Learning plan
Contents |
Abstract
A learning plan is a tool to overcome the challenge of making sound decisions while facing uncertainties. In principle, a learning plan is a document that can be used by a project team to resolve uncertainties in the four relevant categories: market, technical, resource and organizational uncertainty. Over the life cycle of a project, the project team systematically tests assumptions to their uncertainties to build up decision-relevant knowledge throughout several iterations of the learning plan, also called learning loops. This approach is particularly useful in high uncertainty projects, like for example for radical innovations, were other approaches to project planning could lead to early abortion of the idea. In general, learning from experience is one of the key characteristics of successful projects. While the learning plan is a tool that is widely used across industries it is limited to guiding the learning process rather than controlling tasks and responsibilities.
Introduction
The learning plan is a framework to facilitate a learning process that systematically turns un-knowns into knowns. It is applied at the planning stage of a project and gets continuously revised throughout the project life cycle whenever there is a lack of decision-relevant knowledge. As all projects need to deal with uncertainties in multiple dimensions, learning from experience is one of the principles of successful project management. Through the learning plan, a project team can systematically fill its knowledge gaps and gain experience through experimentation. [2].
In short, a learning plan has the following characteristics: [3]
- It catalogues uncertainties
- It connects uncertainties with assumptions
- It prioritizes uncertainties based on their criticality
- It presents testing approaches to resolve critical uncertainties
- It documents a project’s progress in terms of learning outcomes and consequences thereof
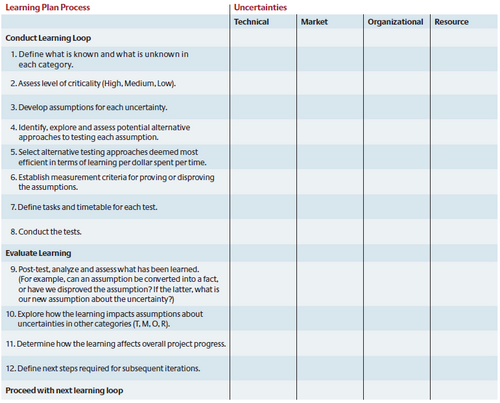
While a learning plan has no universal format, a basic learning plan should consist of at least two sections. In the first section, the participants of the learning process catalogue uncertainties in four categories: market, technical, resource and organizational uncertainty. For the most critical ones the team then develops assumptions that get tested and, if disproved, turn into a new assumption or, if proved, into a fact. In the second section, this is then followed by an evaluation of the learning where results are reviewed and, if necessary, new assumptions and tests are developed to initiate another iteration of the learning plan. The learning plan is therefore continuously revised to adapt to learning outcomes. Figure 1 shows a template of a basic learning plan. Besides the analog version there are various digital project or task management tools that can be used to leverage the learning process.
Uncertainty in Project Planning
A common characteristic of projects is that they all face uncertainty in the planning process. As projects mature the project team will gain experience which increases the availability of decision-relevant knowledge. Nevertheless, this will never fully eliminate all un-knowns. Uncertainty can be seen as the cause of individual project risk which is defined as "an uncertain event or condition that, if it occurs, has a positive or negative effect on one or more project objectives". [4]. Reducing uncertainty to make decisions based on knowledge is therefore a common goal in project management. The process of acquiring new, or modifying existing, knowledge, behaviors, skills, values, or preferences based on experience is called learning [3]. Uncertainty as a lack of knowledge or information can therefore be reduced with an appropriate learning process and is also an essential part of risk and uncertainty management procedures [5].
The learning plan is a tool for systematic learning which ideally results in uncertainty reduction. It is widely used for innovation projects, particularly for radical innovations, where the degree of uncertainty is typically very high. In order for project teams to proceed, assumptions have to be made. Over time, learning reduces the number of these assumptions and turns them into new knowledge. This in turn leads to a higher certainty in management decisions while projects mature. [3]
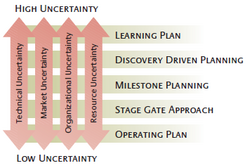
There are different established approaches to cope with project uncertainty. Figure 2 provides an overview of different project planning approaches - each associated with a certain degree of uncertainty where it proved most useful. Here, the learning plan is seen as the project planning framework that should be used in situations of particularly high uncertainty. While the degree of uncertainty ideally gets reduced throughout the lifecycle of a project and several iterations of the learning plan, other project planning approaches may take over. [3]
Application of the Learning Plan
The template in figure 1 shows the steps of the learning plan process in vertical and the categories of uncertainties that are found to occur in projects in horizontal direction. The latter refers to the multidimensionality of uncertainty. For a successful application of the learning plan it is crucial to understand these categories, which are therefore presented in the following before describing the actual learning plan process.
