User-Centered Design
Developed by Cetin Arslan
Contents |
Abstract
As technology and services advance and become more deeply integrated in the daily live of their customers and therefore human lives, the different development processes and projects need to ensure that the offered solutions become more intuitive and user-friendly in order to secure customer satisfaction and stable sales. While taking a closer look on classical development models e.g. Waterfall model, it is clear that during the different project stages the focus of the project managers are only project related and mostly not viewed from an end customer perspective, which can cause usage and understanding problems[1][2].
The User-Centered Design Approach takes these problems into consideration. The goal is to design understandable and enjoyable solutions for the end customers, while either taking their personal opinions into account or lead the project from an end customer optimized view. Therefore the different processes must be lead towards a user's needs, abilities and expectations in order to guarantee a maximized customer focus. The UCD process consists of five steps, of which the last 4 are following a interative logic. Furthermore, the UCD is defined in the DIN EN ISO 9241-210 "Human-centred design for interactive systems " standard[3].
Big idea
The UCD concept was first mentioned by Donald Norman in his publication "User-Centered System Design: New Perspectives on Human-Computer Interaction" in 1986 and further discussed in his book "The Design of Everyday Things"[4] [5]. Norman shows the importance of a users need in a product and the mistakes caused by unappropriate designs, which aren't user focused and don't take these into account. Therefore he gives recommendations based on the users needs and wishes.
In order to reach a high level of usability the following principles must be followed as defined by Gould and Lewis in 1985[1].
- Iterative proceeding
- Early focus on user and task requirements
- empirical review of the designs by users
Besides the classic usage of the UCD in its origin area the software development, a project manager can use the UCD as method to design and produce several products, goods and services. The UCD shows characteristics of iterative and incremental life cycles as discussed by the Project Management Institute[2]. Further the UCD process can be connected to ISO 21500 "DIN ISO 21500:2016-02"[6]. The five process groups described in ISO 21500 namely " Initiating, Planning, Implementing, Controlling and Closing" can be seen as the typical tasks which are necessary to be done during the implementation of the UCD process according to DIN EN ISO 9241-210 "Human-centred design for interactive systems" as described in the following chapter [3].
Application: The User-Centered Design Process
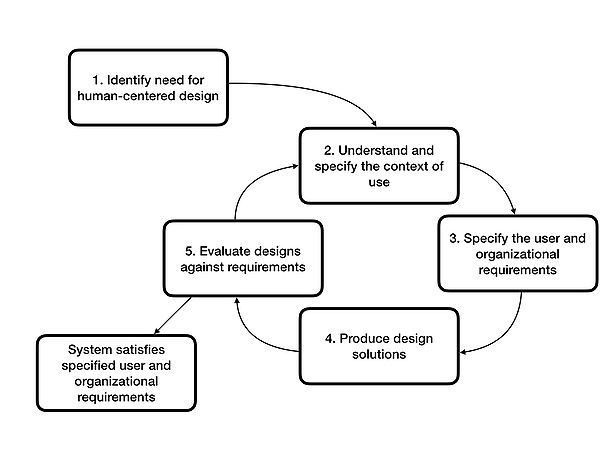
Having a closer look at classic development models shows that the focus of development does not respect the needs of the end users.[2] As technologies advance and become more deeply integrated into human lifes, products or services must become more intuitive and user-friendly. Therefore, the goal is to design easy-to-learn and easy-to-use products that provide the user with an optimal interface and an enjoyable user experience. For this, the development process or project must be geared towards the users and their needs, abilities and expectations must be taken into account[7]. These criteria are fulfilled by the User Centered Design approach. Through the usage of the UCD developments of a wide range of products and services are conceivable. Principles of the approach are an iterative proceeding, an early focus on user and organizational requirements and the empirical verification of users' designs[1]. As mentioned before the UCD process is presented in the standard DIN EN ISO 9241-210: 2011 " Human-centred design for interactive systems"[3]. Since the development of a human-friendly product is in the foreground, the term "human-centered design" is used. The procedure with five distinct phases essentially characterizes the process, whose phases are shown in Figure 1.
