The Blake and Mouton's Managerial (Leadership) Grid
Contents |
Abstract
Managing a project successfully is not a trivial task and it requires capable managers. In Project Management the terms "Manager" and "Leader" are often used with the same meaning. However, several theories about the differences between Management and Leadership have been developed over the years. Even defining exactly what characterizes a good leader is not an easy task and academics have been trying for decades to provide a definition. Despite these attempts, scholars could not find a universal definition and only theories are available.
One of the most relevant theories was firstly introduced by Blake and Mouton in the early 1960 and it has been revised by the authors for more than two decades. The original name of this theory was "The Managerial Grid", however, it was renamed "The Leadership Grid" to better describe its relevance in the Leadership field [1]. It belongs to the group of theories that follow the Behavioral approach, which emphasizes what is the behavior of the leader in the activity of leading an organization. Other relevant perspectives are the Trait approach, which is mainly focused on the personality of the leader, and the Skills approach, which emphasizes his/her capabilities.
The Leadership Grid is a matrix that shows how leaders can be effective in leading an organization by taking into account two parameters: Concern for results and Concern for people. The first one is represented on the x-axis of a 9x9 matrix and the second one on the y-axis. The combinations of the respective relevance of these two factors define five main approaches to leadership that have been analyzed by the authors.
This article aims to describe the main aspects of this theory together with its applications, and its limitations. Appropriate documentation for further readings about the Grid is included.
Introduction
Leadership and Management are often considered interchangeable terms. Even if these two fields have some similarities, it is relevant to mention their differences. Over the years, many authors have tried to define clearly the characteristics of a manager and a leader and which are the respective roles in an organization. A manager is expected to provide stability and order to a company while leadership is about guiding the organization in the process of changing and adapting to a new situation. So, Management and Leadership are not the same, however, they are both necessary for a company to be successful.
Managerial power usually comes from the position of the manager in the organizational structure. The authority does not come from personal skills or abilities, it is determined by a formal structure in the company. Identifying from where the authority of a leader comes from is not as easy and different theories argue for different sources. One of the most famous questions in the Leadership field is "Are Leaders born or made?" and there is no universal answer.
The trait approach supports the theory that Leaders are born and only a few people have these innate qualities. This approach led to famous theories like the Five Big personalities framework, however, it also led to some failures. From these deadends, scholars started to develop theories based on the idea that good leadership comes from the way the leader behaves and that this ability can be trained. This is the fundamental idea of the Behavioral approach and the Leadership Grid belongs to this group of theories. However, neither traits nor behaviors can guarantee success. Supporters of the Contingency approach believe that the context matters as well [2] (ch.12).
Relevance of Leadership in Project Management
Managing successfully a project is not an easy task and it requires capable leaders. However, even effective project management does not guarantee that it will be a success. On the other hand, projects that are considered a failure from the management point of view could turn out to be a great success.
A leader should be able to inspire and create commitment in his followers to lead them successfully. Different approaches have been studied and analyzed to understand what makes a person a good leader. The aim of this article is to provide a better understanding of the behavioral approach and, in particular, of the Leadership Grid.
The Leadership Grid
The Leadership Grid aims to describe different approaches that a leader can adopt in leading an organization. The authors defined two main factors that influence managers' behavior: Concern for production and Concern for people. These two factors are used to define a 9x9 matrix where Concern for production is represented on the x-axis and Concern for people on the y-axis[1] (p.140).
Concern for production refers to the importance of achieving organizational goals for the leader. They might be represented by the organizational mission, a level of performance, or results to be achieved. In this theory, the definition of "Production" is quite broad and it includes any type of goal or task people are hired to accomplish in a company[3] (p.10).
On the other hand, concern for people is entirely about the members of the organization that are involved in the process of achieving the objectives. Leaders can express it through activities like building trust and commitment to the company, improving working conditions, and promoting good social relationships[3] (p.10).
By combining the respective relevance of these two concerns, Blake and Mouton defined five different managerial approaches. To define the position of each one of them, a score is assigned to both concerns for people and production. The grading scale goes from 1, which represents the minimum concern, to 9, which represents the maximum level of concern. Different leadership styles are obtained by plotting the scores for both axes in the matrix. The authors argue that managers usually have a dominant style, that is the one mostly adopted, and a backup style. the second one becomes dominant in difficult situations, where the usual style does not provide results[1].
The main Managerial styles are Authority-Compliance, Country-Club Management, Impoverished Management, Middle-of-the-Road Management, Team Management.
