Adaptive Project Framework
(→Annotated Bibliography) |
|||
| (34 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | '' | + | ''Developed by Tinna Dofradottir'' |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | '''Adaptive Project Framework''' (APF) is used in project management and is part of the group of agile methodologies. In so-called traditional project management managers often approach investment projects as if surroundings and conditions behave in a stable way. However in modern society the volatility and the uncertainty need also to be taken into consideration in its business sector. Therefore traditional project management often does not work in new and difficult economy conditions, especially in software development. At the beginning of 21-century agile project management became widespread in science and practice. However solving the dilemmas of developing project with both agile and traditional project management became more difficult and the adaptive project management approach was invented to take advantage of and eliminating the disadvantages of both approaches mentioned above.<ref name="sciento"/> | ||
| + | The goal of this article is to present an overview of the Adaptive Project Framework and count all its core values, including when to use this method. Then after the overview the application of this method is described with what advantages and disadvantages it comes with, finally a section with its limitation of this method. | ||
=Overview= | =Overview= | ||
| − | Recognised strategic leader in the field of project management, Robert K. Wysocki published the book Adaptive Project Framework in 2010, where he describes the APF approach when managing complexity in uncertainty. The AFP method was created to help teams adapt continuously to projects changing environment. | + | Recognised strategic leader in the field of project management, Robert K. Wysocki published the book Adaptive Project Framework in 2010, where he describes the APF approach when managing complexity in uncertainty. The AFP method was created to help teams to adapt continuously to projects changing environment. It is a systematic and structured process that allows project managers to enhance their decisions and practices during the project life cycle, based on their learning from previous achieved results during the project. APF is designed to continually adapt to the changing situation of a project from its very beginning to its very end. Therefore, with this approach, nothing is fixed: neither the duration of the project, nor the budget, nor the risks, and everything can be continuously adjusted according to changes in the projects characteristics.<ref name="APFG"/> |
| − | To implement the APF methodology successfully, project teams must be willing to accept and | + | To implement the APF methodology successfully, project teams must be willing to accept and to adapt changes. It is a costumer driven process, where the client is involved in every stage of the process and they are even given the opportunity to control the direction of the project. This consequently requires the project team to be effectively involved, acting with an open mind and trusting partnership with the client.<ref name="Howto"/> |
| − | The APF project team is combined of client team and development team. Depending of the size of the project the client team can be a single person or multiple. In the client team there needs to be a single member in charge of the decision making, serving as a co-manager along with the development team leader. The development team is composed of technical professionals who are responsible for developing the project and producing the deliverables.<ref name="APF"/> | + | The APF project team is combined of the client team and the development team. Depending of the size of the project the client team can be a single person or multiple persons. In the client team there needs to be a single member in charge of the decision making, serving as a co-manager along with the development team leader. The development team is composed of technical professionals who are responsible for developing the project and producing the deliverables.<ref name="APF"/> |
| − | A project scope is a variable from a traditional mindset and the general premise underlying | + | A project scope is a variable from a traditional mindset and the general premise underlying the APF project is not to plan the future, the future is unknown. In APF planning is done in each completed cycle, this is to maximise the business value by adjusting the project scope of the solution and make the client a central figure. Giving the client the opportunity to be in charge of deciding what should be changed and what direction the project is heading. It means that APF projects are constantly corrected to ensure maximum business value. When it comes to that time or money or both have been used up, all the deliverables will have the greatest business value that could have been generated from the collective knowledge and learning from the client team and the development team.<ref name="APF"/> |
== Core Values == | == Core Values == | ||
| − | + | The core values of the APF method are six and are described here below: | |
| − | ''' | + | '''1. Client focused:''' The most important value is that the client needs must always come first, as long as they are within the bounds of ethical business practices. |
| − | ''' | + | '''2. Client driven:''' By letting the client take on the project manager role and its responsibilities, will give them the sense that they are controlling the direction of the project and being involved meaningfully. |
| − | ''' | + | '''3. Incremental results early and often''': Deliverables are many and often in APF projects, this gives the client an early delivery and is very valuable when the question is what the client's real needs are. The functionality of the project's first cycles may be very limited, but in any case they are useful when it comes to decision making. |
