Double Diamond Model
Contents |
Abstract
This article will present the Double Diamond Model, including the utilization of the concept and purpose of the model, and further reflect on belonging limitations and advantages of the method presented once applying it in a project management setting. Ensuring the optimal deployment of the model, into how the project is planned, managed and executed once addressing the various needs and concerns of stakeholders, balancing project constraints such as, scope, quality, and risk in various project circumstances and throughout the project life cycle for an optimal outcome.
The Double Diamond was launched by the British Design Council in 2004, as a part of the framework for innovation to deal with complex economic, social, and environmental challenges.[2] The model represents a comprehensive design process and includes key principles in order to achieve significant and long-lasting results for the right problem. The process consists of four stages, Discover, Define, Develop, and Deliver, divided into two Diamonds. The first diamond concentrates on understanding the problem and a problem definition, namely the Discover and Define phase, also referred to as the problem space. The second diamond concerns the problem-solving phase, namely, the Develop and Define phase, also referred to as the solution space. Both the problem and solutions are being approached from a divergent and a convergent approach, which each of the four stages is either characterized by.[2]
The Big Idea
The model has been developed on the basis of a larger study of 11 top companies' design department processes across many industries. The process should not be performed linearly, on the contrary, several iterations of the various stages are encouraged. Particularly in connection with the digital age in which we find ourselves, which is constantly changing. In this age no product or service as such is fully developed, especially considering the constant feedback that is possible to receive, concepts a continually improved. [2] Furthermore, the Double Diamond model is particularly suitable for structuring collaboration and user involvement in the design process of new solutions. [1]
Likewise, the importance of finding the correct problem and understanding it and the cause of the problem in depth and developing and selecting the correct solution for this particular problem or need is emphasized. In reality, the problem identification phase is equated with the solution phase in the Double Diamond model, therefore the involvement of users who are affected by the problem field, as well as testing of a solution concept by these users is a high priority in the model, by including various methods for the respective activities.[2]
The Problem Space
The Double Diamond process has been divided into an investigation phase of the problem, namely the problem space, which concentrates on the importance of thoroughly understanding the problem or need, ensuring the right cause is being determined to correctly solve the identified problem or need. Once entering the problem space, the solution-oriented approach should be abandoned, especially during the divergent Discover stage, it is important to accomplish an in-depth insight of the problem field. Ensuring that once the Define has been initialized the convergent approach of defining the problem, is being performed on well discovered foundation, to make certain the right problem or cause of problem is being processed.
The Solution Space
The second phase of the Double Diamond is referred to as the solution space which is entirely depending on the problem definition produced in the problem space. The solution space is now initiated by the Develop stage which should be managed through a divergent approach, concentrating on developing a wide range of potential solutions and concepts for the identified problem definition. By producing a variety of solutions, the potential of choosing an inefficient concept for related problem has thereby been reduced. The final part of the solution space includes the Deliver stage which assembles and converge a given concept by communicating and testing the different concepts for the belonging problem, refining the concept for an optimal outcome.
The Framework for Innovation
When launched by the British Design Council the Double Diamond Model became a part of the Framework for Innovation to deal with complex economic, social, and environmental challenges. [2] Which also includes the Design Principles, Methods Bank and Culture of success which should be combined during the process in order to achieve significant results. The framework for Innovation outlines four key design principles to adopt for effective problem solving. First principle outlines the importance of understanding the user needs and aspirations by putting people first. The second principle is highlighting to help people to gain a shared understanding of the problem, by communicating visually and inclusively. Third principle of the Framework for Innovation stresses the potential gain from co-creation and collaboration. And finally, the fourth principle considers the value of iterations during the process, to spot and stop errors as early as possible, minimizing the potential of significant risk late the project life cycle.[2]
Furthermore, the Methods Bank elaborates 25 design methods which the British Design Council has authored and adapted to address and identify problems. Structured in three subcategories namely, Explore; the challenges, needs and opportunities, Shape; prototypes, insights and visions, and Build; ideas, plans and expertise.
Finally, the Framework discusses the need of creating a Culture of Success. This element emphasizes the requirement of establishing a robust leadership to encourage innovation, build skills and capability, which allows projects to be agile and thereby ensuring the ability to change. Additionally, the framework details the need of engagement, developing connections and a relationship can motivate and enhance the delivery and receiving of new concepts. [2]
Application
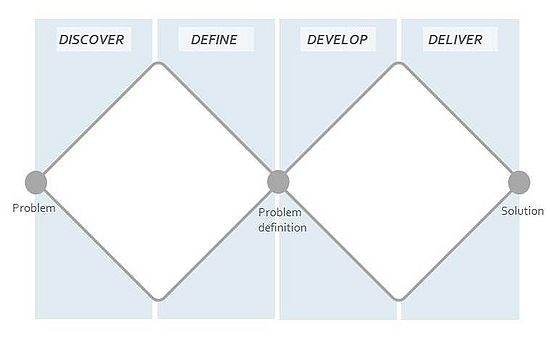
The Double Diamond model is a representation of a design process that presents four stages across two adjacent diamonds. The structure of the model is used to understand a given problem or need, and subsequently work out potential solutions for them. The first diamond in the model deals with problem definition and understanding of a problem field and contains the "Discover" and "Define" phase. The second diamond deals with the problem-solving phase and contains the "Develop" and "Deliver" phase. As a starting point, it can be expected to make several iterations of the different phases, as the process is not linear. Each phase is characterized by either a convergent or divergent approach. The divergent approach is characterized by opening many problems, investigating and investigating, and combining already known facts in new constellations. In contrast, the focus of the convergent approach is to want to narrow down opportunities or focus on a specific problem.Cite error: Closing </ref> missing for <ref> tag
Cite error:
<ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found