Leadership Styles
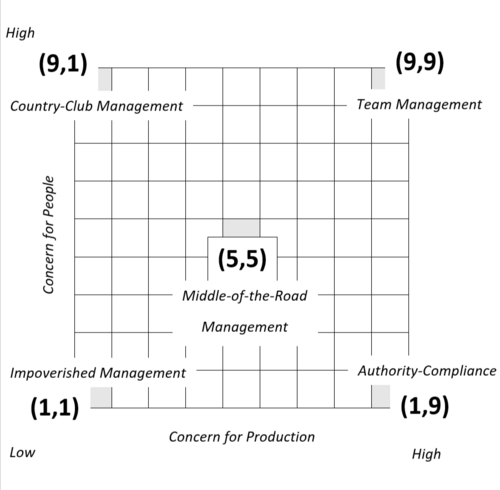
Authority-Compliance (9,1)
This approach is mainly focused on the importance of achieving organizational goals. Indeed, it is located in the bottom-right corner of the matrix with a score of 9 for Concern for production and a score of 1 for Concern for people. It emphasizes the relevance of the tasks over the people involved. This managerial style almost considers employees only a tool to achieve the objectives of the company. This approach is entirely goal-oriented and communication is limited to providing instructions to complete tasks. The main characteristics of this type of leader are authority and control[1] (p.141).
Country-Club Management (1,9)
This approach is completely the opposite of Authority-Compliance Management. It is located in the top-left corner of the matrix with the highest possible score for Concern for people and the lowest one for Concer for production. The main concern of the leader is the well-being of his followers over the achievement of organizational goals. The manager aims to create a good working environment with a friendly atmosphere where employees feel comfortable. The leader is usually eager to help, comforting, and uncontroversial and he tries to ensure that the social needs of the workers are always met[1] (p.141).
Impoverished Management (1,1)
This Management style is located in the bottom-left corner of the matrix and has the lowest possible score in both Concerns for production and people. The leader laks interest in both organizational goals and interpersonal relationships among the employees. The main characteristics are indifference, apathy, and almost no contact with the followers[1] (p.142).
Middle-of-the-Road Management (5,5)
The 5,5 style is located in the middle ground between concern for production and people and it is mainly based on the ability of the leader to compromise. The leader shows an intermediate concern for the people who perform the task and the task itself. This results in a style that, at the same time, pushes the production and shows attention towards the workers' needs. Leaders who belong to this group are usually conflict-avoiding, they prefer the middle-ground, and renounce their beliefs in the interest of the organizational progress[1] (p.142).
Team Management (9,9)
This type of management is located in the top-right corner of the matrix with the highest score in both concerns for people and production. The leader usually promoted teamwork and the goal is to create commitment in the workers to increase the level of their performance. This type of manager is often described as open-minded, determined, interested in their work, and good at stimulating the followers in participating in the activities. Organizations led by 9,9 leaders are characterized by an environment based on trust and respect[1] (p.142).
Additional Management Styles
The authors have identified two additional managerial styles that come from the incorporation of multiple aspects of the Leadership grid.
The Paternalism/Maternalism approach includes both 1,9 and 9,1 without being able of integrating them. This type of leader is usually defined as a "benevolent dictator" because he acts benevolently with the employees but with the only purpose of achieving organizational goals. The company is considered similar to a family and the manager, that is in a position of authority, is responsible to make decisions and punish or reward the followers[1] (p.143).
The last approach is called "Opportunism" because this type of manager is willing to adopt any kind of combination of the grid with the only purpose of obtaining personal advancement. The efforts of the leader are towards achieving his personal goals and he will shift and adapt his managerial style to achieve them. Some argue that these leaders are strategic and adaptable while others define them as ruthless and self-motivated[1] (p.144).
Applications
The Leadership Grid is a theory that belongs to the Behavioural approach. Theories that are part of this approach aim to define which are the main components of a manager's behavior rather than identifying the characteristics of a good leader. In other words, the grid is a good management tool if it is used by people in charge to understand their way of leading. Different situations require a different approach and leaders should be able to combine the two approaches. For example, followers might require a manager who is task-oriented and shows exactly how to proceed, or they could prefer a leader more relationship-oriented that mainly shows support to their activities. It is important to underline that the right way of leading a specific organization depends on the response of the employees to the two different approaches and a leader should be able to adapt in order to improve his management style[1] (p.145).
How to use the grid
In "The Managerial Grid III", the authors Blake and Mouton explain how to effectively use this tool. The aim of their work is to provide a guide that could help leaders improve their skills and strengthen their contribution to their company. They argue that, by using correctly the grid, leaders would get a better understanding of their way of working and, from this starting point, improve their performance[3] (p.1).
