Cross-cultural Management
(→Project Human Resources Management) |
(→Project Human Resources Management) |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
Last but not least, during the team management the conflict management is a subject that have been very demanding, especially when it comes to international projects. Attitude towards conflicts can be very different in different nationalities, as for example Japanese people try to avoid conflicts, in contrast to Americans. <ref>Narkhede, Parag. (2011). '' 'Multiculturalism and Human Resource Management Practices' ''. PCTE Journal Of business Management.</ref>Tools regarding conflict management are confronting, withdrawing, smoothing, compromising, forcing and collaborating. Which tools is to be used in each situation cannot be addressed theoretically but the experience of the manager can help to choose the right tool. Therefore, it is an importantfactor to be examined.<ref>Ganon, M. and Newman, K. (2002), '' 'The Blackwell Handbook of Cross-Cultural Management' '', Project Human Resource Management</ref> | Last but not least, during the team management the conflict management is a subject that have been very demanding, especially when it comes to international projects. Attitude towards conflicts can be very different in different nationalities, as for example Japanese people try to avoid conflicts, in contrast to Americans. <ref>Narkhede, Parag. (2011). '' 'Multiculturalism and Human Resource Management Practices' ''. PCTE Journal Of business Management.</ref>Tools regarding conflict management are confronting, withdrawing, smoothing, compromising, forcing and collaborating. Which tools is to be used in each situation cannot be addressed theoretically but the experience of the manager can help to choose the right tool. Therefore, it is an importantfactor to be examined.<ref>Ganon, M. and Newman, K. (2002), '' 'The Blackwell Handbook of Cross-Cultural Management' '', Project Human Resource Management</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !Game Name | ||
| + | !Time | ||
| + | !Preparation | ||
| + | !Instructions | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Warm Up Game: “Animal Family” | ||
| + | |15 min | ||
| + | |Write down members of animal families (grandpa dog, grandma dog, father dog, etc.) on pieces of paper. Depending on the number of players, families could be 3-10 people. You can have cat, chicken, cow, crab families etc. | ||
| + | |Each person takes a piece of paper, without reading it. Only after all participants have their paper can they read them. | ||
| + | |||
| + | After being given the go-ahead by the facilitator, each player has to find their family as quickly as possible, without talking. They do this by imitating the sound and movement of the animal written on their paper. | ||
| + | |||
| + | When the family has found all their “relatives”, they have to find a way to line up in the correct order (still without talking) based on seniority: grandfather, grandmother, father, mother, son, and daughter. The first family standing in the right order wins. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Main debriefing message: Don’t make quick conclusions if people from different cultures have different ways of expressing their ideas and themselves. Animal sounds for the same animal are different in each culture, for example a dog’s sound is gav in Russian, meong in Korean, wong in Cantonese, and woof in English. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Communication Exercise: “Associations” | ||
| + | |15-20 min | ||
| + | |Pen and paper | ||
| + | |Facilitator asks the audience the following questions and they record the very first images associated with it, whatever comes to mind: | ||
| + | |||
| + | #If a team is a building, it is … | ||
| + | #If a team is a colour, it is… | ||
| + | #If a team is music, it is… | ||
| + | #If a team is a geometrical shape, then it is… | ||
| + | #If a team is the name of a movie, it is… | ||
| + | #If a team is a mood, it is… | ||
| + | Facilitator then carries out a survey to gauge reaction to recorded answers. The result of the exercise is to find out and share which answers the participants found interesting and surprising. It reveals the differences in thinking and cultural background, promoting better communication in their future work together. | ||
| + | |} | ||
===Project Stakeholders Management=== | ===Project Stakeholders Management=== | ||
Revision as of 19:09, 26 February 2018
Contents |
Abstract
Here you will write your draft for your wiki article, include at least 1 reference.