| − | ''' | + | '''4. Continuous questioning and introspection''': This core value expresses to openness and honesty that must exist between the client team and the development team. Both sides must be committed to make the best possible business choices. Only with honest and open dialog can that occur. |
| − | '''6. Don’t | + | '''5. Change is progress to a better solution''': The Project Scope phase begins with the stakeholders coming to an understanding of what is needed and what will be delivered through out the process of the Conditions of Satisfaction (CoS). |
| + | |||
| + | '''6. Don’t speculate on the future''': APF strips out all the work that is not value-adding. Guessing on the future will only add work to the non-value-added section. When in doubt, it should be left out. APF is designed to spend the time and money of the client on maximising the business value that was defined by the client.<ref name="APF"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == When to use it == | ||
| + | Now given a little overview of the APF method, it is time to understand when APF is applicable and the following two questions will be answered; When to use it? and when to not use it? | ||
| + | |||
| + | As mentioned above in the modern world we live in now days, uncertainty and project requirements are changing constantly. This is due to many things for example, growing market trends, accelerating technological development, customer needs and preferences are changing, unclear business objectives and competitors actions. All these factors need to be taken into consideration when managing projects. | ||
| + | Which means projects now days don't fit the traditional linear project management approach, where the first phase must be completed until the next one can begin. So the APF method is relevant to projects that don't necessarily have a certain business objective but the project goal is known, it's just uncertain how achieve it. In other words, when the requirements are vague and the direction can easily be changed or adjusted, then APF method is applicable.<ref name="when"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The method is not very applicable in construction projects and large projects, simply because of its flexibility and its iterative approach are not desired in those kind of projects, it could lead to delays and cost overruns. <ref name="lim"/> | ||
=Application= | =Application= | ||
| − | Taking a closer look at the project framework, it is divided into five | + | Taking a closer look at the project framework, it is divided into five phase strategy designed to provide clients the optimum business value from any cycle within defined limits of time and cost constraints imposed by the client. ''Figure 1'' shows a graphical portrait of the five phases, they consist of the project scope, the cycle plan, the cycle completion, the client checkpoint and finally post-version review. As mentioned before the APF is an iterative process, where in each cycle you iterate and also between cycles. In every cycle the development team and the client team come to learning and discover new potential opportunities to explore.<ref name="APF"/> An application of each phase is described in the following sub-chapters. [[File:APF lifecycle.png|right|300px|thumb|Figure 1: The live cycle of APF <ref name="APF"/>]] |
===Project Scope=== | ===Project Scope=== | ||
| − | + | As Shown in ''Figure 1'', this is the defining phase and the planning phase that both contain approval points. The first phase of the process is identifying the project scope and that involves understanding the needs of the costumer. Therefore stakeholders first step is to determine the '''Conditions of Satisfaction''' (CoS). That is the project goals and the desired outcome, by finding out what are the client's needs and how to meet those needs. From this point the '''Project Overview Statement''' (POS) is written to outline the CoS and it needs to be approved by all stakeholders, this is done to evaluate the effectiveness of the process and how the project will be accomplished.<ref name="Howto"/> | |
| − | As Shown in Figure | + | |
| − | Finally three documents are needed to finish the project scope. First, there is the '''Functional Requirements''', that prioritises actions as well as possible risks, challenges and assumptions. | + | Finally three documents are needed to finish the project scope. First, there is the '''Functional Requirements''', that prioritises actions as well as possible risks, challenges and assumptions that can accrue during the project. But as the project progresses, this may change. Second document is the '''Work Breakdown Structure''' (WBS) that enables teams to estimate the costs, develop a schedule and break down the processes into manageable parts that need to be accomplished in each cycle. Finally there is the triangle scope, which is how time, cost and quality will converge.<ref name="Thinktheme"/> In APF, planning is done within each cycle at micro level. It starts with an RBS-based mid-level component or function, and ends with a WBS-based micro-level activity and task. It should be thought of as scheduling just-in-time and as if each cycle involves work that takes only a few weeks to complete.<ref name="APF"/> |
===Cycle plan=== | ===Cycle plan=== | ||
