DevOps
DevOps, the combination of Development and Operations: How to create agile, reliable, & secure technology organizations.
More than ever, how technology work is managed and performed predicts the success of the entire organization. DevOps describes an approach to create agile, reliable and secure technological organizations. The core of the concept is the cooperation of different functions in small teams which leads to overall organizational success. Safe systems of work are created that are able to quickly and independently develop, test and deploy code and therefore value to customers safely, securely, and reliably. DevOps can have a major impact on the way technology organizations operate. It can be understood as the application of principles taken from physical manufacturing to the IT value stream. DevOps relies for example on Lean manufacturing concepts, on the Theory of Constraints, and the Toyota Kata movement. However, it may also be viewed as the continuation of agile software development.[1]
It is therefore directly relevant for the project management knowledge base as a principle for Agile Project Management and Lean Project Management. It allows for a project to achieve general established goals described by PMI standards, for example to meet business objectives. IT work is hereby important for nearly all business objectives. It should be mentioned that DevOps can in addition be applicable for every organization, no matter what the core business is. Nowadays, every organization, company or NGO, needs a stable and reliable technology infrastructure to be successful. Therefore, DevOps has a relevance for all industries and the DevOps principles can be considered vital for effective and efficient project management. It can be viewed as a strategic competency to allow organizations to: [2]
- Tie technology project results to business goals,
- Compete more effectively in their markets,
- Sustain the organization, and
- Respond to the impact of business environment changes on projects by appropriately adjusting project management plans
Even though the principles can be applicable to every organization this article will focus on IT organizations and on transforming IT project and portfolio management by using the DevOps principles.
A main concept of DevOps is to create shared goals between software development and IT operations. In addition, continuous integration practices are used to make deployment part of daily work. This was first described at the 2009 Velocity conference by John Allspaw and Paul Hammond. [3] This leads to the theoretical foundation behind DevOps, the three ways, which lay the basis for further study and application of the principles. After an organization has made the decision to start their DevOps journey, there are three main areas, correlating to the three ways, which need to be accelerated.
DevOps has been subject to a novel published in January 2013 and written by Gene Kim, Kevin Behr, and George Spafford. “The Phoenix Project” describes the typical issues faced by an IT organization and how DevOps helps to solve them. This homage to “The Goal”, the 1984 novel by Eliyahu M. Goldratt, was accompanied by “The DevOps Handbook” in 2016, which describes how organizations can replicate the success of DevOps.
Contents |
The three ways
To understand the big idea behind DevOps, several important movements in management and technology must be explored. Most importantly, value streams, the application of Lean principles to the technology value stream as well as the three ways must be understood: [1]
- The principles of Flow (accelerate the delivery of work from Development to Operations and to the customer)
- The principles of Feedback (enabling the creation of safer systems of work)
- The principles of Continual Learning and Experimentation (promote trust and a scientific approach to improvement)
What is a value stream? A value stream is defined as "the sequence of activities an organization undertakes to deliver upon a customer request" or "the sequence required to design, produce, and deliver a good or service to a customer, including the dual flows of information and material".[4] In technology work, the value stream is defined "as the process required to convert a business hypothesis into a technology enabled service".[1]
What is Lean? In lean manufacturing, the focus lays on creating a smooth and even flow of work, by using small batch sizes, reducing work in progress (WIP), preventing rework, and optimizing the system towards global goals. These principles are equally applicable to technology work as well as all knowledge work. This application to technology work describes the focus on deployment lead time that the DevOps principles rely on. [1] The lead time describes the time between the moment a change is checked into version control and the moment that this change is running in production. This phase of work includes Testing and Operations and it is akin to Lean Manufacturing in the way that it follows the goal of achieving outputs with minimized variability and high predictability.
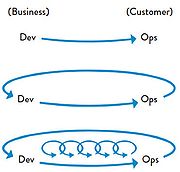
One main concept behind DevOps is that testing and operations work happens simultaneously with design and development. This should allow for fast flow, introducing the first way. Flow enables fast left to right flow of work from development to operations. To do this, work must be visible, batch sizes and intervals of work must be reduced and build quality must be ensured constantly.In addition, work in progress must be limited. Flow can be further amplified through reducing the number of hand-offs. The constraints within the value stream must be continually identified, evaluated and elevated. [5] Specific practices are introduced in the following chapter How to accelerate Flow.
The second way enables the fast flow of feedback from right to left. This helps prevention of problems, enables faster detection of issues as well as faster recovery. Safer systems of work are created that find problems long before they would cause a catastrophic failure. This is critical to achieve quality, reliability and safety standards. Problems must bee seen as they occur and quality must be pushed closer to the source. [5] Specific practices are introduced in the following chapter How to accelerate Feedback.
The third way enables a high trust culture. A dynamic, disciplined and scientific approach to experimentation and risk taking is established to facilitate organizational learning from success and failures. Daily work should be continually improved and local learning must be transformed into global learning. Feedback looks are continually shorted to further amplify the results of the second way, showing that the third way is interwoven with the first and second way. [5] Specific practices are introduced in the following chapter How to accelerate Continual Learning.
