Double Diamond in Project Management
| (47 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==Abstract== | ==Abstract== | ||
| − | Every company could have its own method to face the process behind the design of a new product or for solving a problem but it has been observed that all firms go through the same steps when they have to think, design or solve and this is the reason why Design Council developed and launched the '''Double Diamond''' in 2005. | + | Every company could have its own method to face the process behind the design of a project for a new product or for solving a problem but it has been observed that all firms go through the same steps when they have to think, design or solve and this is the reason why Design Council developed and launched the '''Double Diamond''' in 2005. |
| − | The Double Diamond is a model which aims to let design teams visualise the main steps they have to follow in order to achieve the best result in the best possible way. | + | The Double Diamond is a model which aims to let design teams visualise the main steps they have to follow in order to achieve the best result in the best possible way. As the name suggests, the model is composed by two diamond-shape figures and each of these is divided into two other parts which bring to the four main phases of the Double Diamond: '''Discover''', '''Define''', '''Develop''' and '''Deliver'''. |
| + | |||
| + | The Discover and Define phases describe the first part of a project where a team has to think of different ideas and gather a lot of information through, for example, users and market researches and then define the problem. | ||
| + | The Develop and Deliver phases set in the second diamond when, after the approval of the corporate, the team starts developing possible solutions, prototype and obtain feedback and finally deliver the optimal final solution. | ||
| − | The | + | The purpose of this article is showing how the Double Diamond can be related to project management and why its application can reveal to be very convenient for many companies, especially for those that want to enlarge their customers’ satisfaction. In fact, one of the core principles the model talks about is that companies have to be user-oriented and consider users’ needs since the beginning of the design process. |
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==The Big Idea== | |
| + | In 2003 '''Design Council''' was focused on the importance of the adoption of a strategic approach to design and how much significant was the design management. Richard Eisermann, director of Design and Innovation at the time, asked his team to describe what design process is. As a consequence, they decided to define a model which described the stages behind all design processes. They had regular meetings during which they shared their respective researches on the design methods used across the organisation’s previous works in order to elaborate and design an adaptable structure that could fit all processes. | ||
| − | + | Afterwards, from those analysis, it came up that all firms followed a similar, if not the same, procedure that the Double Diamond model summarises through four principal phases and a divergent and convergent trend. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | The scope was to ''“create something that would be applicable in any field”''<ref name="R1" />, and despite its recent introduction into the process design market, that is why it is widely utilised because thanks to its adaptability it can be used whether you have to develop a new product or you have to face a problem. | |
| + | However, Richard came across the basis concept of the Double Diamond years before, in particular he remembered that ''"Dave Duncanson, an engineer at IDEO, talked to me about the product development process as being like the classic diamond-shaped kite, with a tail composed of progressively smaller diamonds. […]"''<ref name="R1" />. So, the idea of divergent and convergent diagrams had already been founded although it did not have a name yet. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ====The model==== | ||
| + | The Double Diamond consists in a framework which helps teams to go through a project and also help project manager and all the members of the group to stay focused on the goals. This model wants to be as simple as possible, so when you look at it, it should be clear where you begin, where you finished and what is in the middle. | ||
| − | + | When a team starts working on a project, they may know what goals they have to reach but the starting point is not always a clear status, so that is why during the project, and through the Double Diamond, you go from a point where you don’t know to a point where you do know. It has also to be considered that the final goals could be modified or re-assessed during the path due to possible market changes or further analysis which let you have a better understanding of what you have to do. | |
| − | The | + | |
| + | So, the first part of the process, also known as the first diamond, consists in making the right question and establishing the right problem to solve. Afterwards the scope is to find the right answer and develop the right way to solve that problem. Anna White, one of the people behind the Double Diamond, said: ''“For me the first part of the diamond is about questioning the brief and defining the problem statement. I explain it as ‘designing the right thing’. The second part of the diamond is about exploring possibility, iteration, testing and developing, so ‘designing the thing right’.”''<ref name="R1" /> Each of this part go through a convergent and divergent trend that represent the idea to be inspired as much as possible gathering lots of information and do many tests but then you have to narrow down and concentrate in the best result you can get. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We will now analyse the four main phases of the model. | ||
| + | |||
| − | [[File:The double diamond.png|600px|thumb|right|Double Diamond Model. Own creation inspired by]] | + | [[File:The double diamond.png|600px|thumb|right|'''Figure 1''':The Double Diamond Model. Own creation inspired by the British Design Council graphic <ref name="R1" />]] |
====Discover==== | ====Discover==== | ||
| − | + | Also known as Research Phase, this is the first step starting with the single problem and ending with a portfolio of different possibilities that have to be properly evaluated later in the process. In the graphical way, this is the divergent part in which almost every idea is welcome and deserves to be taken into account. In fact, one of the main aspects of this stage is to keep minds open. | |