| − | Second phase of the method is the cycle plan, once the POS has been written and | + | Second phase of the method is the cycle plan, once the POS has been written and a prioritised list of known functionalities that both the client and the project manager have agreed on, that is needed to solve the business problem. A high-level planning is done to priorities the functions into multiple cycles with a defined timeframe to be developed. A typical cycle length is around two to six weeks long and before each cycle the length is defined and agreed along with its expectations. The project is divided into multiple mini-projects or cycles, where each cycle delivers one or more deliverables. This is the iterative part of the process, where the next three steps are repeated over and over again. The cycle plan involves defining each task that needs to be accomplished in each project cycle according to the WBS but end of each cycle it is adapted to the new direction. Order of the tasks is established, interdependencies are identified and assigned to employees with a given deadline.<ref name="APFG"/> |
===Cycle completion=== | ===Cycle completion=== | ||
| − | The cycle work begins and is monitored throughout the cycle, it can be changed as the development team | + | The cycle work begins and is monitored throughout the cycle, it can be changed as the development team works on the project. The cycle is done when the pre-defined time is completed and all the tasks that were not finished during this cycle are reconsidered and reprioritised in the next cycle. Every team member has assigned daily tasks and they need to post updates at the completion of each day. This allows variances to be caught at an early stage and a corrective action is taken into plan. It is critical to ensure consistent contact, noting any demands for change and new ideas for improvement, so that it can be discussed before the next cycle when the team encounters new problems.<ref name="Howto"/> |
===Client checkpoint=== | ===Client checkpoint=== | ||
| − | The Client review is an important step of the process, the client team and the development team come together and review the accomplished deliverables during | + | The Client review is an important step of the process, the client team and the development team come together and review the accomplished deliverables during current cycle and evaluate the quality of the produced functionality features. Together with the project manager a plan will be conducted on any corrections or improvements to be made for the next cycle. Once the review is done the sequence Cycle Plan → Cycle Build → Client Checkpoint are iterated until the project is complete or until the time and/or budget has been exhausted.<ref name="Thinktheme"/> |
===Post-version review=== | ===Post-version review=== | ||
| − | Completion of the project, the project manager, client and the team will come to together and evaluate the success of the project and determine whether project goals have been accomplished and that the client is pleased. | + | Completion of the project, the project manager, the client and the team will come to together and evaluate the success of the project and determine whether project goals have been accomplished and that the client is pleased. |
| − | There are three important questions that need to be answered: | + | There are three important questions that need to be answered during this point: |
| − | '''1. | + | '''1. Was the expected business outcome realised?''' |
| − | '''2. | + | '''2. What was learned that can be used to improve the solution?''' |
| − | '''3. | + | '''3. What was learned that can be used to improve the effectiveness of APF?''' |
Then document of the whole process is done to reflect the effectiveness of the method, lesson learned and possible improvements for future projects.<ref name="APF"/> | Then document of the whole process is done to reflect the effectiveness of the method, lesson learned and possible improvements for future projects.<ref name="APF"/> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=Advantages and Disadvantages = | =Advantages and Disadvantages = | ||
===Advantages=== | ===Advantages=== | ||
'''Finish Sooner''': | '''Finish Sooner''': | ||
| − | + | The APF project will finish sooner than tradition project management project. As APF eliminates all non-value-added work, the reason for this is that the method generates less to do than those projects that follow more traditional approaches. Linear and Incremental models plan the entire project and then the plan has to be redone from the point of change to the end of the project when change comes and is approved. Throughout the project, the situation is repeated several times, therefore making the original plan into non-value-added work that could have been prevented. The more approved modifications, the more non-value-added work there will be. APF does not have any of this excess baggage, so it is guaranteed to finish sooner than traditional approaches.<ref name="APF"/> | |
| − | APF project finish sooner than | + | |
'''Less Expensive''': | '''Less Expensive''': | ||
| − | + | Work that is non-value-adding cost extra money. Due to the frequent project scope changes, there is at least a labor cost for the time spent planning activities and tasks that are never done. In the end, a lot of time was spent for planning and that alone is waste of money and time.<ref name="APF"/> | |
'''Better Business Termination Policy''': | '''Better Business Termination Policy''': | ||
| − | APF | + | In APF, deliverables are often and many. If anything goes wrong, it will be discovered earlier than in traditional project management projects. By providing project managers early on the project with information on which they can decide to terminate the project before any additional time or money is spent. Time and money will be saved by this early termination and instead will be invested in some new direction when using APF approach.<ref name="APF"/> |
| − | money saved by this early termination will be invested in | + | |
'''Produces Higher-quality Deliverables''': | '''Produces Higher-quality Deliverables''': | ||
