Conflict Resolution in Project Management
Contents |
Abstract
Conflicts are unavoidable in projects, as conflicts with others are considered part of human nature. While it is unavoidable it is however of great importance to minimize conflict in projects, as they may lead to delays, improper work and poor results, increased cost etc. When properly handled, conflicts can, however, lead to improved involvement and cohesion as well as clarification of key issues and values. A project manager should thus possess skills in identifying conflict, approaching and managing conflict as well as creating an environment, that aims to reduce conflicts.
Sources of conflict may come from areas as different as poor communication, differences in values or limited resources. As there is no one origin, there can be no one solution, i.e. no one-size-fits-all. Hence the manager must possess knowledge of different ways to handle conflict, and know when to tackle conflict and when not to.
The Importance of Conflict Management
Conflict is unavoidable in human nature, and as all projects involve human interaction conflict is bound to arise. This is not necessarily a negative scenario, as conflict may lead to positive results if managed correctly. The benefits are both personal and professional, where the ones most relevant to project management may be ones such as:[1] [2]
- Increased involvement and coesion.
- Increased innovation and creativity.
- Clarification of key issues and values.
- Better decision making.
- Greater productivity
Mismanaged conflict may however prove destructive, as it can lead to a series of negative results, such as: [1] [3]
- Unclear view on responsibilities.
- Lack of efficiency.
- Lost work time.
- Lowered motivation.
- Bad decision making.
- Health costs.
- Lost employees.
The two final points may affect not only the singular project but the organization as a whole. The long-term stress following an unresolved conflict can lead to sick leave which is expensive for the company, or the stress may ultimately result in the employee leaving the company for good stumping productivity and adding expenses for refilling the position. [3]
Even from this short list, that ignores the more personal aspects of conflicts, it appears evident that proper conflict management is crucial.
What is Conflict?
Webster defines conflict as "competitive or opposing action of incompatibles : antagonistic state or action (as of divergent ideas, interests, or persons)" [4]. In a project or business related view the definition given by Proksch[5], namely " we understand the term conflict to mean a social phenomenon which can arise when people interact and pursue common goals", may be of greater relevance. Proksch goes on to elaborate that there is a difference between a conflict and a disagreement. A disagreement arises occurs when two parties have a difference in interest or opinion and work against each other to reach their own targets. He argues that the situation shall not be labeled a conflict until " the factual problem at hand is further complicated by a relationship problem"[5]. This view is shared by Dana, who further explains that a disagreement becomes a conflict when the parties are interdependent, blame each other, are angry at one another and ultimately cause a problem for the business through their behaviour [6].
Evolution of Conflict
As indicated int he above, conflict does not appear from thin air. It is a process originating in minor disagreements. A common framework for considering the escalation and development of conflict is Glasl's Escalation Model[5].
According to Glasl, there are nine steps to conflict escalation, which are again broken into three stages [5]. Firstly, step 1 through three;
- 1 - Entrenchment of position - the parties are no longer willing to reconsider their point of view, even when introduced to new facts.
- 2 - Debate - the discussion starts focusing on winners and losers.
- 3 - Actions as opposed to words - discussions brake down, and the parties act in attempts to achieve their own targets.
This phase is also known as Resentment. During this phase, it is still possible for the parties to reach a solution through self-help. If they do not manage to do so, the conflict escalates into the next stage;
- 4 - De-personalization - the opponent is no longer considered as a person, but merely as a problem to overcome. The human interaction is lost.
- 5 - Loss of face - attempts are made to make the opponent embarrassed or ridiculed.
- 6 - Threats - threats are put forward in an attempt to put the opponent under pressure
These three steps are known as Exchange of Blows, during which outside mediators are needed to resolve the situation. Otherwise, it may escalate into stage three;
- 7 - Destructive blows - attempts are made at destroying the opponent's defenses while ensuring one's own continued existence.
- 8 - Fragmentation - severe damage to opponent, leaving him or her incapacitated.
- 9 - Into the abyss - being ready to destroy oneself, as long as the opponent goes down.
This final phase is known as Destruction. In this phase, only powerful intervention may aid in resolving the conflict[5].
While Glasl's model is often used, this does not mean that it at all times fits with what is actually observed[5]. As such, many other models exist, including those proposed by Noll, Cornelius, Bramh and more[7]. Some of the highlights of these, including Glasl, is showcased in the figure below.
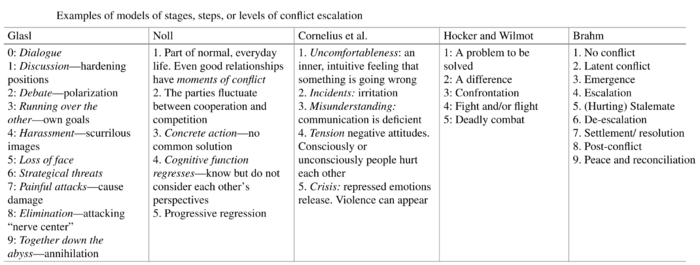
Sources of Conflict
The literature on conflict management lists multiple reasons for a conflict to occur, and each author introduces new suggestions. Some key aspects do, however, appear to reoccur throughout the literature[1][2][5], such as;
- Limited resources - all projects compete for the same pool of resources, which may be insufficient.
- Difference in objectives - not all members of a project necessarily works towards the same goal. One example could be a high-achiever versus a social loafer or freeloader.
- Miscommunication - at times conflict arise from things as simple as poor communication. Meaning can be hard to transfer in writing, or words may be interpreted differently by the receiver than they were intended by the sender.