| − | Initial influences and inspirations can come out from different sides, it could be a product manager, a designer or even a customer | + | Initial influences and inspirations can come out from different sides, it could be a product manager, a designer or even a customer, so the project manager should keep in mind that every idea could be the idea. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Design Council listed some bullets point that have to be kept in mind at this stage <ref name="R2" />: | |
| − | - | + | - Creating a project space |
| − | - | + | - Observation |
| − | + | - User diaries | |
| − | + | ||
| + | - Being your users | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Brainstorming | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Choosing a sample | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Quantitative surveys | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Fast visualisation | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Secondary research | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Hopes and fears | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | It has been noticed that being user-oriented is one of the most important keys for companies, so in this phase is fundamental to understand what the customers need and in which way they would like to being satisfied. | ||
| + | |||
| + | However, there are some possible errors that a team could commit, thus a project manager and his team have to be aware to not go with a biased research and be sure to question everything in order to obtain data from all directions also exploring areas that were not considered relevant before. In addition, too much research is also a not healthy way to proceed. So, remember that it is impossible to know everything. | ||
====Define==== | ====Define==== | ||
| − | Once all the ideas and information are gathered, it is time to define. So, it is important that the whole team | + | Once all the ideas and information are gathered, it is time to define. So, it is important that the whole team works on the project in order to assess possible issues from the beginning. It is fundamental to establish and keep a communication with other experts and department internally. Thus, not only designers have to take part but also all the other employees can contribute in the evaluation of the project. This phase usually finishes with the corporate sign-off that can allow project managers continue their project or not. |
In the Define stage you traverse the convergent part because it starts with numerous possible solutions and it narrows until the definition of the best result. This result represents the proposal that will be presented in order to obtain the corporate sign-off. | In the Define stage you traverse the convergent part because it starts with numerous possible solutions and it narrows until the definition of the best result. This result represents the proposal that will be presented in order to obtain the corporate sign-off. | ||
| + | Methods to review and narrow down your insights and establish your project’s main challenge are:<ref name="R3" /> | ||
| − | + | - Focus groups | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | - Assessment criteria | ||
| − | + | - Comparing notes | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | - Drivers and hurdles | |
| − | - | + | - Customer journey mapping |
| − | |||
| − | + | Since this stage is also known as Synthesis Phase, all the team should focus on prioritising. What they will present in the business case has to be clear and has to focus on the challenge. One problem, one solution; not many problems to solve with just one proposal. | |
| − | + | ====Develop==== | |
| + | At this point the project has been accepted and it has obtained the corporate and financial backing, thus this is the phase where design teams give life to prototypes and try and try and try. It is crucial under both the economical and temporal aspect to gather experts from different departments in order to speed up the process avoiding useless attempts that can be easily cut out just asking questions to the right people. This is the most iterative part because there are continuous tests and feedback until the optimal solution. | ||
| − | + | It is an ideation phase and for a successful project there is the need of methods to brainstorm design concept, test out what works and discard what doesn’t. They are:<ref name="R4" /> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | - Character profiles | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | - Scenarios | |
| − | + | - Role-playing | |
| − | - | + | - Service blueprints |
| − | - | + | - Physical prototyping |
| − | |||
| − | + | It’s good to identify three or four solid solutions and then put the ideas to a quick test in order to get feedback as soon as possible. The steps are: develop, show to your target group, get feedback. | |
| − | + | Thus, there are some points to keep in mind and, even if all the people in the team should do it, a good project manager should be the one who takes a step back. It means for example that he has to ask his team if they narrowed down the solution too quickly because you do not want to discard possible solutions before they had a chance to develop. It is also a good thing to stay away from navel-gazing in order to not fall in love with an idea that may be exciting only for you. | |
| − | - | + | ====Deliver==== |
| + | Finally, the deliver stage consists in taking the concept through the final testing signed-off, produced and launched. | ||
| + | Design Council described some methods in order to be successful in this:<ref name="R5" /> | ||
| − | + | - Phasing | |
| − | + | - Final testing | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | - Evaluation | |
| − | + | - Feedback loops | |
| − | + | - Methods bank | |
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | Basically, companies have to identify any late constraints or problems before manufacture and have to be aware of standards and regulations of the specific sector. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Furthermore, organisations are required to report back on the success of the launched product or service with the particular scope to prove how a good design impacted on the success of the product or service. | |