| − | The | + | The high level of customer participation in APF project means that early in the project the customer will have a look at intermediate deliverables and get the opportunity to adjust them. Therefore the quality of the final product will exceed because it is directly of the costumer needs.<ref name="APF"/> |
'''Delivers Maximum Business Value for the Time and Cost Invested''': | '''Delivers Maximum Business Value for the Time and Cost Invested''': | ||
| − | The | + | The continuous modification and redirection of an APF project means that everything that is delivered is needed and is of the customer's expected quality. The customer is in collaboration with the project manager and they decide at every iteration what goes into the solution. The APF project life cycle will not outlive poor quality deliverables.<ref name="APF"/> |
===Disadvantages=== | ===Disadvantages=== | ||
| + | '''Too much flexibility''': the method can generate constant changes in the requirements of the customer when there is too much flexibility. The client is in charge of the direction of the project and he can change one feature substantially and then change it back to how it was originally.<ref name="lim"/> | ||
| − | ''' | + | '''Higher expectations:''' Supporters of this framework claim immaculate project outcomes, which increase the expectations of the client and the stakeholders.<ref name="lim"/> |
| − | ''' | + | '''Little project control:''' The management of the project is all about controlling the project and the requests for change. The project manager has really negligible control over the project when using APF.<ref name="lim"/> |
| − | + | = Limitations = | |
| + | ===Focus on small teams=== | ||
| + | Because of the features of face-to-face informal communication and cooperation, agile methodologies concentrate on small teams. Face-to-face communication becomes especially difficult when a teams are larger and there is need of more documentation, which is a deviation from the agile spirit. Meanwhile, agile methodologies characterise teams according to the changing environment to be self-organising, which is mainly feasible for small teams and it does not work well for larger teams, where it requires more time to self-organise.<ref name="sciento"/> | ||
| − | + | ===Adapting the framework=== | |
| + | Project managers will try their best to adapt project framework to the project and it does not go the other way around. For every project, all project management activities are unique which is not always a good thing, an unknown territories are often difficult to manage.<ref name="lim"/> | ||
| − | = | + | ===Flexibility=== |
| + | As it is a flexible and iterative approach it can cause delays in time and budget overruns, the Adaptive Project Framework is not suitable for both construction projects or large-scale projects.<ref name="lim"/> | ||
| − | + | ===Documentation=== | |
| − | + | During the maintenance and reuse of projects, the lack of documentation is known to be a main issue. Developers have little knowledge that causes confusion and problems about the entire project. The burn-out of the project team can result in a sudden loss of valuable knowledge which is difficult to complete without compromising cost, time and quality. Due to the lack of documentation, training the new team members is another problem.<ref name="sciento"/> | |
| + | |||
| + | =Conclusion = | ||
| + | Adaptive Project Framework is a flexible project management approach that is an advanced idea of the agile methodologies. It is a good approach to use when the final goal of the project is not certain and it needs to be able to adapt quickly to changing requirements of the client. The method allows the client to be rather involved in the process and to decide the direction of the whole project. The project scope and the planning phase help to outline the project, just like in traditional project management, but in each cycle the scope is reconsidered and new measures are taken, this allows the project to be constantly adapting to clients needs and meet his quality demands. Nevertheless the method of APF can not be called universal, all projects are unique and should be managed in their own certain way, however APF allows this flexibility of the development and comes with many great advantages. | ||
=Annotated Bibliography= | =Annotated Bibliography= | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''Robert K. Wysocki Ph.D. (2010). Adaptive Project Framework. Managing Complexity in the Face of Uncertainty.''' | |
| + | |||
| + | * This is a book is written by Robert K. Wysocki, who is the inventor of Adaptive Project Framework approach. In his book he describes the APF approach when managing complexity in uncertainty and how development teams can adapt to constant project goal changes. This structured process allows project managers to enhance their decisions and practises during the project life cycle based on their learning from previous achieved results. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''M. Rizwan Jameel Qureshi, M. Kashif. (2017). Adaptive Framework to Manage Multiple Teams Using Agile Methodologies.''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | * This article describes the increased demand of agile methodologies in small teams in the software development sector. It goes in the to challenges and the unique problem they face during project development, specially when managing multiple small teams. | ||
| + | '''Umar Farooq (2017) Adaptive Project Framework | Principles and Process of APF.''' | ||
| − | + | * Article describing why teams should dedicate their project management to adaptive project framework. The article goes into the application of the method, description of the six phases and finally what limitations it follows when using APF approach. | |
=References= | =References= | ||
<references> | <references> | ||
