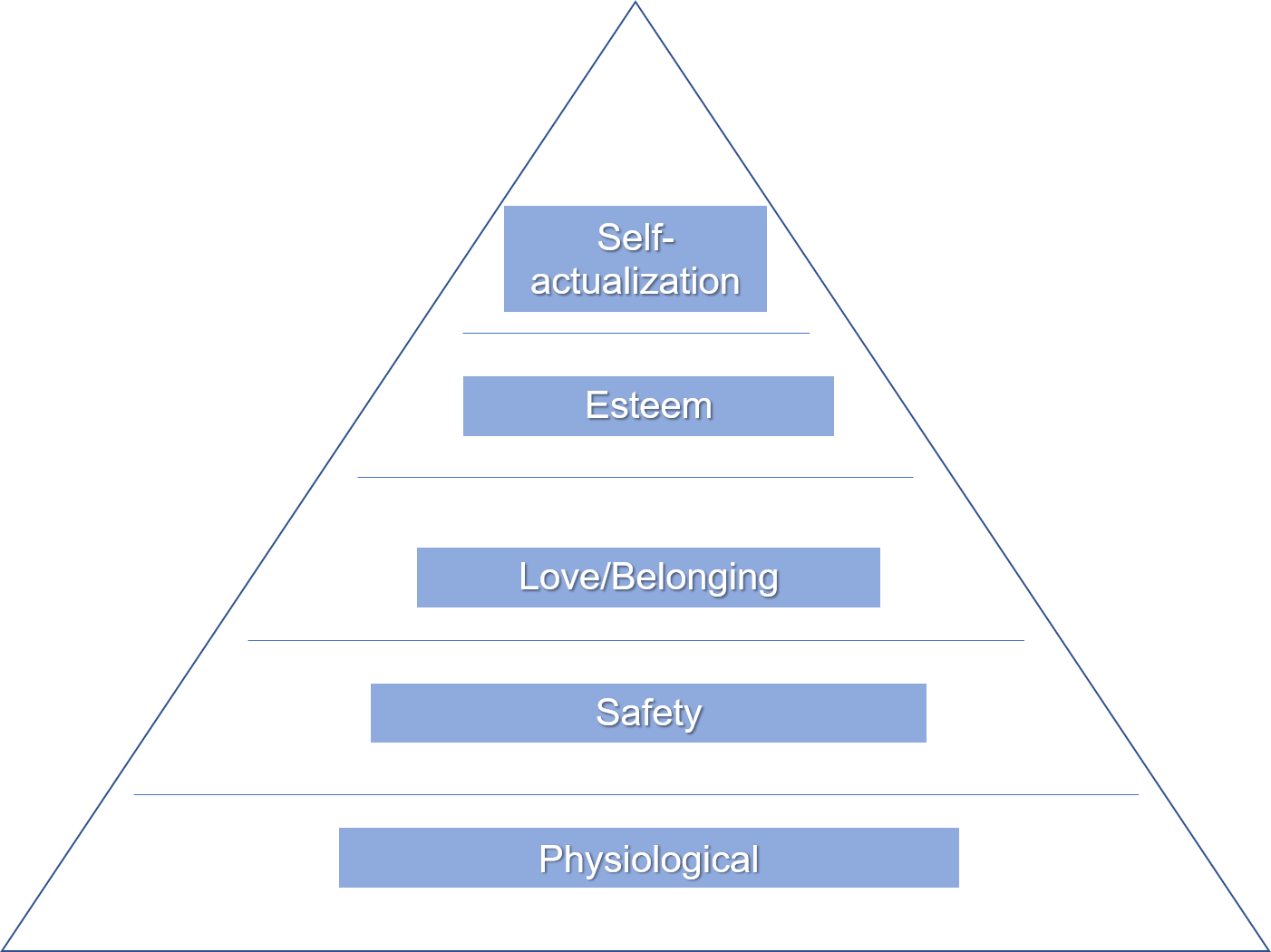
The "Hierarchy of Needs" theory was written by a psychologist named Abraham Harold Maslow through studying the lives and motivation of people who were successful like Eleanor Roosevelt and Albert Einstein. Humans, in general, are motivated with needs that are unsatisfied and basic needs to be satisfied before the complex ones. Maslow divided his pyramid into five different types of needs i.e. physiological, safety, love, esteem, self-actualization. The urge to satisfy the needs with time passing by increases, however people after gratifying the basic needs first moves onto the next on their mind.
