Changing conversations based on the Stacey matrix
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
This report is devised in the course 42433 Advanced Engineering Project, Program and Portfolio Management at the Technical University of Denmark in Autumn 2015. | This report is devised in the course 42433 Advanced Engineering Project, Program and Portfolio Management at the Technical University of Denmark in Autumn 2015. | ||
| − | The Stacey matrix model was proposed by Ralph Douglas Stacey. It gives the possibility to distinguish management decisions and deal with [[Complexity]] and [[Uncertainty]] in organization platform. The result is brought out by usage of the two | + | The Stacey matrix model was proposed by Ralph Douglas Stacey. It gives the possibility to distinguish management decisions and deal with [[Complexity]] and [[Uncertainty]] in organization platform. The result is brought out by usage of the two dimensions Stacey matrix. It allows us to compare the level of agreement amongst stakeholders with the degree of certainty about the relationships between cause and effect. Thus, the decision can fall into the following areas of the matrix for further analysis: Simple, Complicated, Political and Chaotic. |
| − | == The | + | == The idea of the strategic choice theory == |
| − | Ralph Stacey defined management and organization dynamics in frame of the | + | Ralph D. Stacey defined management and organization dynamics in frame of the strategic choice theory. In this view the organization changes over time in a direction chosen by the most powerful individual or small group of managers. The theory of strategic choice displays its theoretical origin in two main pillars; cybernetic system theory and cognitivist psychology. Cybernetic theory is highly focused on control and regulation of a system, which helps to guide and return into the state of stabile equilibrium in order to reach the desired destination. The cognitivist psychology describes the nature of [[Human Behaviour]] in this context. |
| − | In the aspect and understanding of strategic choice, | + | In the aspect and understanding of strategic choice, important parameters are to consider cause and effect uncertainty and conflict. These are main properties of decision-making, which appears in the management of an organization including project, program and portfolio management. |
The '''Stacey matrix model''' introduces the phenomenon of strategic choice in the organization management by taking uncertainty and management agreement into consideration. | The '''Stacey matrix model''' introduces the phenomenon of strategic choice in the organization management by taking uncertainty and management agreement into consideration. | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
=== Background === | === Background === | ||
| − | As antecedent representatives, Thompson and Tuden (1959) have already related to the effect of uncertainty on decision-making mode in a similar manner. They defined that uncertainty | + | As antecedent representatives, Thompson and Tuden (1959) have already related to the effect of uncertainty on decision-making mode in a similar manner. They defined that uncertainty originates in the lack of clarity and the lack of agreement over objectives. Managers are mentioned as objectives. This aligns with the theory of Ralph D. Stacey (2000). |
<ref name="Staceybook"> Ralph D Stacey (2000); Strategic Management and Organization Dynamics, The challenge of Complexity, Pearson Education, England | <ref name="Staceybook"> Ralph D Stacey (2000); Strategic Management and Organization Dynamics, The challenge of Complexity, Pearson Education, England | ||
'''Annotation''': Strategic choice and Stacey matrix </ref> | '''Annotation''': Strategic choice and Stacey matrix </ref> | ||
=== The Stacey matrix === | === The Stacey matrix === | ||
| − | + | The Stacey matrix places a decision by identifying the level of agreement amongst stakeholders and the level of certainty about the cause and effect relationships. There are the parameters appearing on the axes of the matrix as can be seen in Figure 2. The scale is defined between close and far. The closest the parameter is marked, the highest the level is. | |
| − | + | If the relationships between cause and effect are highly certain, as well as having agreement amongst the different stakeholders, the conditions for a simple decision-making case are present. In Figure 2, the area called ''Simple'' shows this situation. In this situation, the management makes the decisions in a rational, logical way. When the aimed direction, destination and circumstances are clear at a company, this can be the case of certain decisions. The right answer exists and a simple fact-based, traditional management situation arises. Although, as moving away from the so-called “Simple” field, the application of rational logic will be critical and different approaches are getting necessary to use. | |
| − | When | + | When there is a high certainty and the causal connections are still clear, but managers conflict then the decision has to be made on ''Political'' manner. This proposes that the one with the biggest power will dominate and the strongest individual who builds coalitions will control the decision-making. Here it is an important aspect to build relationships, negotiate and compromise in order to gain further steps. |
| − | The most problematic situation is when there is | + | When the managers agree on the desires aimed to achieve but the causal connections are uncertain and make the situation unclear how to deal with, then it falls into the zone of so-called ''Complicated''. The usage of judgmental or intuitive modes of decision-making is necessary to execute. In this case, more than one right answer is possible, therefore, the feasibility is judged with the interaction and coordination of expertise. The reasoning is mostly analog. They need think in a literal way, taking trial-and-error cases into account to progress into decision. |
| + | |||
| + | The most problematic situation is when there is not agreement nor certainty, all is unclear and the objectives conflict. This level of complexity is referred to as ''Chaotic''. The atmosphere can be decried with the main factors of tension, turbulence and lack of any patterns. In an organization this is a situation, which really needs to be avoid. Here the manager has to decide based on intuitive individual judgment combined with the political interactions of the group. | ||
<ref>[''Strategic choice and Stacey matrix''] ''Ralph D Stacey (2000) "Strategic Management and Organization Dynamics, The challenge of Complexity", ''Pearson Education, England'' ''</ref> | <ref>[''Strategic choice and Stacey matrix''] ''Ralph D Stacey (2000) "Strategic Management and Organization Dynamics, The challenge of Complexity", ''Pearson Education, England'' ''</ref> | ||
== Models of decision making in conditions of certainty == | == Models of decision making in conditions of certainty == | ||
=== Technical rationality === | === Technical rationality === | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
=== Bounded rationality, bureaucracy and dominant coalitions === | === Bounded rationality, bureaucracy and dominant coalitions === | ||
| − | === Trial and error | + | === Trial and error or logical incrementalism === |
== Limitations of the Stacey matrix model == | == Limitations of the Stacey matrix model == | ||
Revision as of 21:44, 28 September 2015

This report is devised in the course 42433 Advanced Engineering Project, Program and Portfolio Management at the Technical University of Denmark in Autumn 2015.
