Dealing with conflict in project management
Contents |
Abstract
It is of interest for the project manager to deliver a high-quality result on time and on budget. No projects are executed without conflicts and they have the potential to derail a project completely if ignored or improperly managed e.g. via loss of profit, time, quality, creativity or morale. On the other hand, proper conflict management can lead to positive change such as improved respect and understanding for one another. The competent project manager should therefore possess knowledge that allows him or her to identify and classify a conflict, resolve a conflict, and design a working environment that minimizes the risk of conflicts occurring. A conflict is spawned from multiple variables such as interpersonal relations, stress, or the difficulty of the task at hand. As a consequence of the complexity, no best practice exists. A strategy for resolving conflict may be applicable in one scenario, but useless or even damaging in another. The project manager must be able to analyze the situation and chose the correct approach to conflict management based on the information he or she has available. In doing so, a fundamental understanding of human psychology and cultural differences is a plus cf. cross-cultural management.
Definition
Conflict is a state of discord caused by the actual or perceived opposition of needs, values and interests. Conflict as a concept can help explain many aspects of social life and social death such as social disagreement, conflicts of interests, and fight between individuals, groups, or organizations. A conflict can be internal (within oneself) or external (between two or more individuals). Without proper social arrangement or resolution, conflicts in social settings can result in stress or tension among stakeholders.[1]
Looking from a project management perspective, conflicts can be internal e.g. interpersonal conflicts or between groups e.g. if two project groups both claim utilization of scarce resources. This article focuses on the former example, as that is a more typical scenario for the project manager. The latter dispute will often move upwards the organizational hierarchy.[2] When dealing with the latter type of conflict, Pondy’s Model of Organizational Conflict provides a framework for assessing and acting accordingly to the type of conflict.[3]
Why focus on conflicts?
In short, one should manage conflicts to avoid its negative influence and to ensure its positive effects. Project members, including the project manager, might be tempted to shy away from conflict in the fear of dissociation, being wrong, hostility, breaking up interpersonal relationships, etc.[4] This is ill-advised as conflicts that are not resolved tend to snowball or escalate cf. the conflict stages below. This means that the sooner the problem is addressed, the better. Table 1 shows what a project manager might experience if a conflict is looming, and what can be gained from properly solving the conflict:[4]
| Signs of conflict looming | Advantages of conflict resolution |
|---|---|
| Productivity drops off | Intimacy |
| Quality deteriorates | Respect and understanding |
| Sick leave increases | Appreciation |
| Employees quit | A better working environment |
| Bad mood | Positive example for future reference |
| Unease and irritation in the work place | Others realize that you are right |
| Sleep deprivation among the employees | Time and energy |
Reasons for conflicts occuring
Conflicts are the product of countless variables. A seemingly insignificant event will affect the mood and behavior of people on a subconscious level. For instance, teachers grading papers have been shown to give statistical significantly higher grades immediately after eating lunch, as they happen to be in a better mood. Similarly, this is why a formula for the birth of conflicts does not exist. There at too many factors. Even though it is impossible to articulate the reason for a conflict prior to its occurrence, some areas tend to spew more conflicts than others. By knowing and understanding these areas, the project manager can identify and thereby solve conflicts faster. Studies have shown the following points to lead to the most conflicts: [5]
- Unresolved disagreement that escalated to an emotional level
- Poor organizational structure
- Personality clashes / differences in values and goals
- Poor communication / miscommunication
- Lack of cordial relationships between labor and management.
The project manager should be particularly alert regarding the potential for conflict if the project work starts venturing into these areas.
Dimensions of conflict
Conflicts in a project-setting can be divided into one of four basic dimensions.[6] It is noteworthy that in a real-life setting, a conflict can easily be the sum of different dimensions. Nonetheless, it is valuable to understand the different dimensions, as they have different levels of severity and should be tackled in different manners.
- Instrumental dimensions
- Dimensions of interest
- Dimensions of value
- Personal dimensions
Instrumental dimensions occur when disagreeing about objective and methods i.e. what should be done, and how should it be done? Here, parties might disagree and must come up with a solution. These conflicts often occur and can lead to creative decision making. Due to their normality, they rarely lead to animosity. The approach to this type of conflict is problem solving with the purpose of finding a solution.
Dimensions of interest occur when competing for resources. This can happen between project teams e.g. competing for machinery or internally in a project team e.g. competing for space in the project room. The approach to this conflict should be negotiation to come up with an agreement that settles the dispute.
Dimensions of value occur when values of the parties are at stake, which the parties are willing to stand up for. Examples include religion or political belief. This type of conflict is seldom related to the project and has a high potential for creating emotional response and a negative impact on the project. As we cannot negotiate our beliefs, dialogue with the purpose of mutual understanding is the goal here.
