DS Solution
Contents |
Introduction
Tools
SWOT Analysis
Defenition
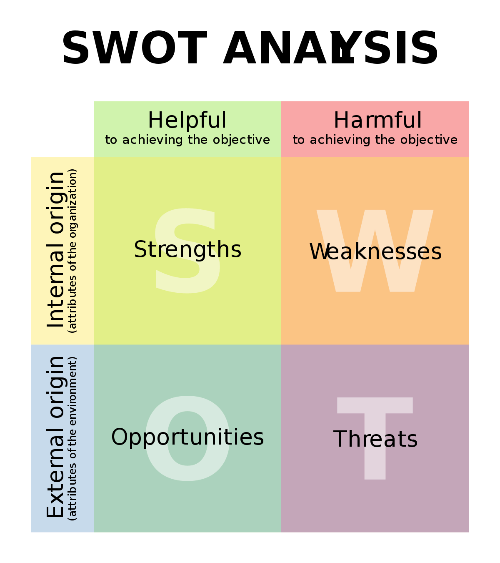
SWOT Analysis [1] is a planning exercise in which managers identify internal organizational strengths (S) and weaknesses (W) and external environmental opportunities (O) and threats (T), using the popular 2x2 matrix.
Practical guidelines
The first step in SWOT analysis is to identify an organization’s strengths (such as high-quality skills in marketing and in research and development) and weaknesses (such as rising manufacturing costs and outdated technology). The task facing managers is to identify the strengths and weaknesses that characterize the present state of their organization.
The second step in SWOT analysis begins when managers embark on a full-scale SWOT planning exercise to identify potential opportunities and threats in the environment that affect the organization now or may affect it in the future. After applying a SWOT analysis on a business project, decision-makers should understand if the goal is attainable or not. In case that the goal is not achievable, decision-makers must select another goal and repeat all the process again.
ADKAR
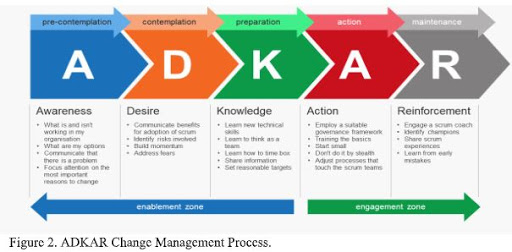
The ADKAR model [2] is a 5-step framework that helps deal with the people-aspect of change management. ADKAR is an acronym that represents the five milestones or outcomes an individual must achieve for change to be successfully realized: awareness (of the need to change), desire (to participate and support the change), knowledge (about how to change), ability (to implement new skills and behaviors) and reinforcement (to keep the change in place).
When applied to organizational change, this model allows leaders and change management teams to focus their activities on what will collectively drive individual change and produce organizational results. The ADKAR Model will highlight the areas where you can take focused, corrective action to improve change success.
HOUSE OF QUALITY
The Quality Functional Deployment is a complex process divided into three steps, with the aim of find out the specific costumer’s requests. Their preferences, collected in the first and second step, are reported in a diagram, called the House of Quality. It’s built in ten different moments:
1. List of costumers’ needs 2. Index of importance according to costumers’ needs 3. Translation od costumers’ needs into technical specifications 4. Units of measurement of technical specifications 5. Correlation matrix 6. Relation matrix 7. Relative importance of technical specifications 8. Comparison with competitor’s products 9. Technical benchmark 10. Analysis of organizational difficulties
This modular tool ensure full coherence between the design of the product and its production, reducing the corrections during the development of the project. The requests without a formal response in quantified attributes appear as an empty column or an empty line in the diagram.
DECISION TREE ANALASYS
Defenition
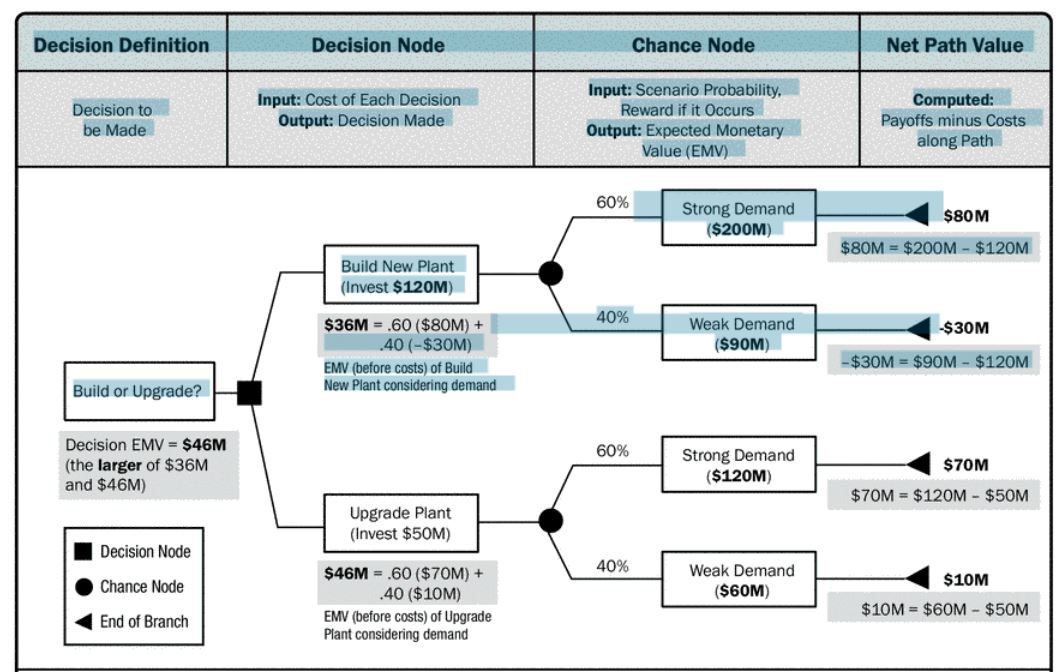
Decision trees are used to support selection of the best of several alternative courses of action. Alternative paths through the project are shown in the decision tree using branches representing different decisions or events, each of which can have associated costs and related individual project risks (including both threats and opportunities). The end-points of branches in the decision tree represent the outcome from following that particular path, which can be negative or positive.