| − | + | ==Application== | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | [[File:Project menagement process groups.png|600px|thumb|right|'''Figure 3''': Graphical description of the relation between the Double Diamond and the Project Management Process Groups. Own creation.]] | |
| + | The Double Diamond has been adopted by numerous organisations, even if it could be considered as a young model considering that it was presented just around fifteen years ago. It is a new model, maybe a new way of designing processes but comparing with some standards we can find similarities. In fact, the PMI standard “Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge” <ref name="R6" /> describes what it called the “Project Management Process Groups” which can be relate to the phases of the Design Council’s model. As shown in the Figure 3, almost every group is linked to a phase, except for the Executing Process Group and Monitoring and Controlling Process Group that both fit in the Develop phase of the second diamond. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Thus, the Double Diamond was not the big reveal but it wanted to simplify and lead companies throughout projects and their design processes. | ||
| + | In 2007 Design Council conducted a study of the design process used in eleven leading global companies <ref name="R7" /> where they could notice and appreciate the used of Double Diamond-based models. In particular, one of them was the British Sky Broadcasting company. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ====BSKYB==== | |
| + | British Sky Broadcasting (BSKYB), also known as Sky, is a British broadcaster and telecommunications company that provides television and broadband Internet services. The company was formed in 1990 by the merger of two early incumbents in the UK multi-channel TV market, Sky Television and British Satellite Broadcasting. | ||
| − | + | Design Council had noticed the particular characteristic of the company to have an internal design management capability together with a strong relationship with an external design consultancy for the execution of product designs. | |
| − | + | [[File:Design at bskyb.png|600px|thumb|right|'''Figure 2''': Graphical comparison between the Double Diamond and the phases of BSKYB's design process. Own creation.]] | |
| − | - | + | At the time of the study, BSkyB was facing the re-designing of its set top boxes which were produced by external manufacturers and originally also the design of the boxes was left entirely to the manufacturers’ discretion. But, around three years before the time of the study, the company’s senior management recognised that it would have be better to deliver a recognisable product as a highly visible element of the company’s presence in the customer’s home and a reinforcing feature for the company’s brand identity. |
| + | The company started working with Frog Design agency for this project. Ed Snodgrass was the project manager and he led the project through an internal process called '''Discover''' – '''Design''' – '''Deliver'''. It basically worked along the same lines of the Double Diamond even if it unified the Define and Develop stages under the Design one. | ||
| − | + | It is a good example of the application of the model because, besides to have an explicit similar way of proceed, it shows how the company took advantage from the principle of the Double Diamond starting with a user-oriented view and completing the project without any waste of time thanks to a consistent and meticulous communication. | |
| − | + | ||
| + | During the Discover part, Frog presented to BskyB some alternatives in order to differentiate from the competitors but also keeping in mind to be user-oriented. | ||
| − | + | In what the company called Design phase, after had chosen the best presented option, they went through the real designing of the product and prototyped it until they got the final version. During this phase the continuous communication between the company, the studio design and the manufacturers was decisive as well as the leading of the project manager. He let the project be fluent and effective. | |
| + | |||
| + | The final step, the Deliver, consisted in evaluating the final product with manufacturers in order to make it suitable with their manufacturing processes. It is the stage when late adjustments were done and then there was the production of the first items sent out for user testing. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Benefits== | ==Benefits== | ||
| − | + | The Double Diamond was developed to be a flexible model that can suit every type of project no matter if a company is going to develop, modify or produce a physical product or a service. Although Design Council gave to the model a sort of linearity with an initial and an ending point, it could be just partially applied depend on the situations and the needs of a project. | |
| − | In addition, | + | |
| − | Moreover, the | + | In addition, since every project is unique, the model you use has to have some level of tailoring, which means ''“adapting a method or process to suit the situation in which it will be used”''<ref name="R8" /> The Double Diamond is a perfect example of model that allows project managers to fit their projects into its structure thanks to the high flexibility and adaptability. |
| + | |||
| + | Moreover, the Double Diamond helps teams and project managers to define a clear roadmap and incorporate users’ feedback since the beginning helping them to keep focusing on the project’s goals. It is also very useful because, besides to give an overall overview of the project, it helps everybody in the team to be aware what phase they are currently at and what the following steps are. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Finally, the model is a visual tool which let project managers communicating to stakeholders in a clearer way when presenting a project. | ||
==Limitations== | ==Limitations== | ||
| − | + | Although the Double Diamond is supposed to be a guide for all kind of steps within a project, one of the main drawbacks is that numerous companies found it too linear. In fact, during the process of developing something it is extremely common to make some mistakes that let you understand that you need to restart the whole process or maybe a part of it, while the model doesn’t say too much about turning back to previous stages. | |
| − | + | ||