The aim of this article is to give an overview of the cross-cultural management. Nowadays, the globalization of economy creates the need for cultural interaction in organizations and their projects. Considering the fact that cultural differences is a factor that can complicate management procedures, a cross-cultural analysis of management is important. This article emphasizes in presenting fundamental management perspectives in a cross-cultural context. The management areas that are examined, are: frameworks for cross-cultural management, organization's strategy and structure, international human resource management, communication and conflict analysis and motivation rewards and leadership behavior.[1] The influence of peoples' behavior and opinion is a crucial factor that needs to be taken into consideration during the project management processes and it is highly developed in two knowledge areas : Human Resource Management and Stakeholder Management which are going to be analyzed from a cross cultural perspective in this article. [2]
Big Idea
Describe the tool, concept or theory and explain its purpose. The section should reflect the current state of the art on the topic.
Nowadays, trade barriers between countries have been diminished and as a result more and more companies have become international. In an international organization, often, projects are handled by international teams and are affected by international stakeholders. People from different cultures need to communicate together during various project management processes and therefore managers need to make sure that the optimum outcome will be succeeded by this interaction. Furthermore, multicultural interactions can usually bring new perspectives that can lead to better results and managers should make sure to exploit the possibilities to the fullest. Therefore, a theory of a cross cultural project management is needed to be developed.
The theory that is analyzed in this article, takes into consideration two main aspects that influence a project: project stakeholders and project teams. Manage stakeholders is a complicated management task because involves different expectations and opposing interests. A variety of nationalities can increase the difficulty of the task, but on the other hand can create opportunities and this theory tries to make full use of and derive benefit from it. Regarding project teams, except the differences that the members may have in their background, personalities, level of commitment, there are also cultural differences or geographical distances that may affect the project. This challenge needs complex managerial skills and this theory aims at helping managers succeed it.
Definition of Culture and Cross-cultural Management

Culture is a complicated concept that basically consists of language, habits, customs, social behavior and beliefs of a specific society. However, the significance of culture sometimes is underestimated and this fact can be explained by the Iceberg theory, which reveals more aspects of culture than it is believed by a shallow thinking. Some of them are navigation skills, physical contact even behavior towards animals as it can be seen in figure. The need for cultural interaction is increased through the years and therefore it is also encountered in the world of business. The cross cultural management is an approach of management that takes into account diversity in the project members and it is a competitive advantage that an organization should use in their favor.
Application
Provide guidance on how to use the tool, concept or theory and when it is applicable.
Project Human Resources Management
Human Resource Management is one of the most significant operations in project management, as people constitute a fundamental factor for the project success. Dealing with people is a complex procedure and it is always a challenge for the management processes. This fact becomes even more complex in a multicultural context and requires special treatment and deep understanding of the meaning of culture and its aspects ( the unseen part of the iceberg, which is under the sea). The first important step is the recognition of the different cultures within the same project and the speculation about each and every aspect concerns the cultures. This helps in avoiding communication problems and misquotation between the project members. A manager which is well aware of the cultural differences can lead the team in a path, where differences become an advantage and not a barrier. Furthermore, exposing the project members to various cultures help them adapt and get accustomed to deal with different habits and behaviors. Cross-cultural training is a way of helping people in this direction and consists of including team members that have lived in a different culture for some a period of time. Therefore, it is important for an organization to promote their employees to live in a different country for some period or recruit people that have experienced this in the past. In an international project the knowledge and experience that these people have obtained can be tremendous. In addition, by promoting the organizational culture project members can find aspects to feel connected and work for a common project and aim the same goal, which is the project success. A group of people with the same target can jump over dissimilarities. Another useful consideration, is that people from different nationalities have acquired different skills and abilities and this fact can be functional in a project. Different ideas and perspectives are often beneficial and if they are handled wisely can lead in innovative techniques and results. [4]
The project human resource management includes four basic processes: Plan human resource management, acquire project team, develop project team and manage project team. During the team acquiring an analysis of various criteria is done in order to rate the team members and their performance in the team, such as availability, experience and attitude. When an multicultural team interacts then the importance of taking in account the cultural background massive and it can be subtracted because the assignments of the team members are decided by this analysis and it can help the productivity of people to be assigned in a task that matches them.
Later on , during the team development and especially at the team building processes, the integration of culture in the analysis is also important. In order a team to function successfully it is important to form relationships, trust and learn how to communicate. The cultural differences can make this merging challenging for the project manager if the cultural information is not taken into consideration. Moreover, the leadership style and the award tactics are also significantly influenced by the team member culture.
