Project Performance Management Scorecard
Abstract
With companies pushed to continuous improve in project management, process efficiency and performance management there is a need to provide processes that can give guides to project managers. The project performance management scorecard is used to increase a projects performance and give an overview of potential obstacles. The projects performance can be measured as the outcome of the different project. The project performance management scorecard incorporates theory from the Balanced scorecard with a slide adjustment, in order to make work with a project point of view. It also used parts from the Project life cycle theory to provide a process of the project life cycles phases. It can help project managers keep track of the complex inter-dependencies factors like project phases, stakeholders and "cause and-effect" inside the project. This paper will show how a strategics organizations tool as the balanced scorecard can be used, in combination with the project lie cycle theory and with a specially developed framework, can provide help to the project manager.
Theory
As the Project performance management scorecard is a combination of different tool as theory there is a need to explain them to fully understand the end idea.
Balanced Scorecard
The idea of developing the balanced scorecard came from, according to Robert Kaplan and David Norton[1], that it is impossible for organizations to effective measure efficiency with a narrow number of indicators. At the same time a organization shouldn't have a to large number and complex indicators as it will lead to a lack of overview and give a high possibility of indicators either being misused or not be used at all.
The Balanced Scorecard (BSC) is then used to help organizations put their cooperate strategy into some more comprehensive objects and Key Performance Indicators(KPI's). It will also help the organization avoid a short sighted perspective and loose focus on the long term view. It will provide companies a robust measurement and management system for them. The first edition consisted of fire elements:
- Financial
The focus here are the identification of financial measurement. Is the classic organisations measurement like cash flow, income, return and more like it.
- Customer
Here the organization must identify what is important for the customers and their needs. It could be quality, on time delivery or similar.
- Internal business process
A organization should also look at what do it what to excel at. It can the quality, cycle time or low price.
- Learning and Growth
This is the most qualitative part where organizations tries to look into the future on where they want to go.
3 elements have the most measurable indicators: Financial, Customer and Internal business. But and at the same time a more soft type of indicators in the ability to learn and Growth.
the first edition was build for a non-divisional organisation and was hard to implement in a more complex structured company as well as the public sector and a non-profit organisation. This lead to the tool quickly being abandoned by organisations [2]. The next generation gave a new measurement that was based on strategic objective that could be linked together as a cause and-effect chain. This is done be linking the different KPI's, in the different areas, together. A Concept used in the BSC is to define indicators as "lead" and "lack" indicators[3]. "Lag" indicators are the after event indicators like production, accident and more. They are useful for measuring the progress of a project in the company but can't be used to influence the future. The "Lead" indicators are useful in trying to change something or predict the future. It can be described as in-process and predictive indicators. The hard part of the lead indicators is to be able to determine them, as they try to say something about the future, as in comparison to the lag indicators that says something about the present. As the lead indicators tries to predict the future it leaves a chance of being wrong and it is hard to choose the right ones.
Adjusted Balanced Scorecard
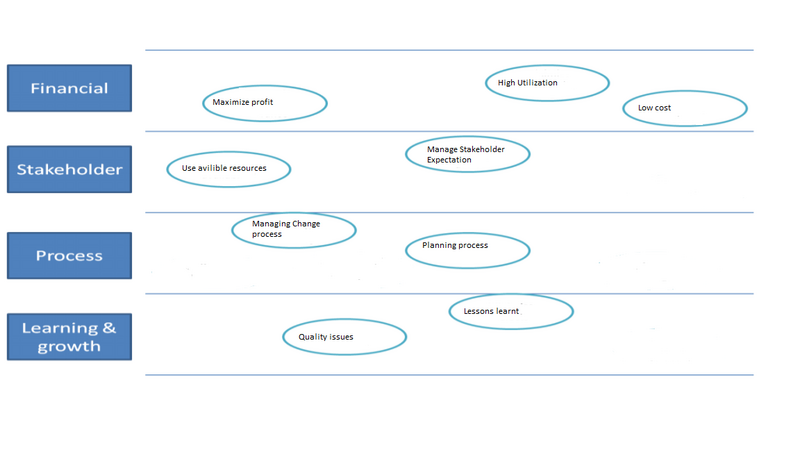
As mentioned in the previous section the BSC is a strategic organizational tool, in order to make the BSC more useful for Project perspective a change in view is needed. So instead looking at customers the Adjusted balanced Scorecard (ABSC)[4] will look at the stakeholders for the project. It will also use the 3 other aspect in a more project orientated view like financial being used as the projects cost. The new four key points are:
- Financial
- Stakeholders
- Internal Business
- Learning and Growth
To help go away from the strategic point of view with the "Lag" indicators being in focus, the "Lead" indicators will be used more, to give some warning signals and actions to help meet the strategy.