| + | <ref name="APFG"> David Galiana (2020) Adaptive Project Framework: an introductory guide for beginners. Available at: https://www.wimi-teamwork.com/blog/adaptive-project-framework-introductory-guide-beginners/ </ref> | ||
| − | <ref name=" | + | <ref name="Howto"> Frank Hamilton (2021) Adaptive Project Framework: How to Implement It. Available at: https://www.startupvalley.news/adaptive-project-framework/ </ref> |
| − | <ref name=" | + | <ref name="Thinktheme"> ThinkTheme (n.d.) Adaptive Project Framework Methodology. Available at: https://thinkthyme.com/project-management/adaptive-project-framework-methodology </ref> |
| − | <ref name=" | + | <ref name="sciento"> M. Rizwan Jameel Qureshi, M. Kashif (2017) Adaptive Framework to Manage Multiple Teams Using Agile Methodologies. Available at: http://j.mecs-press.net/ijmecs/ijmecs-v9-n1/IJMECS-V9-N1-6.pdf </ref> |
| − | <ref name=" | + | <ref name="APF">Robert K. Wysocki Ph.D. (2010) Adaptive Project Framework. Managing Complexity in the Face of Uncertainty. Available at: https://books.google.dk/books?hl=en&lr=&id=M6GDUXXOtxsC&oi=fnd&pg=PT15&dq=adaptive+project+framework&ots=yEHeTTRqmv&sig=Jl-nX12tB_o8DMn-vYijB6R9uio&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=adaptive%20project%20framework&f=false </ref> |
| − | <ref name=" | + | <ref name="lim"> Umar Farooq (2017) Adaptive Project Framework | Principles and Process of APF. Available at: https://www.businessstudynotes.com/finance/project-management/adaptive-project-framework-principles-process-apf/</ref> |
| + | <ref name="when"> Maricel Rivera (2021) The Complete Beginner’s Guide to Adaptive Project Framework (APF). Available at: https://www.fool.com/the-blueprint/adaptive-project-framework/.</ref> | ||
</references> | </references> | ||
Latest revision as of 21:23, 28 February 2021
Developed by Tinna Dofradottir
Adaptive Project Framework (APF) is used in project management and is part of the group of agile methodologies. In so-called traditional project management managers often approach investment projects as if surroundings and conditions behave in a stable way. However in modern society the volatility and the uncertainty need also to be taken into consideration in its business sector. Therefore traditional project management often does not work in new and difficult economy conditions, especially in software development. At the beginning of 21-century agile project management became widespread in science and practice. However solving the dilemmas of developing project with both agile and traditional project management became more difficult and the adaptive project management approach was invented to take advantage of and eliminating the disadvantages of both approaches mentioned above.[1] The goal of this article is to present an overview of the Adaptive Project Framework and count all its core values, including when to use this method. Then after the overview the application of this method is described with what advantages and disadvantages it comes with, finally a section with its limitation of this method.
Contents |
[edit] Overview
Recognised strategic leader in the field of project management, Robert K. Wysocki published the book Adaptive Project Framework in 2010, where he describes the APF approach when managing complexity in uncertainty. The AFP method was created to help teams to adapt continuously to projects changing environment. It is a systematic and structured process that allows project managers to enhance their decisions and practices during the project life cycle, based on their learning from previous achieved results during the project. APF is designed to continually adapt to the changing situation of a project from its very beginning to its very end. Therefore, with this approach, nothing is fixed: neither the duration of the project, nor the budget, nor the risks, and everything can be continuously adjusted according to changes in the projects characteristics.[2]
To implement the APF methodology successfully, project teams must be willing to accept and to adapt changes. It is a costumer driven process, where the client is involved in every stage of the process and they are even given the opportunity to control the direction of the project. This consequently requires the project team to be effectively involved, acting with an open mind and trusting partnership with the client.[3]
The APF project team is combined of the client team and the development team. Depending of the size of the project the client team can be a single person or multiple persons. In the client team there needs to be a single member in charge of the decision making, serving as a co-manager along with the development team leader. The development team is composed of technical professionals who are responsible for developing the project and producing the deliverables.[4]
A project scope is a variable from a traditional mindset and the general premise underlying the APF project is not to plan the future, the future is unknown. In APF planning is done in each completed cycle, this is to maximise the business value by adjusting the project scope of the solution and make the client a central figure. Giving the client the opportunity to be in charge of deciding what should be changed and what direction the project is heading. It means that APF projects are constantly corrected to ensure maximum business value. When it comes to that time or money or both have been used up, all the deliverables will have the greatest business value that could have been generated from the collective knowledge and learning from the client team and the development team.[4]
[edit] Core Values
The core values of the APF method are six and are described here below:
1. Client focused: The most important value is that the client needs must always come first, as long as they are within the bounds of ethical business practices.
