Organizational Socialization
Abstract/intro
Contents |
Why Organizational Socialization is important
Organizational socialization is defined as a dynamic process by which people learn and adjust to the knowledge, skills, attitudes, expectations and behaviors needed to assume a new or changed organizational role. This process results in the employee going from an outsider to an insider. Successful socialization involves mutual influence, meaning the employee adopts organizational values and interest while being able to influence the organization through personal qualities. Consequently, both organizational and individual needs are met. [1]
Organizational assimilation is essential for the integration of a newcomer. The concept entails the newcomer intentionally, as well as, unintentionally is socialized by the organization. They must modify their work procedures to both reach the expectations of the employer and its own, by seeking information about the work place and adapting their behavior towards the behavior of their coworkers. Several different members of the organization influences this process and are pivotal for it to be succesful, ranging from the managers to the peers of the newcomer. Additionally can supervisors and mentors be an effective ressource to use. [2]
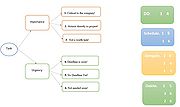
The organizational socialization is often divided in three stages with varying names. The first step being the recruitment process where both the organization and the newcomer collects information about one another. The second step entails the newcomer adjusting to the new work environment, and the third stage is reached when the newcomer has adapted to the given organizational role [3].
Benefits of organizational socialization
Effective and succesful organizational socialization results in considerable benefits for both the employer and the employee. Better communication and coordination can be obtained within the team, it can reduce stress and uncertainties, heighten the organizational commitment and lead to satisfaction and a positive feeling of self worth. Consequently, increasing the productivity and innovation of the employees, leading to making it possible to efficiently achieve organizational and team goals and secure the employees longevity in the organization. [4]
Furthermore, the team obtain a greater cohesiveness and long-term stability by being socialized. Trust between team members is achieved based on shared tasks and projects, making way for better knowledge sharing and improved individual decision performance. [5]
The relation between Organizational Socialisation and Project, Program and Portfolio management
Organizational socialization is an important concept within all levels of management, whether it is within a project, program, or portfolio, as it is pivotal to achieve successful results and positive experiences. It applies to new employees, as well as, existing employees changing role within the organization, department or team.
As it is a dynamic process, it is present during the whole life cycle of a project/program/portfolio. However, it is especially relevant to give focus in the beginning of a new project/program/portfolio, particularly if new members have been added to the associated teams, to establish constructive communication and quality in the decision making. If newcomers are introduces while the project/program/portfolio is running, it also calls for a conscious effort in integrating the newcomer by socialization.
Application
Various means can be used to achieve successful socialization. Which means to utilize depends greatly on the stage of the socialization.
Often the newcomer is connected to a supervisor or mentor providing informal information and advice, as well as, clarifying job instructions and giving social support. Social events within the organization are also a great tool.
Stages
Limitations
Most studies of the concept are revolving around graduates entering the job market or specific professionals changing jobs. It is assumed that the same tendencies are seen in the process of changing role within an organization, but very little empirical evidence exists about this and therefore the specific knowledge is limited. [6]
Annotated bibliography
Virtual organizational socialiazation: http://what-when-how.com/information-science-and-technology/managing-relationships-in-virtual-team-socialization-information-science/
Professional socialization
References
- ↑ B. L. Berkelaar, & M. A. Harrison, Organizational Socialization, Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Communication (May 2019).
- ↑ what-when-how (2021), Managing Relationships in Virtual Team Socialization (information science), http://what-when-how.com/information-science-and-technology/managing-relationships-in-virtual-team-socialization-information-science/.
- ↑ iEdoNote (2021), Organizational Socialization: 3 Stages of Organizational Socialization, https://www.iedunote.com/organizational-socialization.
- ↑ what-when-how (2021), Managing Relationships in Virtual Team Socialization (information science), http://what-when-how.com/information-science-and-technology/managing-relationships-in-virtual-team-socialization-information-science/.
- ↑ M. Handzic, Managing Knowledge through Experimentation and Socialisation, PAKM 2000
- ↑ T. N. Bauer, Organizational Socialization, Encyclopedia of Applied Psychology (2004), p. 743-745.