Early warning signals in project management
Contents |
Abstract
Despite the use of numerous methods and tools for ensuring the success of the development in the project management, still a large number of construction projects experience failure or critical situations. During the front-end stage project, a constant uncertainty last in all critical decisions and corrective actions to reduce possible undesirable impacts to the project.
Identify early warning signal in the early stage is important for the project success, since more time will be available to take corrective actions before negative consequences and problems occur.
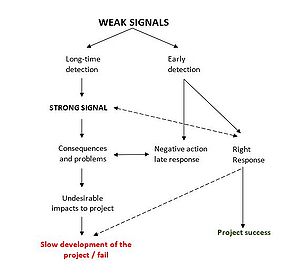
An early weak signal can be a missing project information, lack of documentation or the typical wrong scheduling of activities and allocating workers. Due the level of uncertainty at this stage is not easy to identify early warning signs of potential problems that can arise during the development of the project. Nevertheless, select the right approaches for indicate the signals will aid the managers to take right decisions. Furthermore, weak signals can became stronger if they consider at the time of detection at early stages and anticipating problems.
The article explain the importance of early warning signals, compare with the theory of weak signals by Igor Ansoff (1975) and complemented by Nikander’s (2002) and enumerate the typical barriers to identify it.
Introduction
The thought of early warning signal is a wide-ranging concept. It can be apply to any area where it is crucial obtain indications as soon as possible of any project progress that in the future can be undesirable and change the characteristics of the project prior development.
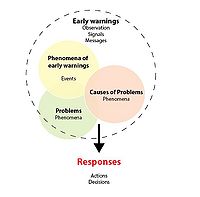
Early warning signals are direct consequences of a critical slowing down of the project development.
Theory of weak signals
Many author have different interpretation and definition for a weak signal. The first who mentioned the weak signal concept was Igor Ansoff in 1975 and later on was supported by Nikander (2002). Ansoff stated that strategic events do not came up from nowhere; it is possible to predict their manifestation by the benefit of signs, which are named weak signals. A weak signal was defined by Ansoff, 1984 as “…imprecise early indications about impending impactful events…all that is known is that some threats and opportunities will undoubtedly arise, but their shape and nature and source are not yet known”
Later on, this definition was supported by Nikanders’s who defined early warning sign as “observation, a signal, a message or some other item that is or can be seen as an expression, an indication, a proof, or a sign of the existence of some future or incipient positive or negative issue” The main purpose of the authors was the improvement in the strategic planning methods, which are not perfect enough. According to them, when companies operates in uncertain environments requires paying specific attention to weak signals before making any strategic decisions. (Igor. Ansoff & McDonnell, 1990)
Levels and groups of early warnings
According with Ansoff (1990), level of information have two stages (strong signals and weak signals): The progressivity of weak signals to get stronger during the time and turn into strong ones.
Weak signals can be classified depending of the sources of data, quality of arguments and future impacts; including moreover feeling signals, uncertain signals or precise signals.
- The feeling signals report that something is going to happen. Directly, is connected with the project manager who can have different feelings about things than the other managers, and take different decisions. The human perception varies depending on the person. Normally, this kind of signal are not reported due the missing strong arguments.
- The uncertain signals indicates changes in the work environment, sources are anonymous but is possible to find good reasons about the matter.
- The almost certain signal, are less uncertain but still there are issue measuring and calculated changes and consequences.
- The exact signals, signals with enough evidences of their occurrence.
Identification early warning signals
Barriers of identification
| Sources for missing EWS | Indication | Possible problems |
|---|---|---|
| New organization of and lack of experience | Not having experience in big projects.
Not being aware of future problems. Not take into account many signals when making critical decisions. Governance is not suitable for a project |
Surprised by unexpected issues
Spend extra time and money for changes Extra time for training |
| Inappropriate Management | No detailed plans for the overall of the project due a non-systematic method of detection of signals
Incomplete risk strategy allocation, no taking into account possible problems |
Disbursing money for wrong working methods
Expend too much money for suddenly changes in the initial project Reactive behavior |
| Conflicts between projects and early stages | Distractions from initial considerations
Inappropriate management Inappropriate strategic decisions |
Changes in the process of the project
Cost and time |
| Delivering project within time and cost budget | No spending time for other considerations
Dismiss strategies due the cost or time consuming Ignorance to the project functionalities and long term perspectives |
Delivering results with lacking of promised technical capabilities and functionalities
Decrease user satisfaction Bad reputation Failure in long term perspective |
| Exceed of contracts | Misunderstanding in the integration of the contract parts
Improperly communication Undefined governance. |
Extra money and time for integration incompatible parts
Communication barriers and conflicts Reactive behavior |
| Long term projects | No considering future risk and opportunities
No consider flexibility of the project No provide enough training in the early stages of the project Undefined project management |
Tight plans and schedules
Spending too much time on training people. Unable to deal with new technologies EWS no updated for the transition of the project |
| Optimism of the members | Ignore project guidelines, laws and requirements | Unaware of the signal cost related, missing signal and increasing cost due failure
Re-plan and changes in the project, time and money consuming |
| Issues in reporting systems | Communication barriers, missing identified signals
Changing meaning of identified signals Ignoring mental models |
Acting different as the identified signal, time and money consuming
Ignore and not consider signals |
| Focus external relations | Missing internal issues, signals
Lack of trust between the members |
Conflicts
Luck of trusts between the members and not expressing identified signals |