Benefits
x
Advantage
x
Disadvantage
x
practical guidelines
Decision trees are commonly used in operations research and operations management. If, in practice, decisions have to be taken online with no recall under incomplete knowledge, a decision tree should be paralleled by a probability model as a best choice model or online selection model algorithm. Another use of decision trees is as a descriptive means for calculating conditional probabilities.
link (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Decision_tree)
S.M.A.R.T
xx
Defenition
x
Benefits
x
Advantage
x
Disadvantage
x
practical guidelines
x
A3 REPORT
xx
Defenition
x
Benefits
x
Advantage
x
Disadvantage
practical guidelines
x
WBS
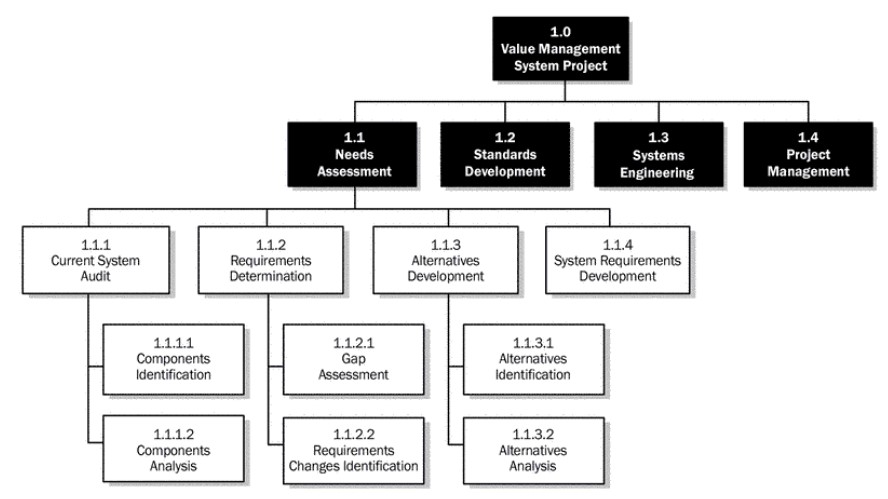
The WBS (Work Breakdown Structure) [3] is a hierarchical decomposition of the total scope of work to be carried out by the project team to accomplish the project objectives and create the required deliverables. Each descending level of the WBS represents an increasingly detailed definition of the project work. The lowest level of the WBS is formed by the work packages with a unique identifier, which can be used to group the activities where work is schedule and estimated, monitored, and controlled.
Create WBS
Decomposition is a technique used for dividing and subdividing the project scope and project deliverables into smaller, more manageable parts. The level of decomposition is related to the degree of control needed to effectively manage the project. The level of detail for work packages depends on the size and complexity of the project. A WBS structure may be created through various approaches. Some of the popular methods include the top-down approach, the use of organization-specific guidelines, and the use of WBS templates. A bottom-up approach can be used to group subcomponent.
THE IRON TRIANGLE
xx
Defenition
x
Benefits
x
Advantage
x
Disadvantage
x
practical guidelines
x
STAR MODEL
The Star Model[4]framework for organization design is the foundation on which a company bases its design choices. The framework consists of a series of design policies that are controllable by management and can influence employee behavior. The Star Model has 5 categories:
- Strategy, it specifies the goals and objectives to be achieved by the company;
- Structure, it determines how the power is distributed;
- Processes, it represents how the information and decisions flow into the organization;
- Rewards, its purpose is to align the organization's goals with the employee's goals;
- People, it produces the talent required by the strategy and structure of the organization;
Implication
Although the structure is usually overemphasized because many people believe that it affects status and power, the Structure in the Star Model is only one facet. Another important feature in the Star Model is that different strategies lead to different organizations. This means that there is no one-size-fits-all organization design. The third implication is that for an organization to be effective, all the policies must be aligned and interacting harmoniously with one another.
STAKEHOLDER ANALASYS
xx
Defenition
x
Benefits
x
Advantage
x
Disadvantage
x
practical guidelines
x
INTERVIEWS
xx
Defenition
An interview is a formal or informal approach to elicit information from stakeholders by talking to them directly. It is typically performed by asking prepared and spontaneous questions and recording the responses. Interviews are often conducted on an individual basis between an interviewer and an interviewee, but may involve multiple interviewers and/or multiple interviewees.
Benefits
Interviewing experienced project participants, sponsors, other executives, and subject matter experts can aid in identifying and defining the features and functions of the desired product deliverables. Interviews are also useful for obtaining confidential information, assumption and constraint analysis.
Disadvantage
x
practical guidelines
x
References
- ↑ Gareth R. Jones and Jennifer M. George, Essentials of Contemporary Management, Eighth Edition, page 198, McGraw-Hill Education, 2019, ISBN 9781259927652
- ↑ The Prosci ADKAR Model: Why it Works - https://www.prosci.com/resources/articles/why-the-adkar-model-works
- ↑ Project Management Institute, Inc.. (2017). Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide) (6th Edition) - 5.4.1.4 Organizational Process Assets. (pp. 156-157). Project Management Institute, Inc. (PMI). Retrieved from https://app.knovel.com/hotlink/pdf/id:kt011DX6D4/guide-project-management/create-wbs-organizational
- ↑ https://www.jaygalbraith.com/images/pdfs/StarModel.pdf