The Blake-Mouton Managerial Grid
Contents |
Abstract
Leading various projects requires a good leader with a wide range of properties, within knowledge about project management as well as knowledge for dealing with different types of people. A good project manager is aware of what it takes to reach the milestones of a project and has the ability to get an overview of the resources, time and economy. It also requires a leader who can communicate with the employees and has a knowledge and understanding for them. Therefore, is the type of leadership an important topic, and the identification of the style can contribute to better project management and to better project results. As a project leader it is an advantage to address your own strengths and weaknesses, so you can become a better leader, but also know your own qualities. It provides an opportunity to be able to develop your abilities and optimize the competencies. In this context will the article be representing the management tool called “Blake-Mouton Managerial Grid”, which is a model developed by Robert R. Blake and Jane Mouton. The tool gives an impression and opportunity for managers to analyze their own leadership styles. The main points of the tool will be covered and a description on how to apply the “Blake-Mouton Managerial Grid” will be included. Moreover, will the Advantages and disadvantages of the tool be discussed.
Introduction
The Blake-Mouton grid is developed in the 1960's (1964) [1] by two management theoreticians, Robert R. Blake, and Jane S. Mouton.The Blake Mouton grid is a matrix which characterizes five different leadership styles based on a two-behavioral dimensional graph. The Y-axis represents the leader behavior, “Concern for people” and the X-axis. represents the “Concern for results”. [2]
In the context of human concern, there are various leadership qualities that primarily are described as the manager´s interest in the employees´ motivation, well-being and needs, which can provide the work effort / performance. While the other interest for the manager is to complete the project with a focus on the production itself, the results, and the economy.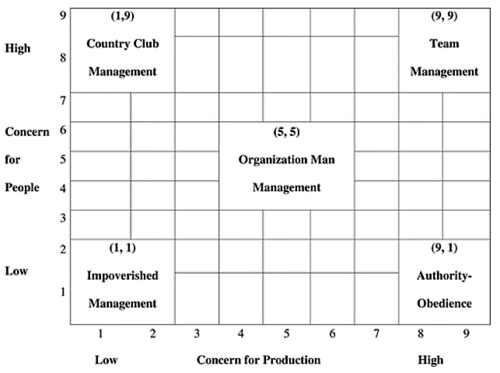
The two dimensions of leader behavior leads into 5 different management styles.
- Impoverished Management
- Authority Obedience
- Organization Man Management
- Country Club Management
- Team Management
Impoverished Management
The improved type of leadership style is an expression of a passive leader. It can be considered as a bad leader but not necessarily, as it is often the organization that has created this leadership type. This may occur when the top of the management already has decided the strategy, and it leaves the leader in a position where the focus is on maintaining and delegating the work tasks. On the other hand, can the improved style appear when the freedom to unfold and applying different management qualities is limited. In general, can it be considered that the project manager is not interested in getting the job done, and either getting created a motivated team. This leadership style is available when you have a highly motivated team working for you, but even then, you should rarely use this style.
Authority Obedience
Authority Obedience also called Produce or Perish Management, is a leadership style, characterized by a strong focus on goals and results. However, the interest in the employee's well-being and motivation is not so big. This management style is a classic one, where the leader uses its power to make the decisions alone, without including the other employees. This can be an advantage under time pressure or if the employees are undisciplined. It won't be easy to keep the high achievement in the long term because of the lack of cooperation between leader and employers. The employee's or organizations' needs are ignored, and the main focus is only on the delivery. When to use this style? The leadership style should be used in urgent situations.
Organization Man Management
Organization Man Management is also called Middle-of-the-Road Management.This type of leader tries to maintain the needs of the employers, and at the same time, the leader is trying to reach the goals of the company. This form of management may look good and balanced, but that is not the whole truth. The never-ending compromise will lead to failure because of the employers' lack of discipline, and the needs of the teams will not be met. The method will lead to an average performance as there is no high performance and the employer's needs are not met fully.