| + | Furthermore, it doesn’t take into account the time factor. Considering that ''“a project is a temporary endeavour undertaken to create a unique product, service, or result”''<ref name="R6" />, the temporal element is fundamental because for a company it means money and opportunities. For example, a fast change of the market situation could be dangerous for the introduction of a new product and, if this doesn’t respect the pre-fixed time, competitors could take advantage from it or the project could lose its usefulness. | ||
| + | |||
| + | So, taking time into more consideration and having more possibility to switch back and forth between phases would help companies to face the ongoing changes of the market and in the organisation themselves. | ||
| + | |||
==Framework For Innovation== | ==Framework For Innovation== | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:Double Diamond Model 2019 - framework for innovation 2.png|600px|thumb|right|'''Figure 4''': Design Council's Framework for Innovation graphic model. Source<ref name="R9" />]] | |
| + | |||
| + | To face some of these drawbacks, Design Council has developed an upgraded version of the Double Diamond called “Framework for Innovation”. This time, the process shown by the diagram is not linear. They added arrows going back which underline that a process is not linear but commonly there is the need to go back. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The framework for innovation highlights four core principles for problem-solvers in order to give them the possibility to work as effectively as possible. These are:<ref name="R9" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | - '''Put people first'''. Start with an understanding of the people using a service, their needs, strengths and aspirations. | ||
| + | |||
| + | - '''Communicate visually and inclusively'''. Help people gain a shared understanding of the problem and ideas. | ||
| + | |||
| + | - '''Collaborate and co-create'''. Work together and get inspired by what others are doing. | ||
| + | |||
| + | - '''Iterate, iterate, iterate'''. Do this to spot errors early, avoid risk and build confidence in your ideas. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The model is embraced by two fundamental concepts: engagement and leadership (respectively “Dealing with people” and “leadership skills” in the PMBOK Guide<ref name="R6" />). | ||
| + | |||
| + | These constitute two fundamental aspects for the success of a project since a project manager has to be a good leader who has the ''“the ability to guide, motivate, and direct a team”''<ref name="R6" /> and dealing with people studying their behaviours and motivations. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''“A project manager applies leadership skills and qualities when working with all project stakeholders, including the project team, the steering team, and project sponsors.”''<ref name="R6" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Bibliography== | ==Bibliography== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *"Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge" (PMBOK® Guide) (6th Edition). It is a set of standard terminology and guidelines for project management. It is a foundation upon which organisations can build methodologies, policies, procedures, rules, tools and techniques, and life cycle phases needed to practice project management. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *"Managing Successful Projects with PRINCE2" (Edition 2017) PRINCE2 (PRojects IN Controlled Environments) is one of the most used methods for managing projects based on experience draw from thousands of projects and from the contributions of countless sponsors, project managers, project teams, academics, trainers and consultants. In this book the method is explained in detail and ways of applying it are described. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *"A study of the design process" (2007) ''Eleven lessons: managing design in eleven global brands''. This is a study conducted by Design Council in 2007 in order to analyse the design processes of eleven global companies and understanding how they faced the design process of a project. At the basis of the study there is the Double Diamond model which can be related to all of these firms. | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| + | |||
| + | <references > | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ref name="R1"> https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/news-opinion/double-diamond-universally-accepted-depiction-design-process </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ref name="R2"> https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/news-opinion/design-methods-step-1-discover </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ref name="R3"> https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/news-opinion/design-methods-step-2-define </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ref name="R4"> https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/news-opinion/design-methods-step-3-develop </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ref name="R5"> https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/news-opinion/design-methods-step-4-deliver </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ref name="R6"> https://app-knovel-com.proxy.findit.dtu.dk/web/toc.v/cid:kpGPMBKP02/viewerType:toc/root_slug:viewerType%3Atoc/url_slug:root_slug%3Aguide-project-management?kpromoter=federation </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ref name="R7"> https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/sites/default/files/asset/document/ElevenLessons_Design_Council%20(2).pdf </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ref name="R8"> https://ebookcentral-proquest-com.proxy.findit.dtu.dk/lib/DTUDK/detail.action?docID=4863041 </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ref name="R9"> https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/news-opinion/what-framework-innovation-design-councils-evolved-double-diamond </ref> | ||
Latest revision as of 14:52, 28 February 2021
Developed by Jacopo Renzi
Contents |
[edit] Abstract
Every company could have its own method to face the process behind the design of a project for a new product or for solving a problem but it has been observed that all firms go through the same steps when they have to think, design or solve and this is the reason why Design Council developed and launched the Double Diamond in 2005.