2. Client driven: By letting the client take on the project manager role and its responsibilities, will give them the sense that they are controlling the direction of the project and being involved meaningfully.
3. Incremental results early and often: Deliverables are many and often in APF projects, this gives the client an early delivery and is very valuable when the question is what the client's real needs are. The functionality of the project's first cycles may be very limited, but in any case they are useful when it comes to decision making.
4. Continuous questioning and introspection: This core value expresses to openness and honesty that must exist between the client team and the development team. Both sides must be committed to make the best possible business choices. Only with honest and open dialog can that occur.
5. Change is progress to a better solution: The Project Scope phase begins with the stakeholders coming to an understanding of what is needed and what will be delivered through out the process of the Conditions of Satisfaction (CoS).
6. Don’t speculate on the future: APF strips out all the work that is not value-adding. Guessing on the future will only add work to the non-value-added section. When in doubt, it should be left out. APF is designed to spend the time and money of the client on maximising the business value that was defined by the client.[4]
[edit] When to use it
Now given a little overview of the APF method, it is time to understand when APF is applicable and the following two questions will be answered; When to use it? and when to not use it?
As mentioned above in the modern world we live in now days, uncertainty and project requirements are changing constantly. This is due to many things for example, growing market trends, accelerating technological development, customer needs and preferences are changing, unclear business objectives and competitors actions. All these factors need to be taken into consideration when managing projects. Which means projects now days don't fit the traditional linear project management approach, where the first phase must be completed until the next one can begin. So the APF method is relevant to projects that don't necessarily have a certain business objective but the project goal is known, it's just uncertain how achieve it. In other words, when the requirements are vague and the direction can easily be changed or adjusted, then APF method is applicable.[5]
The method is not very applicable in construction projects and large projects, simply because of its flexibility and its iterative approach are not desired in those kind of projects, it could lead to delays and cost overruns. [6]
[edit] Application
Taking a closer look at the project framework, it is divided into five phase strategy designed to provide clients the optimum business value from any cycle within defined limits of time and cost constraints imposed by the client. Figure 1 shows a graphical portrait of the five phases, they consist of the project scope, the cycle plan, the cycle completion, the client checkpoint and finally post-version review. As mentioned before the APF is an iterative process, where in each cycle you iterate and also between cycles. In every cycle the development team and the client team come to learning and discover new potential opportunities to explore.[4] An application of each phase is described in the following sub-chapters.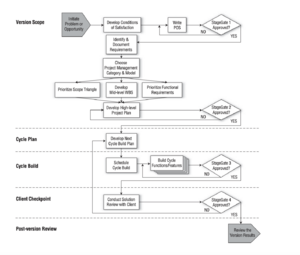
[edit] Project Scope
As Shown in Figure 1, this is the defining phase and the planning phase that both contain approval points. The first phase of the process is identifying the project scope and that involves understanding the needs of the costumer. Therefore stakeholders first step is to determine the Conditions of Satisfaction (CoS). That is the project goals and the desired outcome, by finding out what are the client's needs and how to meet those needs. From this point the Project Overview Statement (POS) is written to outline the CoS and it needs to be approved by all stakeholders, this is done to evaluate the effectiveness of the process and how the project will be accomplished.[3]
Finally three documents are needed to finish the project scope. First, there is the Functional Requirements, that prioritises actions as well as possible risks, challenges and assumptions that can accrue during the project. But as the project progresses, this may change. Second document is the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) that enables teams to estimate the costs, develop a schedule and break down the processes into manageable parts that need to be accomplished in each cycle. Finally there is the triangle scope, which is how time, cost and quality will converge.[7] In APF, planning is done within each cycle at micro level. It starts with an RBS-based mid-level component or function, and ends with a WBS-based micro-level activity and task. It should be thought of as scheduling just-in-time and as if each cycle involves work that takes only a few weeks to complete.[4]
[edit] Cycle plan