Project life cycle
The project life cycle[5] ,also know as the project management life cycle, is a tool that helps project managers narrow the focus, align objects and ensure the project finishing on time. The tool consists of the following steps:
- Initiation
During the first phase, called the initiation phase, the projects objectives are fund. It could be in the form of problem or opportunity statement. The right action to take, to fulfill the need, are planed as a business case. It consist of the appropriate solution to the given problems/opportunity. Each option is then considered to find the right solution to the issues at hand and are tested in feasibility and justification. Ones the best solution have been chosen, a project manager is appointed to initiate the project. Milestones and group members are fund and shaped into the project team that can solve the problem/opportunity. Then the project manager seeks approval, from the organization, to move the project into the next phase, the Planning phase.
- Planning
In this phase of the project the goal is to investigate in as much detail as possible. Find the necessary action required to meet the projects objective is identified and planned. It consistent of three main parts. The needed project task and resources is fund and steps is identified in order to meet them. This can also be called "scope management". Project plan is then created that contains the activities, tasks, dependencies and time frames of the project. With that part complete, the project manager must now identify the risk within the project. This part is also known as "risk management". Here the project manager must identify potential "high-treat" problems and what actions there must be taking in order to counteract them. It can be done by either lowering the risk of the problems ever happening or lower the impact it will have on the project itself. The stakeholders must also be identified and a plan to communicate with the different stakeholders is created. The stakeholder map is a good tool to use here. At the end a quality plan is made. Here the quality targets, control measurement and a list of customer requirement for the project in order for them to accept it. With all these parts done the project manager is now ready to move the project into the Execution phase.
- Execution
The execution phase or also known as the implementation phase, is where the project plan is put into action. The main idea here is for the project manager to monitor and adjust the project if it varies from the plan. Team meetings is a good way for a project manager to keep a finger on the pulse and be able to quickly adjust. If a project starts to deviate from the project plan, the project manager need to take action in order to move to project back on the right path. If that is not possible, the project team should record the change and modify the plan to fit the new path. Key stakeholders and project sponsors should be informed throughout the process. As the project moves along, each of the agreed milestone must be reviewed to check for quality and make sure the measurement meets to demands. With all the milestone complete and the customer having approved the solution, the project can move into the final phase of closing.
- Closure
The finale phase is the closure of the project. All products and documents must be handed over to the customer and communicated to all the different stakeholders. The last part is for the project manager to make a lessons-learned round in order to see what went well and not so well. This is to improve the process for future projects. This is both for the individual project manager but also to help the project organization improve for future projects.
Framework
To help ensure the success of using the framework a series of implementations steps are required. These steps are also used to enhance the learning process form the framework.
- Make the Project objectives and the link to Project life cycle(PLC) if possible.
- Establish the project management KPI's as defined as "Lag" indicators
- Develop KPI's and PLC objects for "Lead" indicators
- Use cause and effect when implementing the KPI's and specify the impact analysis framework
- Keep watch to improve the project management process
It can all in all be described as "Project performance management scorecard". It tries to achieve success by going after at set of objectives:
- Project strategy and objectives
- Project life cycle(PLC) objectives
- Project Management objectives
- Balanced Scorecard practices
Applications
Step 1: Make the Project objectives and the link to Project life cycle(PLC) if possible
Here the objective for the project must be stated. The list of object should be highlevel qualitavice statements but can be in some cases quatitanvie. After the list of object have been identifeid the project manager must find the key stakeholders using different tool. it could be stakeholder maps or other. then make the objects into more specifict KPI*s that can be used troughout the project phases.
A simple table is used to keep track of object and the indicators throughout the different phase of the project
| Objectives | Requirements gathering | Design and development | Phase |
|---|---|---|---|
| Objective n | List of indicators | Phase n |
note that not all objects are directly linked to a specific phase. To then to help identify the fish bone diagram could be used. It could be a enterprise resource planning system or ERP system. By just installing the system won't guarantee a result to the object of increase sales.
Step 2: Establish the project management KPI's as defined as "Lag" indicators
With the objects fund the "lag" indicators is identified and put into the ABSC model.
Then to make keep an overview of the "Lag" indicators and the target measurement a table is used:
| Project management knowledge areas | Objectives | Indicators | Target measurement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Risk | Minimize risk impact on the project | Monitor high risk problem | Don't exceed agreed number of high risk items during the project time |
| Cost | lower cost overrun | Consumer price index (CPI) | Don't let the CPI get over 1.10 during project life cycle |
| Area n | Objective | List of indicators | Measures |
Step 3: Develop KPI's and PLC objects for "Lead" indicators
Here the main oint to identify the "lead" indicators in the project. the targets and who has the resposibillity of makeing these targets. The three point can be seen as a series of steps done by the Project Manager with the team members of the project and key stakeholds.