Last but not least, during the team management the conflict management is a subject that have been very demanding, especially when it comes to international projects. Attitude towards conflicts can be very different in different nationalities, as for example Japanese people try to avoid conflicts, in contrast to Americans. [5]Tools regarding conflict management are confronting, withdrawing, smoothing, compromising, forcing and collaborating. Which tools is to be used in each situation cannot be addressed theoretically but the experience of the manager can help to choose the right tool. Therefore, it is an importantfactor to be examined.[6]
| Game Name | Time | Preparation | Instructions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Warm Up Game: “Animal Family” | 15 min | Write down members of animal families (grandpa dog, grandma dog, father dog, etc.) on pieces of paper. Depending on the number of players, families could be 3-10 people. You can have cat, chicken, cow, crab families etc. | Each person takes a piece of paper, without reading it. Only after all participants have their paper can they read them.
After being given the go-ahead by the facilitator, each player has to find their family as quickly as possible, without talking. They do this by imitating the sound and movement of the animal written on their paper. When the family has found all their “relatives”, they have to find a way to line up in the correct order (still without talking) based on seniority: grandfather, grandmother, father, mother, son, and daughter. The first family standing in the right order wins. Main debriefing message: Don’t make quick conclusions if people from different cultures have different ways of expressing their ideas and themselves. Animal sounds for the same animal are different in each culture, for example a dog’s sound is gav in Russian, meong in Korean, wong in Cantonese, and woof in English. |
| Communication Exercise: “Associations” | 15-20 min | Pen and paper | Facilitator asks the audience the following questions and they record the very first images associated with it, whatever comes to mind:
Facilitator then carries out a survey to gauge reaction to recorded answers. The result of the exercise is to find out and share which answers the participants found interesting and surprising. It reveals the differences in thinking and cultural background, promoting better communication in their future work together. |
Project Stakeholders Management
The interaction of stakeholders within a project constitutes a very important aspect on the project success. Stakeholders who come from different cultures usually have expectations different than was expected and therefore it is important to recognize them and address them beforehand.
During the project stakeholder management, the identification and listing of stakeholders is the first step. All the relevant information about the stakeholders are added. When the project management team using the available tools to identify the level of influence of stakeholders, it is important to include the information about culture and the different point of view in fundamental subjects regarding the project. The need of an expert assessement is important in this part of the project management and regarding the culture the presence of social behaviour experts is crucial.
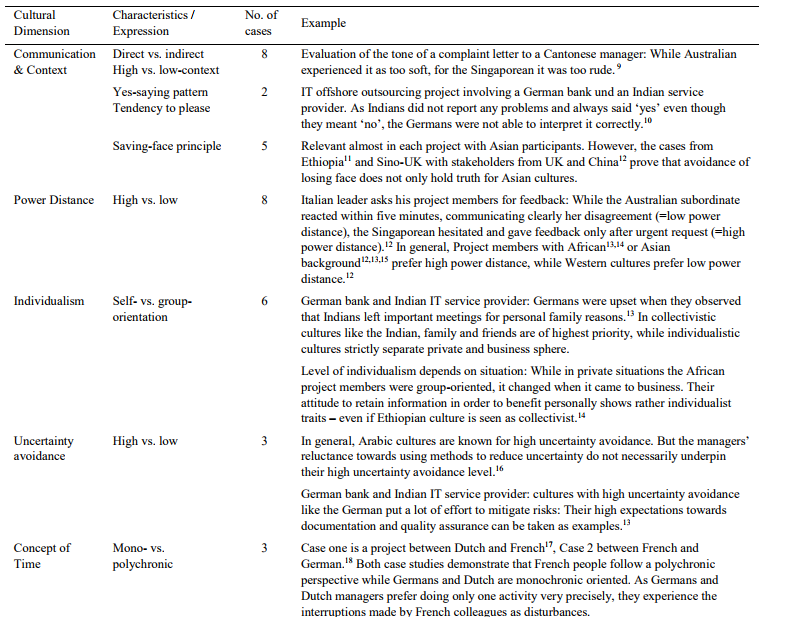
The Table illustrates examples of difficulties caused by the cultural differences between stakeholders and states the source of the problem from a cultural point of view. Communication problems, different comprehension of time concept, important of personal issues are some of the problems that might occur in a multicultural interaction and might lead to costs increasing and delays and in the worst case failure of the project.