Second phase of the method is the cycle plan, once the POS has been written and a prioritised list of known functionalities that both the client and the project manager have agreed on, that is needed to solve the business problem. A high-level planning is done to priorities the functions into multiple cycles with a defined timeframe to be developed. A typical cycle length is around two to six weeks long and before each cycle the length is defined and agreed along with its expectations. The project is divided into multiple mini-projects or cycles, where each cycle delivers one or more deliverables. This is the iterative part of the process, where the next three steps are repeated over and over again. The cycle plan involves defining each task that needs to be accomplished in each project cycle according to the WBS but end of each cycle it is adapted to the new direction. Order of the tasks is established, interdependencies are identified and assigned to employees with a given deadline.[2]
[edit] Cycle completion
The cycle work begins and is monitored throughout the cycle, it can be changed as the development team works on the project. The cycle is done when the pre-defined time is completed and all the tasks that were not finished during this cycle are reconsidered and reprioritised in the next cycle. Every team member has assigned daily tasks and they need to post updates at the completion of each day. This allows variances to be caught at an early stage and a corrective action is taken into plan. It is critical to ensure consistent contact, noting any demands for change and new ideas for improvement, so that it can be discussed before the next cycle when the team encounters new problems.[3]
[edit] Client checkpoint
The Client review is an important step of the process, the client team and the development team come together and review the accomplished deliverables during current cycle and evaluate the quality of the produced functionality features. Together with the project manager a plan will be conducted on any corrections or improvements to be made for the next cycle. Once the review is done the sequence Cycle Plan → Cycle Build → Client Checkpoint are iterated until the project is complete or until the time and/or budget has been exhausted.[7]
[edit] Post-version review
Completion of the project, the project manager, the client and the team will come to together and evaluate the success of the project and determine whether project goals have been accomplished and that the client is pleased. There are three important questions that need to be answered during this point:
1. Was the expected business outcome realised?
2. What was learned that can be used to improve the solution?
3. What was learned that can be used to improve the effectiveness of APF?
Then document of the whole process is done to reflect the effectiveness of the method, lesson learned and possible improvements for future projects.[4]
[edit] Advantages and Disadvantages
[edit] Advantages
Finish Sooner: The APF project will finish sooner than tradition project management project. As APF eliminates all non-value-added work, the reason for this is that the method generates less to do than those projects that follow more traditional approaches. Linear and Incremental models plan the entire project and then the plan has to be redone from the point of change to the end of the project when change comes and is approved. Throughout the project, the situation is repeated several times, therefore making the original plan into non-value-added work that could have been prevented. The more approved modifications, the more non-value-added work there will be. APF does not have any of this excess baggage, so it is guaranteed to finish sooner than traditional approaches.[4]
Less Expensive: Work that is non-value-adding cost extra money. Due to the frequent project scope changes, there is at least a labor cost for the time spent planning activities and tasks that are never done. In the end, a lot of time was spent for planning and that alone is waste of money and time.[4]
Better Business Termination Policy: In APF, deliverables are often and many. If anything goes wrong, it will be discovered earlier than in traditional project management projects. By providing project managers early on the project with information on which they can decide to terminate the project before any additional time or money is spent. Time and money will be saved by this early termination and instead will be invested in some new direction when using APF approach.[4]
Produces Higher-quality Deliverables: The high level of customer participation in APF project means that early in the project the customer will have a look at intermediate deliverables and get the opportunity to adjust them. Therefore the quality of the final product will exceed because it is directly of the costumer needs.[4]
Delivers Maximum Business Value for the Time and Cost Invested: The continuous modification and redirection of an APF project means that everything that is delivered is needed and is of the customer's expected quality. The customer is in collaboration with the project manager and they decide at every iteration what goes into the solution. The APF project life cycle will not outlive poor quality deliverables.[4]
[edit] Disadvantages
Too much flexibility: the method can generate constant changes in the requirements of the customer when there is too much flexibility. The client is in charge of the direction of the project and he can change one feature substantially and then change it back to how it was originally.[6]
Higher expectations: Supporters of this framework claim immaculate project outcomes, which increase the expectations of the client and the stakeholders.[6]
Little project control: The management of the project is all about controlling the project and the requests for change. The project manager has really negligible control over the project when using APF.[6]