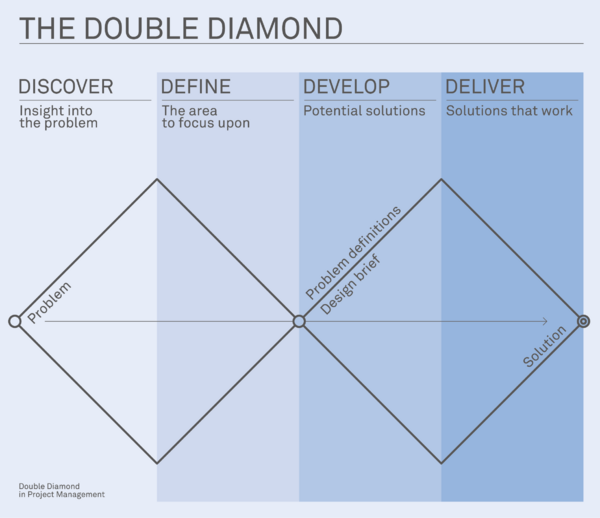
The Double Diamond is a model which aims to let design teams visualise the main steps they have to follow in order to achieve the best result in the best possible way. As the name suggests, the model is composed by two diamond-shape figures and each of these is divided into two other parts which bring to the four main phases of the Double Diamond: Discover, Define, Develop and Deliver.
The Discover and Define phases describe the first part of a project where a team has to think of different ideas and gather a lot of information through, for example, users and market researches and then define the problem. The Develop and Deliver phases set in the second diamond when, after the approval of the corporate, the team starts developing possible solutions, prototype and obtain feedback and finally deliver the optimal final solution.
The purpose of this article is showing how the Double Diamond can be related to project management and why its application can reveal to be very convenient for many companies, especially for those that want to enlarge their customers’ satisfaction. In fact, one of the core principles the model talks about is that companies have to be user-oriented and consider users’ needs since the beginning of the design process.
[edit] The Big Idea
In 2003 Design Council was focused on the importance of the adoption of a strategic approach to design and how much significant was the design management. Richard Eisermann, director of Design and Innovation at the time, asked his team to describe what design process is. As a consequence, they decided to define a model which described the stages behind all design processes. They had regular meetings during which they shared their respective researches on the design methods used across the organisation’s previous works in order to elaborate and design an adaptable structure that could fit all processes.
Afterwards, from those analysis, it came up that all firms followed a similar, if not the same, procedure that the Double Diamond model summarises through four principal phases and a divergent and convergent trend.
The scope was to “create something that would be applicable in any field”[1], and despite its recent introduction into the process design market, that is why it is widely utilised because thanks to its adaptability it can be used whether you have to develop a new product or you have to face a problem. However, Richard came across the basis concept of the Double Diamond years before, in particular he remembered that "Dave Duncanson, an engineer at IDEO, talked to me about the product development process as being like the classic diamond-shaped kite, with a tail composed of progressively smaller diamonds. […]"[1]. So, the idea of divergent and convergent diagrams had already been founded although it did not have a name yet.
[edit] The model
The Double Diamond consists in a framework which helps teams to go through a project and also help project manager and all the members of the group to stay focused on the goals. This model wants to be as simple as possible, so when you look at it, it should be clear where you begin, where you finished and what is in the middle.
When a team starts working on a project, they may know what goals they have to reach but the starting point is not always a clear status, so that is why during the project, and through the Double Diamond, you go from a point where you don’t know to a point where you do know. It has also to be considered that the final goals could be modified or re-assessed during the path due to possible market changes or further analysis which let you have a better understanding of what you have to do.
So, the first part of the process, also known as the first diamond, consists in making the right question and establishing the right problem to solve. Afterwards the scope is to find the right answer and develop the right way to solve that problem. Anna White, one of the people behind the Double Diamond, said: “For me the first part of the diamond is about questioning the brief and defining the problem statement. I explain it as ‘designing the right thing’. The second part of the diamond is about exploring possibility, iteration, testing and developing, so ‘designing the thing right’.”[1] Each of this part go through a convergent and divergent trend that represent the idea to be inspired as much as possible gathering lots of information and do many tests but then you have to narrow down and concentrate in the best result you can get.
We will now analyse the four main phases of the model.
[edit] Discover
Also known as Research Phase, this is the first step starting with the single problem and ending with a portfolio of different possibilities that have to be properly evaluated later in the process. In the graphical way, this is the divergent part in which almost every idea is welcome and deserves to be taken into account. In fact, one of the main aspects of this stage is to keep minds open.
