Metro Opening
SMART-Method - How to formulate goals correctly
(individually and in a company)
In order to set goals in a meaningful way, the method of smart goal setting has become established. The acronym SMART stands for
S - specific The objectives should be clearly and positively described.
M - measurable The achievement of objectives should be measurable.
A - attractive For you personally it should be attractive (motive-congruent) to reach the goal.
R - realistic The objective should be realistically achievable.
T - timely The objective should be clearly defined in terms of deadlines.
A SMART formulation of the goal “I want to exercise more often” could look like this:
I am going for a run two times a week every monday and thursday between 6 and 7pm for the next three months till May the 20th, to feel more comfortable in my body.
2.
3.
4.
5.
FMEA – Failure Mode Effect Analysis
For every organization or project, risk management is a crucial tool to handle, combat, and reduce risks. FMEA is a tool in risk management that can help a project manager to systematically identify potential failures and help make a contingency plan for minimizing and even avoiding the risk associated with the project. FEMA is for example used when:
- A service is being designed or redesigned
- Improvement goals are planned for an existing process, product, or service
- Analyzing failures of an existing process, product, or service
The FMEA was developed in the 1950s but is continuously evolving, and are getting refined. It is important that the tool is fitted for the needs of the organization or the event that it is used on.
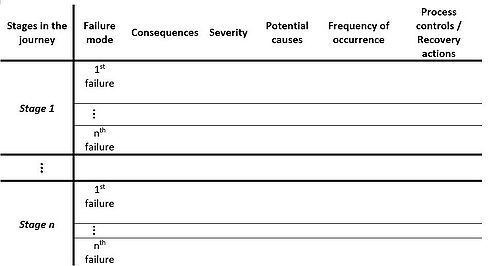
FMEA is essentially a brainstorming exercise where the team in a systematic fashion identify:
- Failure mode. The possible failures or risks at a stage.
- Consequences of the failure.
- The severity of the impacts of the failure. This is a scale from 1 to 10.
- Potential courses for why and how the failure happened.
- Frequency of occurrence. This is a scale from 1 to 10.
- Process controls / Recovery actions. How to recover from the failure.
This is done in a matrix form like the one illustrated below:
To expend the FEMA, one could include
- Detection rate that estimates how well the failure can be detected before the customer notices. This is a scale from 1 to 10.
- The risk priority number is ranking the potential failures in the order they should be addressed. This is calculated by multiplying the severity of the occurrence.
7.