The user-centered design (UCD) design process for interactive systems according to ISO consists of five steps, of which the steps two through five are iterative. Since UCD can also be used to manage projects besides the development of interactive systems, the five phases according to ISO can be used by project managers of every kind. The following is a detailed description of the procedure:
Step 1: Identify need for human-centered design
UCD activities should play a central role as a guiding principle in all areas of project or product development. An involvement of all project members is important in order to avoid conflicts and to achieve an integration into all previous processes. A first meeting of all persons involved in the development represents the start of the UCD process. During this meeting general questions about the use of the product or the service should be answered.
Step 2: Understand and specify the context of use
The understanding and definition of the context of use is a central point in the UCD. Collecting information about the future users, their wishes and needs must be essential[8]. In order to get to know the potential users, the use of an audience analysis is conceivable. This should result in a concrete distinction between different target groups from the mass of all users. Different attributes help during the division into different groups. These may be demographic characteristics, such as age or gender, socioeconomic as well as education and occupation and psychological characteristics and attitudes and values. The data can be used as a first source for creating personas. The execution of a task analysis is conceivable as the next step[8]. Here, the tasks that are important for the achievement of the objectives are broken down into small sub-steps and the sequence of orders and their execution conditions are analyzed[8]. In this case, the results may represented in a hierarchy of goals up to the smallest steps required to solve the request. Last but not least, the analysis of the work or application environment may be an option. Many systems are exposed to very different environmental conditions, e.g. large temperature differences. In the environmental analysis, it is important to record all significant environmental influences, thus a system can be designed that works flawlessly under all expected environmental influences.
Step 3: Specify the user and organizational requirements
The determination of the usage requirements and thus the development of requirements for the use of the product or the service refer to the requirements of the users including the usage context defined in the previous step. In terms of content, these refer to the requirements of the users and thus exceed the descriptions of purely functional aspects[8]. Realistic use cases or scenarios help to integrate the personas into lifelike user experiences, whereby the involvement of personas in them realistically describes how to perform a specific task and what motivates the user to perform a task.
Step 4: Produce design solutions
Following the elaboration of the context of use and the user requirements, first solutions of the future product will be developed during this step[8]. These are realized in different prototypes for visualization but also for evaluation. At the beginning, cost-effective and low-effort prototypes are presented to the customer, such as paper prototypes or simple forms on a screen. Customer wishes can be implemented quickly and easily. As development progresses, the prototypes become more and more complex and similar to the final product. Functionalities and structure of the product approach the final version and thus implement findings from previous versions.
Step 5: Evaluate designs against requirements
In order to optimally integrate the wishes and needs of the customers into the process, prototypes should be tested and evaluated by them early on. Evaluation in development is one of the key points of the UCD process[8]. At the outset, it is conceivable to carry out an expert evaluation, whereby a trained expert, who as yet has had as little involvement as possible in the previous development steps, evaluates the system from the point of view of a persona and documents problems that occur in the design solutions. A controlled testing with people from the targeted user group represent the standard of development, Once the design solution meets all user requirements, the process is completed and the product or service is fully developed.
Analysis Tools
There are several tools which can be used during a UCD project to optimize the outcomes and goals. All of them try to help the project team to slip into the role of an user and understand its needs and wishes regarding a product. In the following three important tools are described, while still a lot of tools e.g. scenarios, use cases etc. could be mentioned.
Personas
After a closer look at the UCD method, it is obvious that it is suitable for organizing a customer-oriented development. In the worst case of a development, companies rely on their own experiences when developing new products or services. Thus, these products and services would be developed for already known users. Alternatively, the selection of target groups from a variety of data, which are based on fact-based data in the format "age", "income" or "marital status" are an option.[9]. A grouping of these data which is understandable for all employees is often difficult, as the implementation into projects are another difficulty and aggravate the communication in a project team. In addition, different images of the respective target group and its needs and wishes arise. Persona development is an interesting option to analyze and exploit these needs of the end user or target group during the usage of the UCD.
The so-called personas represent archetypically users of products or services that address a specific target group and their needs, interests and wishes. These are based on analysis, testing and observations, or are developed from existing information to influence decisions for a particular process or long-term decisions from the customer's perspective[9]. In addition, they help companies to understand, describe and identify functionalities of their target groups and to optimize processes and products of the company in a customer-oriented manner[9]. The founder of the Persona method was Allen Cooper in the early 1980s[10]. Long loading times and confusing user interfaces disrupted his everyday life decisively.