Initial influences and inspirations can come out from different sides, it could be a product manager, a designer or even a customer, so the project manager should keep in mind that every idea could be the idea.
Design Council listed some bullets point that have to be kept in mind at this stage [2]:
- Creating a project space
- Observation
- User diaries
- Being your users
- Brainstorming
- Choosing a sample
- Quantitative surveys
- Fast visualisation
- Secondary research
- Hopes and fears
It has been noticed that being user-oriented is one of the most important keys for companies, so in this phase is fundamental to understand what the customers need and in which way they would like to being satisfied.
However, there are some possible errors that a team could commit, thus a project manager and his team have to be aware to not go with a biased research and be sure to question everything in order to obtain data from all directions also exploring areas that were not considered relevant before. In addition, too much research is also a not healthy way to proceed. So, remember that it is impossible to know everything.
[edit] Define
Once all the ideas and information are gathered, it is time to define. So, it is important that the whole team works on the project in order to assess possible issues from the beginning. It is fundamental to establish and keep a communication with other experts and department internally. Thus, not only designers have to take part but also all the other employees can contribute in the evaluation of the project. This phase usually finishes with the corporate sign-off that can allow project managers continue their project or not.
In the Define stage you traverse the convergent part because it starts with numerous possible solutions and it narrows until the definition of the best result. This result represents the proposal that will be presented in order to obtain the corporate sign-off.
Methods to review and narrow down your insights and establish your project’s main challenge are:[3]
- Focus groups
- Assessment criteria
- Comparing notes
- Drivers and hurdles
- Customer journey mapping
Since this stage is also known as Synthesis Phase, all the team should focus on prioritising. What they will present in the business case has to be clear and has to focus on the challenge. One problem, one solution; not many problems to solve with just one proposal.
[edit] Develop
At this point the project has been accepted and it has obtained the corporate and financial backing, thus this is the phase where design teams give life to prototypes and try and try and try. It is crucial under both the economical and temporal aspect to gather experts from different departments in order to speed up the process avoiding useless attempts that can be easily cut out just asking questions to the right people. This is the most iterative part because there are continuous tests and feedback until the optimal solution.
It is an ideation phase and for a successful project there is the need of methods to brainstorm design concept, test out what works and discard what doesn’t. They are:[4]
- Character profiles
- Scenarios
- Role-playing
- Service blueprints
- Physical prototyping
It’s good to identify three or four solid solutions and then put the ideas to a quick test in order to get feedback as soon as possible. The steps are: develop, show to your target group, get feedback.
Thus, there are some points to keep in mind and, even if all the people in the team should do it, a good project manager should be the one who takes a step back. It means for example that he has to ask his team if they narrowed down the solution too quickly because you do not want to discard possible solutions before they had a chance to develop. It is also a good thing to stay away from navel-gazing in order to not fall in love with an idea that may be exciting only for you.
[edit] Deliver
Finally, the deliver stage consists in taking the concept through the final testing signed-off, produced and launched.
Design Council described some methods in order to be successful in this:[5]
- Phasing
- Final testing
- Evaluation
- Feedback loops
- Methods bank
Basically, companies have to identify any late constraints or problems before manufacture and have to be aware of standards and regulations of the specific sector.
Furthermore, organisations are required to report back on the success of the launched product or service with the particular scope to prove how a good design impacted on the success of the product or service.
[edit] Application
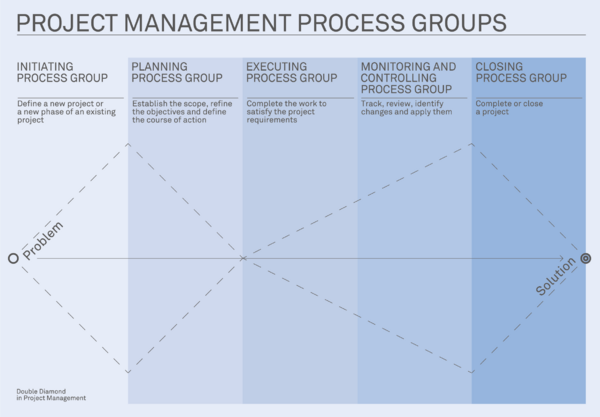
The Double Diamond has been adopted by numerous organisations, even if it could be considered as a young model considering that it was presented just around fifteen years ago. It is a new model, maybe a new way of designing processes but comparing with some standards we can find similarities. In fact, the PMI standard “Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge” [6] describes what it called the “Project Management Process Groups” which can be relate to the phases of the Design Council’s model. As shown in the Figure 3, almost every group is linked to a phase, except for the Executing Process Group and Monitoring and Controlling Process Group that both fit in the Develop phase of the second diamond.