Blake and Mouton identified six fundamental components of leadership. These elements are initiative, inquiry, advocacy, conflict resolution, and critique. For each one of them, the authors defined six statements that represent the different managerial approaches described in the same work. To use efficiently this tool, leaders are asked to identify which statement better represents their approach in leading. This exercise should help them better understand their practice and the authors provide suggestions for improvements. All six components are analyzed in this section.
Identification of the Management style
As mentioned above, leaders are requested to identify which management style better suites their leading approach. The following section provides a brief description of the six components of leadership and the related statements provided by the writers to help managers in the identification of their style.
Initiative
Initiative is related to starting something that has been done before, stopping ongoing activities, or shifting the current direction[3] (p.2).
| A | I put out enough to get by |
|---|---|
| B | I initiate action the help and support others |
| C | I seek to maintain a steady pace |
| D | I drive myself and others |
| E | I stress loyalty and extend appreciation to those who support me |
| F | I exert much effort and on others to join in enthusiastically |
Inquiry
Inquiry is strictly related to the leader's thoroughness. Indeed, it is the ability to obtain information and data from people or other sources. Generally speaking, a leader might be more or less interested in learning as much as possible about the activities in his company[3] (p.2).
| A | I go along with facts, beliefs, and positions given to me. |
|---|---|
| B | I look for facts, beliefs and positions that suggest all is well. I don’t like challenging others. |
| C | I take things at face value but check facts, beliefs and positions, if critical. |
| D | I investigate facts, beliefs and positions, to control and so nobody makes mistakes. |
| E | I double-check what others say and verify their positions before complimenting. |
| F | I search for information and validate it. I am inviting and listen for others’ opinions and acknowledge them. |
Advocacy
Advocacy refers to taking a position and standing by it facing its risks. A leader that does not advocate is usually not sure about his position[3] (p.3).
| A | I respond if asked, but avoid taking sides by not revealing my opinions, attitudes or ideas. |
|---|---|
| B | Even having some reservations, I embrace opinions, attitudes and ideas of others. |
| C | I try to meet others halfway and express my opinions, attitudes and ideas. |
| D | I stand up for my opinions, attitudes and ideas, even if it means rejecting others. |
| E | I hold strong convictions but let others express ideas and help them to think objectively. |
| F | I tell my convictions and concerns but if others’ idea is sounder, I acknowledge it. |
Conflict resolution
Conflicts arise easily and managing them in the right way is not trivial. A good leader should be able to handle and resolve them while evoking respect. On the other hand, a manager that is unable to deal with conflicts could be perceived as not worthy of respect[3] (p.3).
| A | I seek to stay out of conflict by remaining neutral. |
|---|---|
| B | I avoid conflicts but if they appear, I keep people together by soothing feelings. |
| C | I try to find a reasonable position that others find suitable, when a conflict arises. |
| D | I try to cut off a conflict when it arises or try to win my position. |
| E | I terminate conflicts when they arise but thank people for expressing their mind. |
| F | I seek out reasons for conflicts, to resolve possible underlying causes of it. |
Decision making
Decision-making is a key ability for a leader. He might have to take solo decisions or he is required to delegate responsibilities while working with a team[3] (p.4).
| A | I let others make decisions. |
|---|---|
| B | I make decisions that maintain relations and encourage others to make decisions. |
| C | I search for decisions that others accept. |
| D | I am seldom influenced by others and I make my own decisions. |
| E | I make an effort so that my decisions are accepted, and I must have the final say. |
| F | I seek understanding and agreement of others, as I feel it is important to arrive at a sound decision. |
Critique
Critique is related to problem-solving activities. Indeed, a capable leader should be able to anticipate and avoid activities that risk having adverse consequences. This ability comes mainly from experience and feedback from other people in the organization. Both elements are key work more effectively[3] (p.4).
The following table is based on The Managerial Grid III[3]
| A | I avoid giving feedback. |
|---|---|
| B | I avoid giving negative feedback but give encouragement given an opportunity. |
| C | I give indirect feedback as a suggestion for improvement. |
| D | I pinpoint weakness to measure up. |
| E | I give others feedback and consider that it is for their best interest to accept it. |
| F | I encourage a two-way feedback in order to strengthen performance. |
As mentioned above, statements corresponding to the same letter refer to the same Management style. The following table is based on The Managerial Grid III[3] and summarizes these references.
| Statement | Style |
|---|---|
| A | 1,1 |
| B | 1,9 |
| C | 5,5 |
| D | 9,1 |
| E | Paternalism |
| F | 9,9 |
Suggestions for improvements
Blake and Mouton provide a detailed description of each one of the leadership styles and they are all completed by a list of suggestions for leaders to improve their practice. This section provides a summary of these advices that lead towards the Team management approach.