Through the use of fictional characters, which reflected the needs of future users, it was possible for him to empathize with the user. With this method Cooper developed some software for which he designed personas for each user group. For the time being, he gave personas only a name and a goal, which the user wanted to achieve with the use of a software program. In 1998 he published the book "The inmates are running the asylum", in which he presented his persona method to the world public[10]. At the present time, the Persona method is not only used in software development, but also in other disciplines such as computer science or marketing and sales.
The descriptions of the properties of personas are usually very similar in contemporary literature, but sometimes differ in the details. Goodwin's description, however, captures many similarities and will be explained in more detail below. Figure 2 shows a persona from Kim Goodwin's book "Designing for the Digital Age"[11].
One of the most important elements of a persona is its name. Each persona should have a realistic first and last name, as this increases the authenticity of the persona and thus increases its value at the same time[11]. Using an authentic photo increases this value even more. Names of people known by the team should not be used as they could otherwise create strong associations to known people. The persona should, if possible, include a description of abilities, as well as information about technical know-how. Further the training background is helpful in planning the future use of a product or service[11]. The description of feelings, attitudes and expectations helps to empathize even deeper into the persona. The question which activities provide joy and which are particularly tedious is experienced by the development team. In order to further increase the relation to reality, the use of demographic characteristics from field research is recommended. The persona's behavior in certain situations, general frustrations and problems of the represented user group and descriptions of the usage environment complete the desired properties. In particular, the usage environment can be of great importance, as it can be important to understand the context of product usage. Finally, it should be mentioned whether the persona interacts with other personas, products, and services, and how they involve the tasks of the persona. In addition, relationships and interactions with other personas can be linked and recorded, if they influence the usage behavior.
Customer Journey Mapping
The Toolbox's second tool is Customer Journey Mapping, or CJM in short. A customer who buys a service or a product of a company usually has several so-called contacts with areas and employees of a company that influence his or her perception. To increase customer satisfaction and build long-term customer relationships at the same time, this approach seeks to make a customer's "journey" as comfortable and hassle-free as possible[12]. CJM enables a project team to recognize, track and describe various customer experiences that arise when using the product and thus describe the central aspects that form the basis for customer satisfaction[13]. By deriving measures from the acquired knowledge conclusions can be drawn on the composition of the own portfolio and these can be adjusted to the customer. In this case, the customer's journey can be described by the use of one or more Personas, which are particularly useful because they not only represent a whole audience. Additionally Personas allow the emotional attachment of the project team to an users wishes and needs, what makes the implementation easier than purely fictional characters.
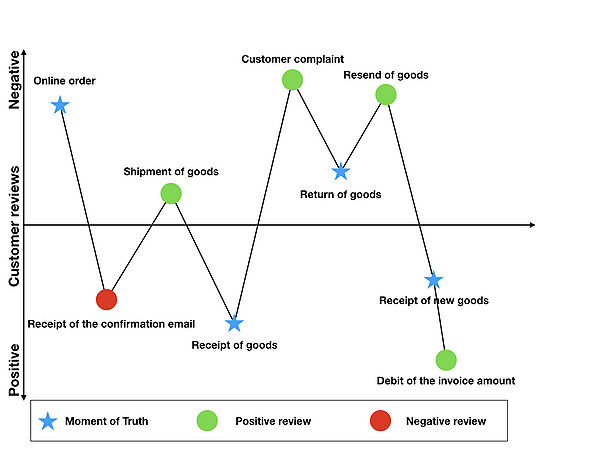
The first step of a CJM development is the definition and focus on the customer group. Here, the Personas are used and represent the most important customer group[14]. In the second step, it is important to identify and document the various points of contact of the selected personas with the company. Here is to think of all points of contact, which may come into question. This also includes all points of contact before the purchase, but also all during the purchase and afterwards occurring. In order to avoid a confusing and thus unusable CJ map, the third step is to focus on the so-called Moments of Truth. The Moments of Truth method describes the most important or insignificant contacts to the company from the customer's point of view with a simple point scale of one to five. The most important contacts for the customer are rated one, whereas the less important contacts are rated five. Consequently, in order to prioritize the points of contact, a focus is placed on the points with a rating of one to three[14]. Subsequently, in the fourth step, an overview of the departments and persons with whom the customer comes into contact during the course of the CJM is provided. In addition, the documentation of possible internal problems, which could influence the customer satisfaction, is suitable. In the fifth step, CJM, the evaluation of the individual points of contact along the customer journey is to be assessed from the customer's point of view. On an scale of one to ten, an objective assessment will be made, which may be based on analyzes and figures. If none of these are available, surveys of employees involved in the touchpoints or customer surveys are also useful. The number ten describes exceeded expectations, whereas the number one represents the opposite of these. The central step of the method is the graphical representation of the customer journey. This step can be implemented in different variations, but most solutions have a similar structure. The Y-axis of the graph shows customer satisfaction, whereas the X-axis describes the duration of the trip. An example presentation might look like Figure 3.