Thus, the Double Diamond was not the big reveal but it wanted to simplify and lead companies throughout projects and their design processes. In 2007 Design Council conducted a study of the design process used in eleven leading global companies [7] where they could notice and appreciate the used of Double Diamond-based models. In particular, one of them was the British Sky Broadcasting company.
[edit] BSKYB
British Sky Broadcasting (BSKYB), also known as Sky, is a British broadcaster and telecommunications company that provides television and broadband Internet services. The company was formed in 1990 by the merger of two early incumbents in the UK multi-channel TV market, Sky Television and British Satellite Broadcasting.
Design Council had noticed the particular characteristic of the company to have an internal design management capability together with a strong relationship with an external design consultancy for the execution of product designs.
At the time of the study, BSkyB was facing the re-designing of its set top boxes which were produced by external manufacturers and originally also the design of the boxes was left entirely to the manufacturers’ discretion. But, around three years before the time of the study, the company’s senior management recognised that it would have be better to deliver a recognisable product as a highly visible element of the company’s presence in the customer’s home and a reinforcing feature for the company’s brand identity.
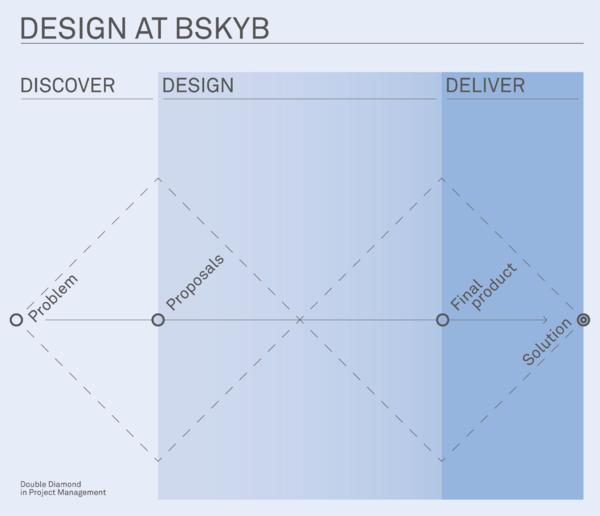
The company started working with Frog Design agency for this project. Ed Snodgrass was the project manager and he led the project through an internal process called Discover – Design – Deliver. It basically worked along the same lines of the Double Diamond even if it unified the Define and Develop stages under the Design one.
It is a good example of the application of the model because, besides to have an explicit similar way of proceed, it shows how the company took advantage from the principle of the Double Diamond starting with a user-oriented view and completing the project without any waste of time thanks to a consistent and meticulous communication.
During the Discover part, Frog presented to BskyB some alternatives in order to differentiate from the competitors but also keeping in mind to be user-oriented.
In what the company called Design phase, after had chosen the best presented option, they went through the real designing of the product and prototyped it until they got the final version. During this phase the continuous communication between the company, the studio design and the manufacturers was decisive as well as the leading of the project manager. He let the project be fluent and effective.
The final step, the Deliver, consisted in evaluating the final product with manufacturers in order to make it suitable with their manufacturing processes. It is the stage when late adjustments were done and then there was the production of the first items sent out for user testing.
[edit] Benefits
The Double Diamond was developed to be a flexible model that can suit every type of project no matter if a company is going to develop, modify or produce a physical product or a service. Although Design Council gave to the model a sort of linearity with an initial and an ending point, it could be just partially applied depend on the situations and the needs of a project.
In addition, since every project is unique, the model you use has to have some level of tailoring, which means “adapting a method or process to suit the situation in which it will be used”[8] The Double Diamond is a perfect example of model that allows project managers to fit their projects into its structure thanks to the high flexibility and adaptability.
Moreover, the Double Diamond helps teams and project managers to define a clear roadmap and incorporate users’ feedback since the beginning helping them to keep focusing on the project’s goals. It is also very useful because, besides to give an overall overview of the project, it helps everybody in the team to be aware what phase they are currently at and what the following steps are.
Finally, the model is a visual tool which let project managers communicating to stakeholders in a clearer way when presenting a project.
[edit] Limitations
Although the Double Diamond is supposed to be a guide for all kind of steps within a project, one of the main drawbacks is that numerous companies found it too linear. In fact, during the process of developing something it is extremely common to make some mistakes that let you understand that you need to restart the whole process or maybe a part of it, while the model doesn’t say too much about turning back to previous stages.