The project managers with the help of this theory can create a hierarchy of needs to achieve their objectives since they are directly involved with the team. They need to understand the needs and motivation for the project's aims because in case of dissatisfaction the level of efficiency might reduce. Therefore for an efficient and effective team, the project managers need to consider the factors and create a more flexible strategy in regard to needs and cultural background, etc. While some behaviors have more motivations, Maslow noted that any behavior is determined by a multiplicity of basic needs rather than one.
- Physiological Needs
These are the basic needs that are for survival and universal for human beings. Primarily these needs should be satisfied in order to be motivated towards higher needs i.e. breathing, sleeping, eating, etc. Unless these needs are met others need an unfulfilled. This aspect is essential for a project manager and it needs to be satisfied with the team since physiological conditions are critical. Facilities should be available to the team members such as eating, drinking and resting while enough rest is required before work.
- Safety Needs
Safety needs are second after physiological needs are gratified. Humans will usually think about their safety, which helps them be consistent and stable. Categories of safety can be freedom from fear, dependency, security, stability, etc. The project manager needs to focus on the safety needs of their team after physiological needs are met. The project manager needs to understand the psychology of each team member and needs to create an environment where the team members feel secure. The project manager also needs to make sure that the team members receive their salaries in time, are healthy and safe. The team members must not be in fear of getting fired due to minor faults otherwise they will not be able to work as efficiently.
- Love/Belonging Needs
The fact that humans are social animals, therefore, it makes them feel good when they are part of a team/group or around loved ones. The absence of this can cause a person to be depressed, cause social anxiety and loneliness. In terms of management's perspective, belonging to the team is one of the most critical needs. It is the duty of the project manager to create an awareness of being a team within each member and bring them together by arranging social events. This way collaboration becomes smoother and there is efficiency in the team. The members work better when they feel they are a part of a team towards a common goal. The team members should also feel like they are treated equally and with justice as well as respect or else they might lose the feeling of being an equal team member.
- Esteem Needs
Esteem can be of two types, self-esteem which is a product of becoming a master in a particular task while the second one is being respected and given attention from the team members. After a person's need for belonging is satisfied they want to see recognition and respect in life. For example, when a scientist makes a breakthrough and receives an award, they will see respect from the community which satisfies their level of self-esteem, while it is also imperative that a person builds their self-esteem internally. From a project management perspective, a project manager should essentially show respect to the team members and appreciate their contribution to their team to boost their esteem. This makes the team members more confident and creative while project managers should also satisfy their own esteem needs.
- Self Actualization
This is the top of the hierarchal pyramid of needs, in which Maslow argues a person ought to be what he is. In other words, a person who loves music must make music, while an artist must produce art which is essentially called self-actualization. Finally, Maslow argues, curiosity and need for knowledge is the top of the pyramid. In the scope of project management, for a project manager, it is important to identify the motivation of a team member to be in the team, since it is different with each individual. In the process of team building, the project manager should learn the team member's purpose and their expectation. When the team member has a specific interest in the project and curious for gaining knowledge, the success chance of the project increases.
Benefits
Xxx
Limitations
Xxx
Annotated Bibliography
Xxx
Business Canvas Model
Xxx
Definition
Xxx
Benefits
Xxx
Limitations
Xxx
Annotated Bibliography
Xxx
Star Model
Xxx
Definition
Xxx
Benefits
Xxx
Limitations
Xxx
Annotated Bibliography
Xxx
The Iron Triangle
Xxx
Definition
Xxx
Benefits
Xxx
Limitations
Xxx
Annotated Bibliography
Xxx
Gantt Chart
Xxx
Definition
Xxx
Benefits
Xxx
Limitations
Xxx
Annotated Bibliography
Xxx
SWOT
Xxx
Definition
Xxx
Benefits
Xxx
Limitations
Xxx
Annotated Bibliography
Xxx
Expectancy Theory
Xxx
Definition
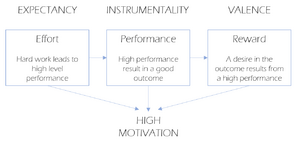
Expectancy theory is a motivation theory build on the expectancy of a good result or outcome. It covers the three factors that determine a person’s motivation; expectancy, instrumentality and valence. The level of expectancy in a n outcome determine the level of effort which is expected to be needed to get a certain result. If a person believes that a high level of effort lead to a high performance the motivation will be high.