Step 3.1: Identify the different indicators
The team must now find the different performance "Lead" indicators that will be usefull in the project. It could be view from a project life cycle point of view as the "Requirments gathering" phase.
Step 3.2: Set targets for mesauring
As the indicators are fund there is a need to make targets for the indicators for measuring the success.
Step 3.3: Assign responsibilities
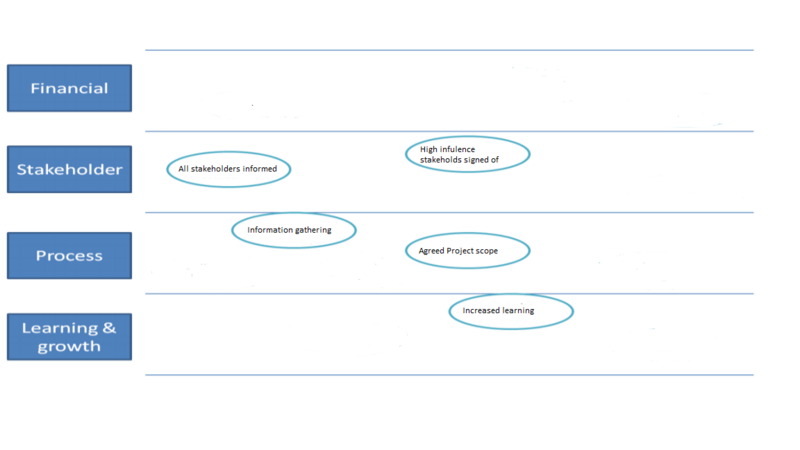
for each of the different target a team member must be assigned. This team member then have the responsibility of keeping track of the performance and monitor the progress. This is especially important during the implementation/execution phase as there is a need of monitor the progress status. To give and overview of theses 3 step the "Lead" indicators, target and the responsibilities is combine in a table:
| Project Phase | Indicators | Target measurement | Responsibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Execution phase | All stakeholders informed | 100% informed | Project manager |
| High influence stakeholders sign off on project process | 100% Papers signed | Project manager | |
| Phase n | List of indicators | Measures | Responsibility owner |
Step 3.4: Add the "Lead" indicators in ABSC
With the "Lead" indicators identified it can now be put into the ABSC. this is done to later create the cause and-effect properties.
Step 4:Use cause and effect when implementing the KPI's and specify the impact analysis framework
Now the project manager must identify the cause and effect between the two indicators.
Step 4.1: Combine
With the "Lead" and "Lag" indicators identified in the previous steps it should now be combined into a single ABSC.
Step 4.2: identify Cause and effect
The project manager must now take one indicator at the time and see what cause and effect it will have one the other indicators and there measurement done previous.
Step 4.3: High impact, High risk
Different "Lead" indicators have different important. a way to see which are the most important is to make a diagram with high-low impact on one axis and high-low risk on the other. When the most high risk high indicators(cause) have been fund the "Lag" indicators that will be impacted(effect) must be fund as well. This leads back to the object that therefore also will be impacted. summarized in this table:
| "Lead" indicators(cause) | Impacted "Lag" indicators(effect) | Impacted objects |
|---|---|---|
| On time high influence Stakeholder sign off | Time overrun | Need to make change move the time schedule |
| Cause | Effect | Objects |
Step 5: Keep watch to improve the project management process
Now the whole process is complete and the project manager can use the ABSC to keep track of the projects performance. Here it is important the the Project manager plans project review meetings to make sure he/she gets the right status of the project to monitor possible problems.
This process helps the project manager identify key projects measurement and KPI's and the link between them. With this a projects chance of succeeding will increase and keep track of stakeholders and their interest in the project.
Limitations
This Framework is new and not very wildly used so there is a leak of test and understanding. This leads to uncertainty as there not experience in the field. It also tries to use the balanced scorecard that as mentioned earlier is a strategic tool and use it as a project tool where it wasn't designed to use. Some problems with this process is linked to the "Lead" indicators as the determination of these are critical and hard to get right. If the wrong "Lead" indicators are chosen a project manager will loose focus on potentially problems for the project.
Annotated Bibliography
References
- ↑ [Conceptual Foundations of the Balanced Scorecard] http://www.hbs.edu/faculty/Publication%20Files/10-074.pdf
- ↑ [Balanced Scorecard] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Balanced_scorecard
- ↑ [Lead and lag indicators ] https://www.intrafocus.com/lead-and-lag-indicators/
- ↑ [Project performance mangement using balanced scorecard(BSC) approach] http://sarasconsulting.com/downloadfiles/Manage%20project%20performance%20using%20balanced%20scorecard.pdf
- ↑ [Project life cycle phases] https://opentextbc.ca/projectmanagement/chapter/chapter-3-the-project-life-cycle-phases-project-management/