- Personality clashes - some people just don't get along, so to say. One example could be introverts and extroverts.
One common trait for all sources of conflict is, that the origin of the conflict must be known in order to solve the problem optimally and reduce the risk of the conflict reoccuring[1].
Conflict Management Strategies
Avoiding
As the name suggest this strategy centers on avoiding or withdrawing from conflict. This strategy may be chosen when the issues at hand are trivial or of minor importance. The thought i that the issues may pass on their own, that time is needed to be properly prepared or that others may be better suited to solve the matter. Avoidance is a dangerous strategy as the issues, if left unresolved, may resurface at a later time if not dealt with in a fitting matter.
Accommodating
Compromising
Competing
Collaborating
Pros and cons to each strategy
Prevention of Conflict
As stated previously conflict can, when handled properly, benefit the project in various ways, but might have dire consequences as well. As such, it is of equal importance to attempt to minimize grounds for conflict. This is to a large extent done through preemptive measures, some of which are listed below.
Effective Team Building
(De Janasz) At the early stages of project forming, it is crucial to form well-structured teams and to ensure that the members of these function ideally both professionally and personally. This can be achieved by setting clear objectives, attempting to develop common goals and guidelines and streamlining expectations. Many companies offer courses on effective team building, and many larger corporations handle such matters internally in Human Ressources-departments. This is covered in greater detail in Managing groups for high performance (I really need to figure out how to reference and link stuff in this silly format - it's on the 2018 article list).
Conflict Management Training
(De Janasz) While efforts can be put forth to lessen the risk of conflict, it cannot be prevented that some conflict will arise. Thus there are benefits to be found, in training not only managers but also the staff involved in the projects on ways to manage conflict. Among other things, it may allow personnel to identify potential conflict at earlier stages and addressing it prior to it becoming a concern. I may also allow staff to handle conflict constructively and solve problems in collaborations when they inevitably arise.
Mapping Personality Traits
Multiple companies use various systems to identify and map out personality traits, in order to improve understanding of the individual's characteristics, and how this may affect communication with others. One of these systems is Insights.
Insights Personality Tests
Insights personality tests is based on the work of Dr. Jung, who proposed that our personalities are made up of two traits, Introversion, and Extroversion, as well as four functions, Thinking, Feeling, Sensation and Intuition. (https://www.insights.com/media/1169/insights-discovery-validating-the-system.pdf) Based on the results from the personality test participants will be ranked in four groups; Fiery Red, Sunshine Yellow, Earth Green, and Cool Blue. Typically one or two traits will be dominant and dictate the preferred style of thinking and working, while the remaining are less defining of the individual's personality. In short, the four dominant traits are as follows: (http://www.inside-inspiration.com.au/insights-discovery/insights-colour-energies.html)
- Fiery Red
- People in the Fiery Red-category are high-energy extroverts and oriented towards action. They approach others with authority and emit a desire for power and control.
- Sunshine Yellow
- Sunshine Yellow indicates extroversion and friendliness. People in this category are focused on positivity and human relations, and approach their surroundings with a desire for sociability.
- Earth Green
- Value and depth in human relations are key points for a person in this category. They want to be considered a reliable resource. They value democratic relations and radiate a desire for understanding.
- Cool Blue
- Cool Blue defines introverts with a desire to understand the world around them. Written communication is preferred over oral delivery, as to maintain precision and clarity, ensuring the best baseline for analysis.
Each group has strengths and weaknesses, but knowing these aid people in communicating well with each other. For instance, while Fiery Red and Cool Blue have a desire for details and clarity Sunshine Yellow accepts meetings going off topic and has little interest in detail. Many more such clashes in communication exist, and knowing how to approach a peer may greatly reduce the risk of conflict. (https://aaps.ubc.ca/insights-learning-system-personality-type-communication-tips)
It should be noted, that Insights® maintains strict control over their material, why only very few valid sources on the methods and personality types are available, and no scientific research on the application of methods have been located.
Case Studies
Vastly different companies and organizations have used Insights® to better certain situations. These include organizations as far apart as the national Danish Football Association (DFA) and social media networking platform LinkedIn. LinkedIn is a rapidly growing company in a global market, which meant multiple newly formed teams at all times. LinkedIn trained internal staff to work as Insights Discovery Practitioners, in order to ensure that all teams have the best possible chances to succeed efficiently without conflict from the very start, and without having to rely on external labor. (https://www.insights.com/us/case-studies/)
On a smaller scale, the Danish energy provider Ørsted has implemented Insights Discovery among their staff. The majority of staff participated in mapping personality traits, and the results have since been presented on each individual's desk, ensuring that it is clearly illustrated which traits the person identifies with allowing for more precise communication between personnel.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 De Janasz, S., Wood, G., Gottschalk, L., Dowd, K. and Scneider, B. (2007). Interpersonal skills in organizations. North Ryde, N.S.W.: McGraw-Hill.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 A guide to the project management body of knowledge. (2017). 6th ed. Newtown Square, Pennsylvania, USA: Project Management Institute.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Caspersen, D. (2015). Changing the conversation. Penguin Books.
- ↑ Merriam-webster.com. (2019). Definition of CONFLICT. [online] Available at: https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/conflict [Accessed 26 Feb. 2019].
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 Proksch, S. (2016). Conflict Management. Springer.
- ↑ Dana, D. (2001). Conflict resolution. McGraw-Hill Professional Book Group.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 D'Errico, F., Poggi, I., Vinciarelli, A. and Vincze, L. (2015). Conflict and Multimodal Communication: Social Research and Machine Intelligence. Springer International Publishing