In order to achieve a good outcome both the expectancy and the motivation must be high. It is the managers responsibility to ensure the workers are motivated and believe that a high effort leads to high performance and result in a good outcome.
Instrumentality describes the perception about the level of effort which will lead to a good outcome. People are motivated to perform high if only the think a high performance will lead to a good outcome or result.
In expectancy theory the valence is important to consider when motivating employees. The desirable outcome is different from person to person, so to ensure a high motivation it is important for a manager to know what has a high valence. This can be pay, accomplishment or enjoying work.
If all these three factors are high the motivation will be high. On the other hand if one of the factors are low, the motivation is most likely to be low. Regarding waste management, the theory can be relevant to use as the waste sorting is a new or improved procedure that need to be implemented. The motivation to do that for the crafstmen is important to get the desired outcome – better waste sorting.
Benefits
Xxx
Limitations
Xxx
Annotated Bibliography
Xxx
Fish Bone Diagramme
Definition
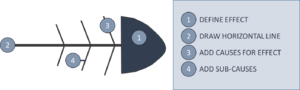
A fish bone diagram is used to identify the cause/causes of an effect or in other words, to look at a problem and its origin/origins. The diagram has its name from the visual structure of it but is also referred to as the Ishikawa diagram, which is the name of its creator. The procedure of using the diagram can very easily be divided into four steps as shown in the figure. 1. First the effect that is going to be investigated is defined and placed in a box on the right side of the diagram. 2. A horizontal line is then drawn from the effect box creating the spine of the fish. 3. All causes for the effect is defined and attached to the spine which leads to the effect. Examples of causes could be the three M’s (Materials, Methods, Machines, Mother Nature, Manpower and Measurements ) or the three P’s (People, Process, Policy , Plant, Program and Product) [KILDE2]. 4. Depending on the complexity of the effect there might occur sub-categories. After these have been defined, they should be attached to the causes.
Benefits
Xxx
Limitations
Xxx
Annotated Bibliography
Xxx
Efficiency and Effectiveness Matrix
Definition
The efficiency and effectiveness matrix is a common used project management tool. The main purpose with the tool is to recognize and detect the courses of low efficiency and effectiveness in the current situation so it can be improved. It is a tool that strives to reach the goal for a high performance regarding providing a service or product for the costumers. Efficiency measures how well the resources is used to achieve the goals and effectiveness measures how appropriate the goals are.[1]
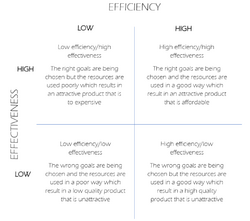
The matrix consists of two axes; a vertical which goes from low to high and a horizontal going from low to high. This matrix creates four boxes; low efficiency/low effectiveness, high efficiency/low effectiveness, low efficiency/high effectiveness, high efficiency/high effectiveness.
- Low efficiency/low effectiveness
The wrong goals are being chosen and the resources are used in a poor way which result in a low quality product that is unattractive.
- High efficiency/low effectiveness
The wrong goals are being chosen but the resources are used in a good way which result in a high quality product that is unattractive
- Low efficiency/high effectiveness
The right goals are being chosen but the resources are used poorly which results in an attractive product that is to expensive
- High efficiency/high effectiveness
The right goals are being chosen and the resources are used in a good way which result in an attractive product that is affordable
In the case of waste management, the tool can be useful to detect the courses of why waste sorting on building sites are not working and help to figure out how to improve that.
Advantages The efficiency and effectiveness matrix is good to show the current situation in a company. It can provide a overview of how the efficiency and effectiveness in a company is and help in the process of improving the two factors.
Limitations The matrix provides an overview of the situation in the company or organization. It is up to the user of the matrix to decide the way to use it and thereby the detail level. It is important to use a certain level of detail to be able to use it properly and to get a useful outcome. It can be easy just to use it with a low level of detail which will not lead to a useful outcome.