Dimensions of Uncertainty
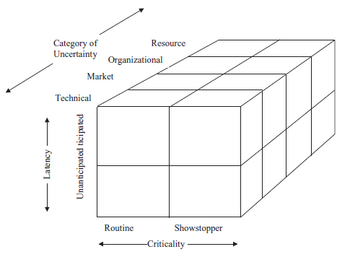
Figure 3 shows the three dimensions of uncertainty in the context of project management described by O'Connor and Rice [5]: category, latency and criticality.
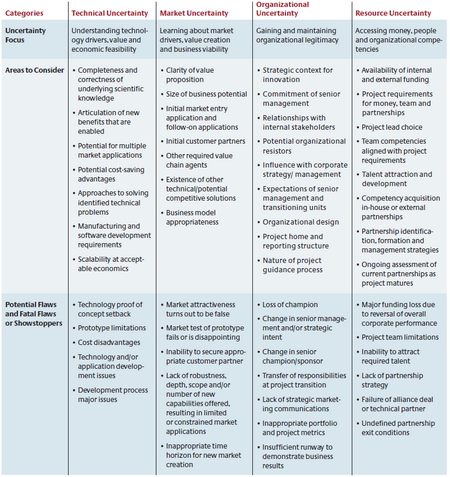
The first dimension, the uncertainty category, is dividing uncertainties into the four content areas technical, market, organizational and resource uncertainty. In relation to the learning plan, the following learning objectives can be defined for each: [1]
- Market uncertainty: Learning about market drivers, value creation and business viability
- Technical uncertainty: Understanding technology drivers, value and economic feasibility
- Resource uncertainty: Accessing money, people and organizational competencies
- Organization uncertainty: Gaining and maintaining organizational legitimacy
Projects can differ largely in their level of uncertainty in each dimension. Moreover, the uncertainties in different categories can interact with one another so that resolving an uncertainty in one category can also have an effect on other categories. Splitting up the uncertainties into these categories helps a project team analyzing the entire spectrum of uncertainties and avoiding the pitfall of focusing only on such categories that the project team is comfortable with. For successful projects it is particularly important to reduce uncertainty and accumulate learning over all categories. In practice, managers were often found to focus on technical uncertainties instead. [3]
The second dimension of uncertainty, latency, refers to the degree to which an uncertainty can be anticipated. The higher the latency, the more difficult is it to perceive the uncertainty and to find appropriate assumptions for it. As a result, high latency uncertainties may not be resolved with assumption testing before the uncertain event occurs. The concept of latency is not explicitly noted in the learning plan. The concept is important nevertheless as project teams need to put effort into cataloguing also those uncertainties that are difficult to anticipate and that might have a large influence on the project's progress. Moreover, they need to be flexible in their learning approach as they need to adapt the learning plan to unanticipated events as the project matures.
The third dimension of uncertainty refers to the criticality of the uncertainties. An uncertainty is found to be critical if it is a potential showstopper for the project. In order to ensure a project's success these therefore need to be resolved immediately. On the other hand, an uncertainty which is routine does not threaten a project's survival. The assessment of criticality takes place in the second step of the learning plan process. The most critical uncertainties should be targeted by assumptions and tests as soon as possible.
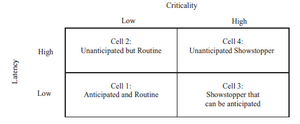
The dimensions latency and criticality are found to interact with one another as shown in figure 4. The uncertainties which are anticipated and routine are fairly easy to handle as they are known from project start and can be targeted with an appropriate set of assumption testing approaches. Unanticipated but routine uncertainties occur without prior perception but due to their routine property can be treated quickly through the next iteration of the learning plan. Anticipated showstoppers need to be targeted immediately with a more comprehensive set of actions while unanticipated showstoppers need to be addressed aggressively upon occurrence which may require a substantial amount of resources. The occurrence of uncertain events during a project's lifecycle is not necessarily negative but can as well be an opportunity for further progress beyond the original plan.
The Learning Plan Process
The learning plan process as described by Rice et al. [1] is divided into two main parts. First, a learning loop is conducted and second, the learning from this loops gets evaluated. Following the steps of the learning plan template in figure 1, each iteration through the learning plan starts with the identification of explicit uncertainties in all four uncertainty categories (1.). It can also be beneficial to write down what is already known at this step of the process. Figure 5 provides a non-comprehensive list of uncertainties that potentially arise in projects that can serve as a starting point for creative thinking.