With the creation of the CJ Map the process is almost finished. It is now necessary to analyze the knowledge gained and to develop concrete suggestions for improvement and to optimize processes. Changes can be made internally, e.g. by extending the authority of employees, or externally, e.g. through the optimization of advertising content. After a pre-defined period, the effectiveness of the strategies should be evaluated and reviewed. This can happen on the one hand by comparison with the values before a conversion, but on the other hand also by internal employee surveys.
Jobs-to-be-done
The idea of the job-to-be-done approach goes back to Ted Levitt's statement that customers do not want to buy a drill, but a hole in the wall[15]. Christensen, who developed the method to detect customer expectations, says that customers "hired" a product to do a job[16]. This is to show that a customer acquires the benefit of a product and not the product itself, but also the situational context of a use plays a crucial role. Therefore, this method is particularly useful in the context of the UCD and the use of personas to observe customer actions and understand their goals[17]. A simple example is the optimization attempt of a fast-food manufacturer, who wanted to optimize his milkshake offer with the Jobs-to-be-done method, as classic analyzes could not succeed[18]. Customer behavior was analyzed with the question "For which job are my products hired?" As a result of this research, the company found that the majority of Milkshake shoppers consisted of two groups, the first being the product as a pastime for a longer journey to work, and parents who bought the product as a dessert for their children. Based on this knowledge, the product range could be optimized according to the needs and wishes of both groups. On the one hand the offering of thicker straws and the thinning of the shake to achieve a faster consumption of the children to reach on the other hand, the offer of milkshake varieties with small pieces to the pastime of the first group[18]. Another advantage of jobs is their solution neutrality, whereas the tools used for their realization are subject to technological change.
Limitations of User Centered Design
The UCD process described above may seem easy to follow, however it is difficult to implement, while offering certain advantages e.g. a higher user satisfaction or less service costs and hours due to adaption to user abilities. Besides that some prominent problems for project managers are mentioned below:
- Higher development costs: As a lot of data are the basis for the UCD process, the research which is needed in forehand can cause budget problems for project managers. Not only interviews but also market research, working with an external consulting partner or simply the detailed use of the tools described previously can blow up a budget. Further as the process is iterative, too many circles in the several phases can cause high development costs.
- Time consuming development : As not only the costs are affected directly by too many circles in the process, also the development time needs to be considered by project managers. Delays caused by not satisfied user needs and the wish the deliver a 100% perfect product can cause problems with the set schedule of development. Further the different interactions which are needed in order to gain useful data are time consuming, as also the meetings that are needed to discuss the different results.
- No guarantee that a user sample will fit into the real world: In the end there is no guarantee that a project, which is developed under UCD rules will produce a perfect product. The aim is still to deliver a highselling product which satisfies the customers needs, abilities and wishes. There are still high risks that the market will not approved the developed solution although it fits into the preferences of several user groups. History has shown that also products which where not designed under UCD rules, still where successful on the markets and "teached" the users themselves how to use them properly.