How and where to start
The following chapters will describe the Application of DevOps To start a DevOps transformation several factors must be considered:
- Which value stream should the transformation start with?
- What work must be done in the value streams?
- How can an organization and architecture be designed?
- How can market oriented outcomes be enabled?
- How can teams be protected and enabled?
Choosing a value stream
Value Streams are evaluated in a number of ways:
- Greenfield vs Brownfield services:
- Greenfield projects are software projects describe a new project or initiative. New applications and infrastructure are built with few constraints. Starting with such a project can be easier since there are no existing code bases, processes, and teams that must be considered.
- Brownfield projects are existing products or services that are already in service. They often come with a significant amount of technical debt, complicating the DevOps steps. This does however not mean that such projects are not applicable for DevOps. Existing performance gaps between customer needs and business deliveries can be closed. In addition, existing teams may be open to experimentation with DevOps if they believe traditional methods might not be sufficient to reach their goals.
- A significant factor is therefore not the age of the project but rather its architecture and whether it could be re-architected for testability and deployability.
- Systems of engagement and systems of record
- Risk/reward balance
- Resistance from teams
Evaluating work that must be done
Designing an organization and architecture
Market oriented outcomes
Enabling and protecting teams
How to accelerate
Flow
Feedback
Continual Learning
Integrate Security and Compliance
Applicability for other sectors and limitations
This chapter will provide a critical reflection of DevOps
Annotated bibliography
The following list provides resources for further research and study on DevOps principles:
- Kim, G.; Humble, J.; Debois, P.; Willis, J. (2016): The DevOps Handbook: How to Create World-Class Agility, Reliability, and Security in Technology Organizations
- - The DevOps Handbook describes how using the DevOps principles can integrate Product Management, Development, QA, IT Operations, and Information Security to help effective management of technology. It provides a theoretical explanation of the principles as well as a practical approach to applying the DevOps principles.
- Kim, G.; Behr, K.; Spafford, G, (2013): The Phoenix Project: A Novel About IT, DevOps, and Helping Your Business
- - The Phoenix Project is a novel about an IT manager that uses the DevOps principles to lead a technology organization to new success. It introduces the Three Ways and shows a fictive success story of the DevOps principles.
- Kim, Gene (2019): The Unicorn Project: A Novel about Developers, Digital Disruption, and Thriving in the Age of Data
- - The Unicorn Project is the continuation of The Phoenix Project. It takes the perspective of the software development department and introduces the "Five Ideals" to further introduce the theroy of DevOps.
- Goldratt, Eliyahu M. (1984): The Goal
- - The Goal is the inspiration for The Phoenix Project. It explains the theory of constraints in physical manufacturing. This theory is used in the DevOps principles extensively. It is regarded as an important work in operations research to teach students about the importance of strategic capacity planning and constraint management.
- Puppet Lab: State of DevOps Report
- - This yearly report (2011 - 2020) provides new insights into how organizations evolve the DevOps practices. The ninth publication of the report includes over 2,400 participants who work in IT, development, information security and related areas. The newest edition focuses on a platform approach to software delivery and applying DevOps principles to change management.
- Farley, D.; Humble, J. (2010): Continuous Delivery: Reliable Software Releases Through Build, Test, and Deployment Automation
- - Continuous Delivery describes principles and technical practices that enable rapid, incremental delivery of high quality, valuable new functionality to users and therefore laying the basis for the DevOps principles. Through automation of the build, deployment, and testing process, and improved collaboration between developers, testers and IT operations, teams can release changes quicker and safer.
- Allspaw, J.; Hammond, P (2009): 10+ Deploys Per Day: Dev and Ops Cooperation at Flickr [conference]; available at: https://tech-talks.code-maven.com/ten-plus-deploys-per-day.html
- - Video taken from the Velocity conference in 2009. Key concepts for DevOps are introduced (shared goals between development and operations, and continuous integration practices) through an exploration of the technology work performed at flickr (American image hosting and video hosting service).
- Ries, Eric (2011): The Lean Startup
- - The Lean Startup describes how to create a successful entrepreneurial business and explains how the principles could be used in other organizations. The principles resemble the DevOps principles. The book argues that the customer needs should be at the center of each organization. Working towards the business objectives can help the creation of shared goals between development and operations, a key concept behind DevOps.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Kim, G.; Humble, J.; Debois, P.; Willis, J. (2016): The DevOps Handbook: How to Create World-Class Agility, Reliability, and Security in Technology Organizations
- ↑ Project Management Institute, publisher (2017): A guide to the project management body of knowledge (PMBOK guide)
- ↑ Allspaw, J.; Hammond, P (2009): 10+ Deploys Per Day: Dev and Ops Cooperation at Flickr [conference]; available at: https://tech-talks.code-maven.com/ten-plus-deploys-per-day.html
- ↑ Martin, K; Osterling, M (2013): Value Stream Mapping, How to Visualize Work and Align Leadership for organizational Transformation
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Kim, Gene (2012): The Three Ways: The Principles Underpinning DevOps, IT Revolution Press blog, available at: http://itrevolution.com/the-three-ways-principles-underpinning-devops/