The cataloguing of uncertainties is followed by an assessment of their criticality (2.) to identify potential showstoppers and to make a decision on where to learn first. Mostly this is done with the levels high, medium and low. In the next step, the project team needs to develop assumptions (3.) while potentially focusing on the most critical uncertainties depending on time and resource constraints. Assumptions are accepted as true as long as they are not disproved. While a project can potentially progress based on these assumptions it is key to the learning plan that these assumptions get further tested to either turn them into facts or find better suitable assumptions. This is done through the remainder of the steps of a learning loop starting with the identification, exploration and assessment of alternative testing approaches to each assumption (4.). Then, the most efficient testing approaches in terms of “learning per dollar spent per time” are selected (5.). This can be understood as the value of the cumulative learning outcome that can be expected from the test compared to the costs it causes. If no testing approach is found to deliver sufficient value, the project can either continue based on the assumption or managers might decide on terminating the project. The overall goal is to maximize learning while minimizing spending. After that, the measurement criteria for either proving or disproving an assumption through the test get defined (6.). In the following step, the timetable gets defined and resources get assigned to the tests (7.) which are then finally conducted (8.). The test outcomes get also noted down in the learning plan. The tests do not necessarily have to be executed by the project team but can as well be outsourced to other parts of the company or even external providers.
In the second part of the learning plan the evaluation of the learning loop takes place. This part can be performed by the project team itself or by an oversight board or project evaluation board that continuously monitors the learning outcome. It starts with an analysis and assessment of the test results and whether they prove or disprove the assumptions based on the measurement criteria (9.). In case an assumption is disproved it needs to be evaluated which other assumption might then be more appropriate to the respective uncertainty. Then, as uncertainties in the four categories potentially interact with one another, it has to be further assessed if the learning from testing one assumptions has potentially affected assumptions about uncertainties in other categories (10.). Finally, the learning gets evaluated in terms of its effect on the overall project progress (11.) before the steps required for following learning loops get defined (12.). In practice, teams are found to have taken three to four learning loops until they reached an appropriate level of certainty to apply another approach to project planning.
Conclusion
The learning plan is a systematic approach to project planning in highly uncertain environments. Due to this, the success of the learning plan framework is highly dependent on the members of the project team and the oversight board and their experience with (radical) innovation projects. The effective application of the learning plan can improve both project management and project managers as they get able to make decisions based on knowledge gained through rapid, low-cost experiments rather then killing project ideas to early due to the lack of decision-making knowledge. In order to be effective, the learning plan needs continuous revision to monitor what has been learned and what still needs to be learned. [1]
Nevertheless, the learning plan is not the only approach to project planning. When uncertainty level has been reduced to a certain level, project teams might choose to adopt other project management techniques to proceed. For radical innovation projects however, the learning plan can be a useful tool throughout the entire project as even the residual level of uncertainty remains high. In these cases, a project planning approach like the stage-gate-model tends to kill innovation too early. [3]
Limitations
The first step to applying the learning plan is the definition of knowns and un-knowns in the project area. Project teams can have a hard time in cataloguing uncertainties as also many uncertainties may emerge during the lifecycle of the project. Therefore, it is important to think ahead and be creative while this may also lead to wasted efforts when it later turns out that certain knowledge gained through assumption testing isn't relevant anymore for the project's scope. As a result, the uncertainty level fluctuates a lot over the life cycle of a project and learning loops may not necessarily lead to uncertainty reduction. This in turn may make it difficult to get the required support from management to constantly reassess and apply the learning plan in a project. However, overall there can still be seen a general trend of uncertainty reduction in various case studies to the application of the learning plan in projects. [3]
Furthermore, the main benefit from applying the learning plan is to be able to follow a structured approach to project planning in uncertain situations. The framework is used for monitoring and guiding the learning progress rather than controlling tasks and responsibilities. In this capacity it does not provide guidance for example on how to find appropriate assumptions, how to identify the most efficient tests or how to determine timetables. This means that there is still a lot of subjectivity in how project teams execute the steps of the learning plan process. On the other side, this does also make the learning plan a very flexible framework which can be customized to the needs of any project team. [1]
Finally, the learning plan as a standalone framework can not ensure a learning organization. For this, the company must develop its learning capacities in the long term and pass on experience gained in one project to other projects. Therefore, when seeing the big picture, a learning plan is rather useless when it is applied only in the context of one project. The results of all learning within an organization must be accumulated to sustain the knowledge and improve overall project management especially in the light of uncertainty. In practice, it is often seen that the commitment to developing the capacity of learning is cyclic rather than long-term oriented. [3]
Annotated bibliography
Text
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Rice et al., Implementing a Learning Plan to Counter Project Uncertainty, MIT Sloan Management Review, 49, 2008.
- ↑ AXELOS, The Stationery Office Ltd, Managing Successful Projects with PRINCE2, 2017 Edition.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 Leifer et al., Radical Innovation: How Mature Companies Can Outsmart Upstarts, Harvard Business School Press, 2000.
- ↑ Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, PMBOK Guide, 6th Edition, 2017.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Perminova et al., Defining Uncertainty in Projects - A New Perspective, International Journal of Project Management, 26, 2008.