[edit] Limitations
[edit] Focus on small teams
Because of the features of face-to-face informal communication and cooperation, agile methodologies concentrate on small teams. Face-to-face communication becomes especially difficult when a teams are larger and there is need of more documentation, which is a deviation from the agile spirit. Meanwhile, agile methodologies characterise teams according to the changing environment to be self-organising, which is mainly feasible for small teams and it does not work well for larger teams, where it requires more time to self-organise.[1]
[edit] Adapting the framework
Project managers will try their best to adapt project framework to the project and it does not go the other way around. For every project, all project management activities are unique which is not always a good thing, an unknown territories are often difficult to manage.[6]
[edit] Flexibility
As it is a flexible and iterative approach it can cause delays in time and budget overruns, the Adaptive Project Framework is not suitable for both construction projects or large-scale projects.[6]
[edit] Documentation
During the maintenance and reuse of projects, the lack of documentation is known to be a main issue. Developers have little knowledge that causes confusion and problems about the entire project. The burn-out of the project team can result in a sudden loss of valuable knowledge which is difficult to complete without compromising cost, time and quality. Due to the lack of documentation, training the new team members is another problem.[1]
[edit] Conclusion
Adaptive Project Framework is a flexible project management approach that is an advanced idea of the agile methodologies. It is a good approach to use when the final goal of the project is not certain and it needs to be able to adapt quickly to changing requirements of the client. The method allows the client to be rather involved in the process and to decide the direction of the whole project. The project scope and the planning phase help to outline the project, just like in traditional project management, but in each cycle the scope is reconsidered and new measures are taken, this allows the project to be constantly adapting to clients needs and meet his quality demands. Nevertheless the method of APF can not be called universal, all projects are unique and should be managed in their own certain way, however APF allows this flexibility of the development and comes with many great advantages.
[edit] Annotated Bibliography
Robert K. Wysocki Ph.D. (2010). Adaptive Project Framework. Managing Complexity in the Face of Uncertainty.
- This is a book is written by Robert K. Wysocki, who is the inventor of Adaptive Project Framework approach. In his book he describes the APF approach when managing complexity in uncertainty and how development teams can adapt to constant project goal changes. This structured process allows project managers to enhance their decisions and practises during the project life cycle based on their learning from previous achieved results.
M. Rizwan Jameel Qureshi, M. Kashif. (2017). Adaptive Framework to Manage Multiple Teams Using Agile Methodologies.
- This article describes the increased demand of agile methodologies in small teams in the software development sector. It goes in the to challenges and the unique problem they face during project development, specially when managing multiple small teams.
Umar Farooq (2017) Adaptive Project Framework | Principles and Process of APF.
- Article describing why teams should dedicate their project management to adaptive project framework. The article goes into the application of the method, description of the six phases and finally what limitations it follows when using APF approach.
[edit] References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 M. Rizwan Jameel Qureshi, M. Kashif (2017) Adaptive Framework to Manage Multiple Teams Using Agile Methodologies. Available at: http://j.mecs-press.net/ijmecs/ijmecs-v9-n1/IJMECS-V9-N1-6.pdf
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 David Galiana (2020) Adaptive Project Framework: an introductory guide for beginners. Available at: https://www.wimi-teamwork.com/blog/adaptive-project-framework-introductory-guide-beginners/
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Frank Hamilton (2021) Adaptive Project Framework: How to Implement It. Available at: https://www.startupvalley.news/adaptive-project-framework/
- ↑ 4.00 4.01 4.02 4.03 4.04 4.05 4.06 4.07 4.08 4.09 4.10 4.11 Robert K. Wysocki Ph.D. (2010) Adaptive Project Framework. Managing Complexity in the Face of Uncertainty. Available at: https://books.google.dk/books?hl=en&lr=&id=M6GDUXXOtxsC&oi=fnd&pg=PT15&dq=adaptive+project+framework&ots=yEHeTTRqmv&sig=Jl-nX12tB_o8DMn-vYijB6R9uio&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=adaptive%20project%20framework&f=false
- ↑ Maricel Rivera (2021) The Complete Beginner’s Guide to Adaptive Project Framework (APF). Available at: https://www.fool.com/the-blueprint/adaptive-project-framework/.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 Umar Farooq (2017) Adaptive Project Framework | Principles and Process of APF. Available at: https://www.businessstudynotes.com/finance/project-management/adaptive-project-framework-principles-process-apf/
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 ThinkTheme (n.d.) Adaptive Project Framework Methodology. Available at: https://thinkthyme.com/project-management/adaptive-project-framework-methodology