Leadership style (9,1)
Motivation: Utilize your subordinates as resources by involving them in problem-solving activities.
Initiative: Instead of taking immediate action every time you see a void try to invite others to take initiative.
Inquiry: Listen to ideas different from yours and take into account also the opinions of people you might dislike.
Advocacy: Encourage people to share their opinion and ask for feedback about yours.
Conflict: Suppressing differences does not prevent conflicts from arising. Listen to others' points of view and respect their opinions.
Decisions: Listen to people's opinions before announcing your decision and try to explain the rationale behind them.
Critique: Feedback should be a two-way street. Allow people to tell you what they think about your leadership, they might help you improve.
Leadership style (1,9)
Motivation: When you are polite and solicitous you might obscure the real issues and people might feel uneasy.
Initiative: Take initiative where you tend to back off, stop thinking "I had better not" and start thinking "I should".
Inquiry: Be more prepared before meetings to increase your confidence in expressing your point of view.
Advocacy: Try to be among the first to speak so that you do not allow others to influence you in deciding if you should express your opinion or not.
Conflict: Remember that conflict is inevitable. If others do not agree with you, restate your opinion and ask for further explanations.
Decisions: Do not postpone unpleasant decisions because the problems will not diminish, they are likely to increase.
Critique: Feedback does not have to be painful, people would probably be helpful.
Leadership style (1,1)
Motivation: Reevaluate the degree of your involvement, ask yourself if your job is a pleasant way of spending eight hours per day.
Initiative: If you are uninvolved, your subordinates would probably notice it. If they see your interest increasing they would probably encourage you.
Inquiry: Ask more questions to your subordinates to rebuild the necessary knowledge.
Advocacy: Ask straightforward questions and show where you stand with your opinion.
Conflict: Avoiding disagreement is not rewarding. Remember that people are usually willing to find a middle ground.
Decisions: Find a way to involve different subordinates in solving a problem by understanding how they could be helpful.
Critique: Ask for feedback about your performance and provide them with information about how you think things are going.
Leadership style (5,5)
Motivation: Reflect if your subordinates communicate what they truly believe in or just what they think you want to hear.
Initiative: When something needs to be done, do it without overreliance on traditions.
Inquiry: When you think you have enough information, ask additional questions to ensure you are well informed.
Advocacy: Express what you think without reshaping it to make it agreeable.
Conflict: It is ok disagreeing with others because from conflicts might arise innovation.
Decisions: Remember that there are some decisions that only you can take. Accept inputs from other people but the outcome needs to come from you.
Critique: Ask for feedback and remember that if the critique is negative it is even more valuable.
Limitations
The main limit of the Leadership grid, together with the behavioral approach, was the impossibility to identify a relationship between being a leader task or people-oriented and a higher level of performance or employees' morale.
Furthermore, the approach has failed in identifying a style of leadership that is universally recognized as suitable for all the different situations. The aim was to identify a set of managerial behaviors that would lead consistently to successful leadership. This goal has not been achieved and the behavioral approach failed in a similar way to the trait approach that tried to define the right personal characteristics to be an effective leader.
Some argue that this approach did not lead to consistent results because it failed in taking into account the impact of the context. They argue that the managerial style should be based on the requirements of every single team that needs to be led. This argument is partially based on the idea that a 'high-high' approach is not always the answer. The Leadership grid suggests as the best style is the Team Management that has the highest score in both concerns for people and production. However, different situations might require a different approach that does not have such a high score in both the concerns. It still remans unclear if the Team Management is actually the best style of leadership.
Bibliography
The following sources have been used as the main references for this article and they can be used for further readings.
- Northouse, P. G. (2018), Leadership: Theory and Practice (8th Edition), SAGE Publishing
- Robbins, S. P. and, Judge T. A. (2013), Organizational Behavior (15th Edition), Pearson Education
- Blake, R. and Mouton, J. (1985), "The Managerial Grid III: The Key to Leadership Excellence", Houston: Gulf Publishing Company.
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 Northouse, P. G. (2018), Leadership: Theory and Practice (8th Edition), SAGE Publishing
- ↑ Robbins, S. P. and, Judge T. A. (2013), Organizational Behavior (15th Edition), Pearson Education
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 Blake, R. and Mouton, J. (1985), "The Managerial Grid III: The Key to Leadership Excellence", Houston: Gulf Publishing Company.