The personal dimension is the type of conflict that hits the involved people the hardest and has the most potential for disrupting the project-work. Again, dialogue and mutual understanding is the end-goal here to create a better and healthier atmosphere.
Conflict stages
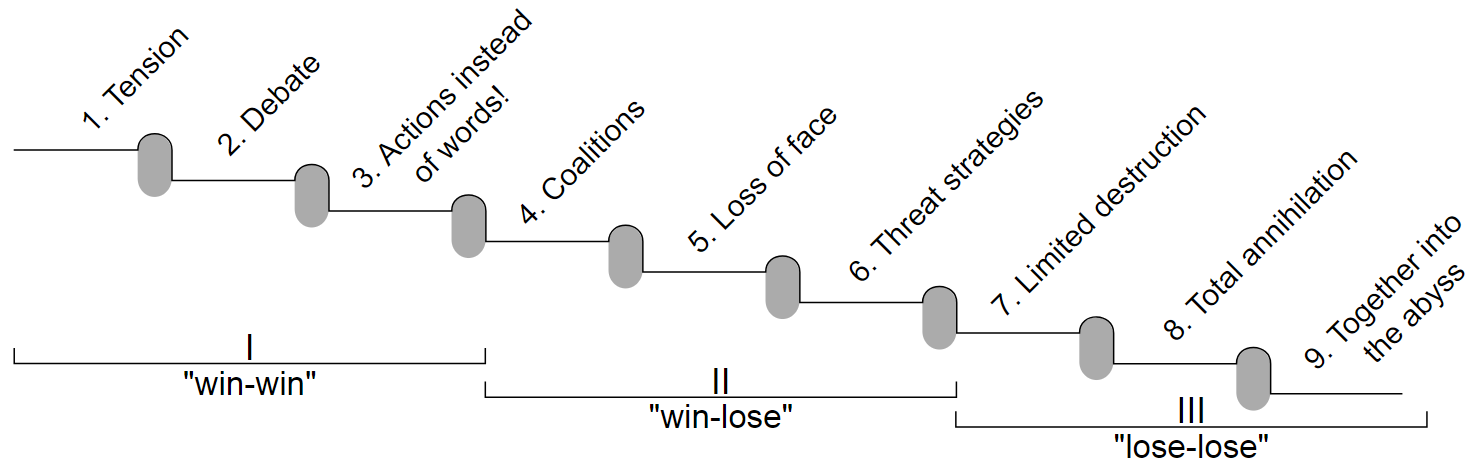
Recall that conflict can lead to positive change if managed correctly. It is very much a case of identifying and dealing with the conflict in an early stage. In doing so, the conflict escalation model can be applied. The model, developed by Australian conflict expert Friedrich Glasl, states that all conflicts will move through some general steps, each with its own dynamics, figure 1:
A brief explanation of the stages are:
Stage 1: Tension: Tensions exist. It can be any of the four dimensions of conflict. Tensions often occurs and may perhaps not even be noticed.
Stage 2: Debate: A debate occurs, where one party tries convincing another party that his or her take on the subject is correct.
Stage 3: Actions instead of words: Pressure rises without resolving the conflict, which manifests to actions. Such actions could be starting to ignore each other or talking badly about the other party.
Stage 4: Coalitions: One party starts looking for sympathizers, that share his or her position, in order to win the conflict. The argument starts expanding from the initial subject of the dispute. From here on, the major interest is that the opponent loses.
Stage 5: Loss of face The desire for winning starts erasing the moral principles of the actors. The thought of the opponent losing face is attractive.
Stage 6: Threat strategies The actors try to establish control of the situation by threatening the opponent with various demands. Typically, these ultimatums have the opposite effect.
Stage 7: Limited destruction The opponents sensitively try harming each other. From here on, the party disregards the damage that their own actions infect upon them.
Stage 8: Total annihalation The actions are now more destructive and the severity increases. The actors can no longer stop or control the escalation.
Stage 9: Together into the abyss One continues to attack the opponent, knowing that it also causes the destruction of him or herself.
The three classes win-win, win-lose, and lose-lose represent the acceptable outcome of the conflict through the eyes of the person amidst the conflict. That is, in the first stage the actor wants to come to a solution that satisfies all parts. In the second stage, it is not only about winning; it is also about the other party losing. In the third stage, the individual is willing to sacrifice himself to see the opponent lose. A project manager's level of involvement and decisiveness should increase as a conflict progresses through the stages. A conflict moves from potentially yielding a positive outcome, to leading to a negative outcome when the parties move from win-win to win-lose.