Benefits
Xxx
Limitations
Xxx
Annotated Bibliography
- ↑ Jones, Gareth R. and George, Jennifer M.,Sixth edition, Essentials of Contemporary Management, 2015
Value Propositions Canvas
Definition
xxx
Benefits
Xxx
Limitations
Xxx
Annotated Bibliography
Xxx
Problem Tree
Definition
The problem tree is a central tool of many project planning. The function of this tool is to find solutions on the problem by mapping the causes and effects. This is done by use the similar essential tool as in mind mapping, but where structure is a focus element in this method. The solution will be a prioritised presentation of a problem, its causes and consequences.
The problem tree is a tool based on the general tree diagram, which is a tool used to communicate the hierarchy of elements in a project and to clarify the relations the between main, subordinate, and supporting ideas. [1]
The use of the tool is divided in four parts [2]
- First a brainstorming is used to identify the major problems of a project. Each of these problems may result in a problem tree analysis. One problem is chosen.
- The possible causes to the problem are defined. The causes might be responsible for the problem situation but can further be causes of other causes. The causes can have internal relationships or be directly related to the main problem. All causes are being listed.
- When all causes are found, the consequences can be defined. As the causes, the consequences are being listed with their internal relationships.
- When all elements of a specific problem have been identified, the problem tree can be presented. It is viewed as a tree, where the causes are the “roots”, the main problem is the trunk and the consequences the crown.
Benefits
The advantages of using the problem tree is understanding the problem by breaking it down. By doing it in this way, the chunks will be easier to analyse and understand. Further these will be more manageable when chunking up and down. By expand and elaborate the problems, causes and effects it might be easier for all stakeholders to understand, because of a shared sense of purpose and action. This will clarify the processes in the different stages, and the different stakeholders and participants will be related and connected to specific parts. The issues forward will further be identified and thus handled early in the process, which e.g. can prevent a leak in the budget. [3]
Limitations
Xxx
Annotated Bibliography
- ↑ Martin, Bella; Hanington, Bruce, 2012. Universal Methods of Design – 100 Ways to Research Complex Problems, Develop Innovative Ideas, and Design Effective Solutions. Rockport Publisher
- ↑ Thakur, Sidhart, 2020. Using a Problem Tree Analysis in Project Management. https://www.brighthubpm.com/project-planning/118441-problem-tree-a-comprehensive-analysis-tool/
- ↑ Overseas Development Institute (ODI). 2009. Planning tools: Problem Tree Analysis. Successful Communication: A toolkit for reserachers and civil society organisations. https://www.odi.org/publications/5258-planning-tools-problem-tree-analysis
Stakeholder Analysis
The stakeholder analysis is a way to manage the stakeholders in a project, which is often used by project and program managers.
Definition
A stakeholder analysis is a process of identifying people, which is involved, affecting or affected by the project or the problem going to be solved. The focus is to map them in groups of interest and influence and find out, e.g. how to communicate to each of the stakeholders to avoid conflicts. Further this tool is a good way to define and understand the goals and plans for each stakeholder.
The analysis can be based on more tools. In the following four different tools will be mentioned and explained. Current for all tools are, that the stakeholders have to be determined and identified at first. Stakeholders is basically all persons or companies, which have an interest or influence on the project scope; it is all from the general public to investors. The stakeholders can then be grouped by using tools.
- Interest/influence matrix: the stakeholders are placed in a graph based on the power or influence on the project. This graph can be made both before and after a project to see the change of mindset or value for the individual stakeholder.
- Stakeholder and benefit mapping: a scheme of interests and stakeholders, where the two parts are being connected crisscross. By using this tool, the most important focus areas can be identified.
- Stakeholder map: The identified stakeholders are being connected to eachother to visualise their relationships and thereby point out the key players and their specific roles related to other stakeholder. [1]
Benefits
Xxx
Limitations
Xxx
Annotated Bibliography
- ↑ Martin, Bella; Hanington, Bruce, 2012. Universal Methods of Design – 100 Ways to Research Complex Problems, Develop Innovative Ideas, and Design Effective Solutions. Rockport Publisher
References
Xxx