The Stacey matrix model was proposed by Ralph Douglas Stacey. It gives the possibility to distinguish management decisions and deal with Complexity and Uncertainty in organization platform. The result is brought out by usage of the two dimensions Stacey matrix. It allows us to compare the level of agreement amongst stakeholders with the degree of certainty about the relationships between cause and effect. Thus, the decision can fall into the following areas of the matrix for further analysis: Simple, Complicated, Political and Chaotic.
Contents |
The idea of the strategic choice theory
Ralph D. Stacey defined management and organization dynamics in frame of the strategic choice theory. In this view the organization changes over time in a direction chosen by the most powerful individual or small group of managers. The theory of strategic choice displays its theoretical origin in two main pillars; cybernetic system theory and cognitivist psychology. Cybernetic theory is highly focused on control and regulation of a system, which helps to guide and return into the state of stabile equilibrium in order to reach the desired destination. The cognitivist psychology describes the nature of Human Behaviour in this context.
In the aspect and understanding of strategic choice, important parameters are to consider cause and effect uncertainty and conflict. These are main properties of decision-making, which appears in the management of an organization including project, program and portfolio management.
The Stacey matrix model introduces the phenomenon of strategic choice in the organization management by taking uncertainty and management agreement into consideration.
Application of the Stacey matrix
Background
As antecedent representatives, Thompson and Tuden (1959) have already related to the effect of uncertainty on decision-making mode in a similar manner. They defined that uncertainty originates in the lack of clarity and the lack of agreement over objectives. Managers are mentioned as objectives. This aligns with the theory of Ralph D. Stacey (2000). [1]
The Stacey matrix
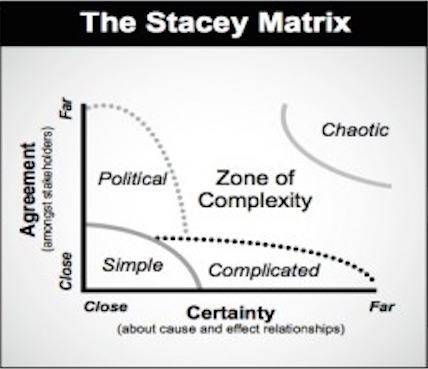
The Stacey matrix places a decision by identifying the level of agreement amongst stakeholders and the level of certainty about the cause and effect relationships. There are the parameters appearing on the axes of the matrix as can be seen in Figure 2. The scale is defined between close and far. The closest the parameter is marked, the highest the level is.
If the relationships between cause and effect are highly certain, as well as having agreement amongst the different stakeholders, the conditions for a simple decision-making case are present. In Figure 2, the area called Simple shows this situation. In this situation, the management makes the decisions in a rational, logical way. When the aimed direction, destination and circumstances are clear at a company, this can be the case of certain decisions. The right answer exists and a simple fact-based, traditional management situation arises. Although, as moving away from the so-called “Simple” field, the application of rational logic will be critical and different approaches are getting necessary to use.
When there is a high certainty and the causal connections are still clear, but managers conflict then the decision has to be made on Political manner. This proposes that the one with the biggest power will dominate and the strongest individual who builds coalitions will control the decision-making. Here it is an important aspect to build relationships, negotiate and compromise in order to gain further steps.
When the managers agree on the desires aimed to achieve but the causal connections are uncertain and make the situation unclear how to deal with, then it falls into the zone of so-called Complicated. The usage of judgmental or intuitive modes of decision-making is necessary to execute. In this case, more than one right answer is possible, therefore, the feasibility is judged with the interaction and coordination of expertise. The reasoning is mostly analog. They need think in a literal way, taking trial-and-error cases into account to progress into decision.
The most problematic situation is when there is not agreement nor certainty, all is unclear and the objectives conflict. This level of complexity is referred to as Chaotic. The atmosphere can be decried with the main factors of tension, turbulence and lack of any patterns. In an organization this is a situation, which really needs to be avoid. Here the manager has to decide based on intuitive individual judgment combined with the political interactions of the group. [2]
Models of decision making in conditions of certainty
Technical rationality
Bounded rationality, bureaucracy and dominant coalitions
Trial and error or logical incrementalism
Limitations of the Stacey matrix model
Related Articles
Annotated bibliography
- ↑ Ralph D Stacey (2000); Strategic Management and Organization Dynamics, The challenge of Complexity, Pearson Education, England Annotation: Strategic choice and Stacey matrix
- ↑ [Strategic choice and Stacey matrix] Ralph D Stacey (2000) "Strategic Management and Organization Dynamics, The challenge of Complexity", Pearson Education, England