Annotated Bibliography
Cooper, A., The Inmates Are Running the Asylum: Why High Tech Products Drive Us Crazy and How to Restore the Sanity: Revised and Expanded Edition, Sams Publishing, 1998: In the book the author describes current software development behaviors and which problems occur by not focus on the endusers. Further it elaborates the importance of focusing on the needs of users and how to address these in the different development and design stages.
Donald A. Norman, User-Centered System Design: New Perspectives on Human-Computer Interaction, CRC Press, 1986: The book introduces the User Centered Design approach to the worldwide audience and explains how the people focused approach can help programers to develop software for customer needs, abilities and wishes.
Donald A. Norman, The Design of Everyday Things: Revised and Expanded Edition, Basic Books, 2013: The book is a continuation of the book "User-Centered System Design". It contains personal experience from the author Donald Norman, who gives examples from his working experiences at different multinational companies e.g. BMW or Apple in which he observed the importance of user focused development processes and projects. Further he describes how humans see and understand their (working) environment and works out how these insights can be used to optimize design processes.
Goodwin, K., Designing for the Digital Age: How to Create Human-Centered Products and Services, John Wiley & Sons, 2009: The book provides tools, guides and references for human-centered projects. It contains a great collection of information regarding the complex UCD (HCD) approach which a clear and easy understandable language. As the book is not using the common complex language, the book can be read by any level of project managers.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Gould, J. D. & Lewis, C. Designing for Usability: Key Principles and What Designers Think, "https://www.research.ibm.com/compsci/spotlight/hci/p300-gould.pdf",(Accessed on 28th of February
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Project Management Institute, A Guide to Project Management Body of Knowledge, (Project Management Institute, 2013),
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Human-centred design for interactive systems, "https://www.beuth.de/en/standard/din-en-iso-9241-210/135399380",(Accessed on 28th of February)
- ↑ Norman D. A. User-Centered System Design: New Perspectives on Human-Computer Interaction, (CRC Press, 1986)
- ↑ Norman D. A. The Design of Everyday Things: Revised and Expanded Edition, (Basic Books, 2013)
- ↑ Guidance on project management, https://www.beuth.de/en/standard/din-iso-21500/207461260 , (Accessed on 28th of February),
- ↑ Beier, M. Usability,(Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2002)
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 8.5 Fischer, T., & Postert, D. USER-CENTERED DESIGN, "http://www.mittelstand-digital.de/MD/Redaktion/DE/PDF/user-centered-design,property=pdf,bereich=md,sprache=de,rwb=true.pdf",(Accessed on 28th of February)
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Zeidler, S. In 6 Schritten zur eigenen Persona, "https://www.gruenderszene.de/operations/persona-personas-entwickeln",(Accessed on 28th of February)
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Cooper, A. The Inmates Are Running the Asylum: Why High Tech Products Drive Us Crazy and How to Restore the Sanity, (Sams Publishing,1998)
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 Goodwin, K. Designing for the Digital Age: How to Create Human-Centered Products and Services, ( John Wiley & Sons, 2009)
- ↑ Janson, A. Der Kunde im Fokus: Das Konzept der Customer Journey, ( GRIN Verlag, 2012)
- ↑ Ohtonen, D. J. Customer Journey Mapping, ( Bookboon, 2016)
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Zeidler, S. Mit Customer-Journey-Mapping die Kundenzufriedenheit steigern, "https://www.gruenderszene.de/allgemein/mit-customer-journey-mapping-die-kundenzufriedenheit-steigern",(Accessed on 28th of February)
- ↑ Levitt, T. Marketing Myopia, "https://razaleads.files.wordpress.com/2013/09/marketing-myopia_t_levitt.pdf",(Accessed on 28th of February)
- ↑ Christensen, C. M., & Raynor, M. E. The Innovator's Solution: Creating and Sustaining Successful Growth , (Harvard Business School Press, 2003)
- ↑ Šáchová-Kleisli, A., & Walther, B. Job-to-be-done-Logik in der Praxis, "http://www.vendbridge.com/files/V-Transformation-150414-DE-newlayout-inclCharts.pdf",(Accessed on 28th of February)
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Nobel, C. Clay Christensen's Milkshake Marketing, "http://hbswk.hbs.edu/item/clay-christensens-milkshake-marketing",(Accessed on 28th of February)