Country Club Management
The Country club leader style is characterized by a leader who focuses on the social between the employees. The well-being and motivation of the employees. This type of leadership believes in the community, and it contributes to better results. Therefore, is an increased commitment and community an advantage for the organization and the team. The employers will probably be happy to work with this type of leader, but there is a risk of they will lose respect for the leader if there occurs a failure of the work delivery. The chance of not achieving good results is big because of the lack of focus on production and results.
Team Management
This type of leader takes responsibility for the organization's goals and the development, motivation, and well-being of the employees. This method of management has benefits for both leaders and employees. From the employees' point of view, they are allowed to develop and learn from the mistakes they make. The project manager will be busy, but over time it will create some freedom for the manager, as the employees will be self-driving. The "Team management style." It is a coveted style of management among small and more significant companies.
How to use the tool
The grid is a two-dimensional Managerial Grid that characters a leader based on a manager's concern for people and the production. The Y-axis in the coordinate system is standing for the focus of the employees/ concern for people and the x-axis is standing for the production/results. And each axis consists of a nine-point scale, where the lowest number means a low concern and the high number indicates a high concern.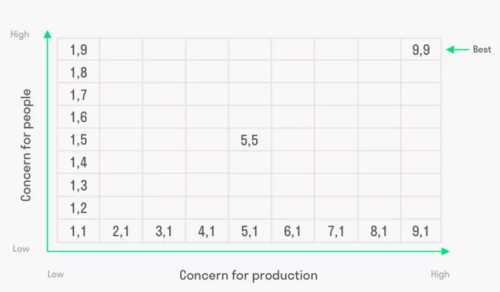
The first step is to complete a leadership self-assessment questionnaire based on statements about leadership behavior. The topic of the leadership questions involves the concern of people and production. After completing the questionnaire, then must the transformation of the answers be included in the scoring section. Here you will find out how many points you have within the two topics. The last step is to plot the final scores on the graph by drawing a vertical line from the score of the x-axis(Production/ Results) and a horizontal line from the score of the y-axis ( People). The two lines will meet, and then you have the point of intersection. The area where the point is located shows which leadership dimension you operate out of. There are pros and cons of using the Blake-Mouton Grid method to define and analyze a leader. The Blake-Mouton grid provides a simple way to understand "Your" leadership style. And that makes it easier to takes steps to address your weaknesses, so you can develop and become a better leader.
Limitations
On the other hand, is Blake-Mouton's grid overly simplistic, and the tool has a big focus on the leader and does not pay attention to other factors there may be. Therefore, is this type of leader analyzes limited, but it can provide a direction and create an overall picture of the leadership style.[5] The best form of leadership is accepted as the position of team management. This may not be practical or indeed advisable. In many industries, concern for the task may be more important than concern for people and vice versa, and it will always depend on which industry you are into. The Managerial Grid is fundamental knowledge that will provide the basic understanding of management, even if the interest in using it is not present.
References
[1] Blake, R, and Mouton, J. (1985). The Managerial Grid III: The Key to Leadership Excellence. Houston: Gulf Publishing Company.
[2] https://harappa.education/harappa-diaries/managerial-grid-theory-of-leadership
[3] https://www-tandfonline-com.proxy.findit.dtu.dk/doi/full/10.1080/12294659.2018.1471029
[4] https://www.toolshero.nl/leiderschap/blake-mouton-managerial-grid/ (Grøn)
Mulder, P. (2012). Managerial Grid by Blake and Mouton. Retrieved [18-02-2021] from ToolsHero: https://www.toolshero.com/leadership/managerial-grid-blake-mouton/
[5] https://www.managementstudyguide.com/blake-mouton-managerial-grid.htm (Pros and cons)
- The Managerial Grid: Key Orientations for Achieving Production Through People by Robert Rogers Blake, Jane Srygley Mouton
Cite error:
<ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found