If a conflict is in stage 2 and a project manager chooses to force a decision to stop the conflict, he or she removes the chance of reaping the benefits of proper conflict solution. Further, the project team might be frustrated that they are being monitored and limited. Oppositely, if a conflict is in stage 7, and a project manager chooses to avoid or accommodate the conflict, the PM becomes a hostage of the conflict and can only watch as the project deteriorates.
Conflict management styles
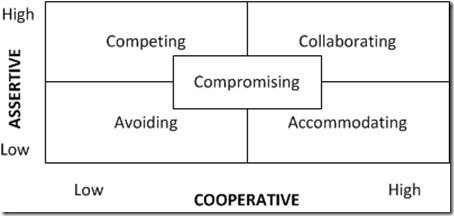
Whenever a conflict is looming in a project, the project manager is faced with a choice regarding how to address the conflict. To illustrate this dynamic, the Conflict Mode Instrument developed by Kenneth W. Thomas and Ralph H. Kilmann can be applied. A good project manager must understand in what instances the different styles are applicable.[7]
The cooperative axis speaks addresses to what extent the other party’s goal is achieved, while the assertive axis states whether one’s individual goals are achieved. The table below[4] highlights some scenarios where the different styles of management can be used, and some scenarios where the project manager should steer clear of them.
| Conflict style inventories | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Forcing/competing | When decisive action is needed
When unpopular and determined actions must be taken |
May destroy inter-personal relations when fulfilling own goals on
someone else’s account |
| Collaborating | When important decisions with long-term effects are to be taken | Often time-consuming, thus not suitable for trivial problems |
| Compromising | Good if pressed for time | May lead to two somewhat discontented parties |
| Avoiding | Postpone a conflict until emotions have cooled off.
When dealing with trivial problems and more important issues should have priority |
The conflict is not resolved |
| Accomodating | When collaboration is more important than the reason for conflict.
When the problem is more important for the other part |
Accommodation may deprive respect.
When important issues are at stake |
Relating to Friedrich Glasl and his conflict stages, one must understand that the cooperativeness falls and assertiveness rises, whenever a conflict is escalating to a stage, where it has profound negative impact on the project.
Conflict resolution
Additionally than knowing
Monitoring Meidating Convicting
Minimizing conflict as the project manager
Recall that it is impossible to avoid conflicts altogether in any project-setting. However, it is possible for the project manager to minimize the risk of severe conflicts occurring. A common cause of conflict is dissatisfaction with the organizational structure from the workers point of view[5]. Even though it is not something that the project manager may decide, he or she should still identify its potential for issues.
If a company applies a matrix organizational structure, employees become so-called two-boss employees, as they answer both to the functional manager and product team manager.[2] This structure can lead to a dimensions of interest conflict, where different managers compete for claiming resources and attention to their projects. Ideally, this type of conflict is solved in a logical manner via tools such as critical path analysis and multi-project resource scheduling. If a settlement cannot be made, support from higher-level management can be called upon[8].
The project plan is drafted to provide structure and to create an overview of a given project. A detailed and accurate project plan creates the basis for constructive communication in the project-setting. This can prevent conflicts occurring in relation to the scope of the project and who is in charge of a task. Moreover, a realistic project plan has a feasible time and resource allocation for the team. By not stressing the team, the team members will be more in control of their feelings and the way that they communicate. (RELATE TO e.g PERT)
Conflicts spawning from dimensions of value can also be controlled by defining team ground rules and group norms before the conflicts happen.
Chairman portion in text.
//Relate to WBS //Relate to CCM //Relate the 5 styles to the PM book 9.4
An example with three conflict scenarios and corresponding actions from the project manager is shown:
References
- ↑ Definition of ”conflict”, Merriam-Webster’s Collegiate Dictionary, 11th
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Jones, Gareth. 7th, 2013. Organizational Theory, Design, and Change, p.301 (Pearson).
- ↑ Jones, Gareth. 7th, 2013. Organizational Theory, Design, and Change, p.417 (Pearson)
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Tonnquist, Bo. 1st, 2008. Project management, chapter 10 (Bonniers)
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Ajibolays, Y, 2017. Conflict Management in Projects, [Online], p5. Available at: http://ieeexplore.ieee.org.proxy.findit.dtu.dk/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=8095588&tag=1 [Accessed 8 February 2018].
- ↑ Spiess, Wolfgang. 1st, 2008. Conflict Prevention in Project Management, p.48 (Springer).
- ↑ Project Management Institute, 5th, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (Project management institute).
- ↑ Lock, Dennis. 9th, 2007. Poject management p. 136 (Gower).