A framework for cultural issues has been established and it is important for the stakeholder management to be considered, in order to get a better understanding of cultures and how the project can be affected from them.
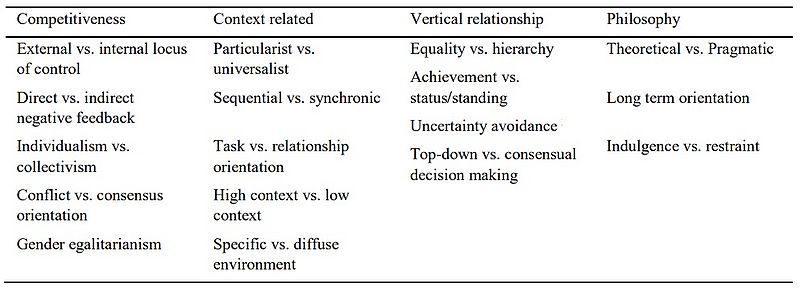
As it can be seen in the table, there are 4 basic categories in which various aspects of cultures are determined. As an example, the concept of individualism vs collectivism can be referred. The societies that can be characterized as the one way or the other, also develop other similar characteristics and by know them, risks and uncertainties can be avoided. Furthermore the topic of conflict vs. consent is important in order the manager to handle situations and identify the method to introduce ideas to stakeholders.
Consequently, regarding the stakeholders and cultures, it is significant to identify the potentially affected from the project communities and list them. During the process or analyzing their needs and expectation, managers need to study and analyze the cultural context of the stakeholders and base their management methods considering this aspect as well. This can help avoid financial problems, and delays that it is possible to occur if multicultural dimension be left unattended.
Limitations
Critically reflect on the tool/concept/theory. When possible, substantiate your claims with literature.
The cross cultural management approach is really important nowadays and can help to accomplish the goals of international projects or projects in which multicultural teams are involved. Books and articles are important for project managers in order to learn how to deal with cultural differences and broaden their horizons regarding the management methods. However, it is difficult to make a solid method about this subject because it contains unlimited aspects, as culture is a multidimensional phenomeno.
Annotated Bibliography
Provide key references (3-10), where a reader can find additional information on the subject. Summarize an outline the relevance of each reference to the topic. (around 100 words per reference). The bibliography is not counted on the 3000 word target length of the article.
1. Anbari, F. T., Khilkhanova, E. V., Romanova, M. V., Ruggia, M., Tsay, C. H.-H., & Umpleby, S. A. (2010). Cultural differences in projects. Paper presented at PMI® Research Conference: Defining the Future of Project Management, Washington, DC. Newtown Square, PA: Project Management Institute.
An article that summarizes the basic aspects of multiculturalism in projects. Gives an overview of what culture is and which are the fundamental categories of it that affect the project management. Attitude towards schedules and deadlines, communication and trust issues are common in a multicultural team and project management implementation becomes more complex and this article helps in understanding the concept.
References
- ↑ Ganon, M. and Newman, K. (2002), ' The Blackwell Handbook of Cross-Cultural Management ', Figure I.1
- ↑ Project Management Institute. (2013), ' A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide), Fifth Edition ', Table A1-1
- ↑ https://www.medialocate.com/2015/09/3-reasons-why-your-website-may-sink-your-international-profits/
- ↑ Narkhede, Parag. (2011). Multiculturalism and Human Resource Management Practices. PCTE Journal Of business Management.
- ↑ Narkhede, Parag. (2011). 'Multiculturalism and Human Resource Management Practices' . PCTE Journal Of business Management.
- ↑ Ganon, M. and Newman, K. (2002), 'The Blackwell Handbook of Cross-Cultural Management' , Project Human Resource Management
- ↑ Lückmanna,P and Färbera,K. (2016). 'The impact of cultural differences on project stakeholder engagement: a review of case study research in international project management' . Elsevier Journal. Table 1.
- ↑ Lückmanna,P and Färbera,K. (2016). 'The impact of cultural differences on project stakeholder engagement: a review of case study research in international project management' . Elsevier Journal. Table 2.