Furthermore, it doesn’t take into account the time factor. Considering that “a project is a temporary endeavour undertaken to create a unique product, service, or result”[6], the temporal element is fundamental because for a company it means money and opportunities. For example, a fast change of the market situation could be dangerous for the introduction of a new product and, if this doesn’t respect the pre-fixed time, competitors could take advantage from it or the project could lose its usefulness.
So, taking time into more consideration and having more possibility to switch back and forth between phases would help companies to face the ongoing changes of the market and in the organisation themselves.
[edit] Framework For Innovation
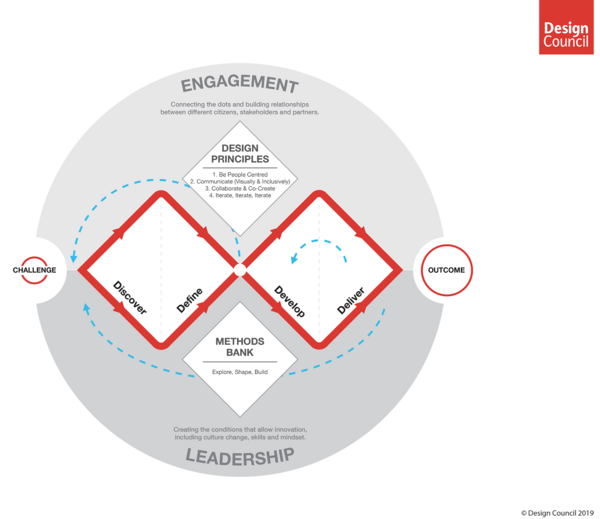
To face some of these drawbacks, Design Council has developed an upgraded version of the Double Diamond called “Framework for Innovation”. This time, the process shown by the diagram is not linear. They added arrows going back which underline that a process is not linear but commonly there is the need to go back.
The framework for innovation highlights four core principles for problem-solvers in order to give them the possibility to work as effectively as possible. These are:[9]
- Put people first. Start with an understanding of the people using a service, their needs, strengths and aspirations.
- Communicate visually and inclusively. Help people gain a shared understanding of the problem and ideas.
- Collaborate and co-create. Work together and get inspired by what others are doing.
- Iterate, iterate, iterate. Do this to spot errors early, avoid risk and build confidence in your ideas.
The model is embraced by two fundamental concepts: engagement and leadership (respectively “Dealing with people” and “leadership skills” in the PMBOK Guide[6]).
These constitute two fundamental aspects for the success of a project since a project manager has to be a good leader who has the “the ability to guide, motivate, and direct a team”[6] and dealing with people studying their behaviours and motivations.
“A project manager applies leadership skills and qualities when working with all project stakeholders, including the project team, the steering team, and project sponsors.”[6]
[edit] Bibliography
- "Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge" (PMBOK® Guide) (6th Edition). It is a set of standard terminology and guidelines for project management. It is a foundation upon which organisations can build methodologies, policies, procedures, rules, tools and techniques, and life cycle phases needed to practice project management.
- "Managing Successful Projects with PRINCE2" (Edition 2017) PRINCE2 (PRojects IN Controlled Environments) is one of the most used methods for managing projects based on experience draw from thousands of projects and from the contributions of countless sponsors, project managers, project teams, academics, trainers and consultants. In this book the method is explained in detail and ways of applying it are described.
- "A study of the design process" (2007) Eleven lessons: managing design in eleven global brands. This is a study conducted by Design Council in 2007 in order to analyse the design processes of eleven global companies and understanding how they faced the design process of a project. At the basis of the study there is the Double Diamond model which can be related to all of these firms.
[edit] References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/news-opinion/double-diamond-universally-accepted-depiction-design-process
- ↑ https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/news-opinion/design-methods-step-1-discover
- ↑ https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/news-opinion/design-methods-step-2-define
- ↑ https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/news-opinion/design-methods-step-3-develop
- ↑ https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/news-opinion/design-methods-step-4-deliver
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 https://app-knovel-com.proxy.findit.dtu.dk/web/toc.v/cid:kpGPMBKP02/viewerType:toc/root_slug:viewerType%3Atoc/url_slug:root_slug%3Aguide-project-management?kpromoter=federation
- ↑ https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/sites/default/files/asset/document/ElevenLessons_Design_Council%20(2).pdf
- ↑ https://ebookcentral-proquest-com.proxy.findit.dtu.dk/lib/DTUDK/detail.action?docID=4863041
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 https://www.designcouncil.org.uk/news-opinion/what-framework-innovation-design-councils-evolved-double-diamond