Forming the Project Coalition
| Line 98: | Line 98: | ||
== The formation of project coalitions == | == The formation of project coalitions == | ||
| − | [[File:s170060formingprojectcoalition.PNG|800px|thumb|Figure | + | [[File:s170060formingprojectcoalition.PNG|800px|thumb|Figure 2: Formation of project coalition]] |
Project coalition creates structures for organizations and individuals to share resources and common goals. Coalition tasks and responsibilities should be clearly defined and assignments equitably distributed on the basis of the members’ areas of expertise. At the heart of every successful coalition, there should be a small group of leaders who are deeply committed to both the issue, and to ensuring that the overall goals of the coalition take precedence over the narrow interest of individual member organizations. In the building industry where big number of suppliers is present, project coalition creates hierarchy of project participants, communication plan and ………. (management , design execution tool) COLABORATION | Project coalition creates structures for organizations and individuals to share resources and common goals. Coalition tasks and responsibilities should be clearly defined and assignments equitably distributed on the basis of the members’ areas of expertise. At the heart of every successful coalition, there should be a small group of leaders who are deeply committed to both the issue, and to ensuring that the overall goals of the coalition take precedence over the narrow interest of individual member organizations. In the building industry where big number of suppliers is present, project coalition creates hierarchy of project participants, communication plan and ………. (management , design execution tool) COLABORATION | ||
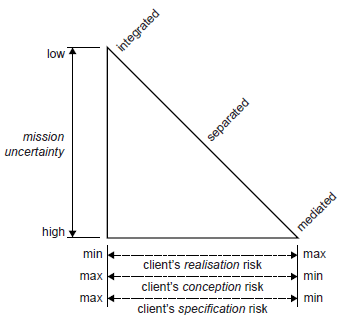
We can distinguish three main type of project coalitions: integrated, separated, and mediated. And fourth called unmediated coalition where client is in direct contact with all suppliers. Client selects most appropriate depend on the project risk and uncertainty. For the simple project where the uncertainty is small the integrated coalition is most comment. With the increase of project complexity the separated or mediate coalitions are more favourable. Dependence of the coalition type in respect to uncertainty and risk is show on the graph in figure 2. | We can distinguish three main type of project coalitions: integrated, separated, and mediated. And fourth called unmediated coalition where client is in direct contact with all suppliers. Client selects most appropriate depend on the project risk and uncertainty. For the simple project where the uncertainty is small the integrated coalition is most comment. With the increase of project complexity the separated or mediate coalitions are more favourable. Dependence of the coalition type in respect to uncertainty and risk is show on the graph in figure 2. | ||
| + | |||
| + | • Separated project coalition | ||
| + | |||
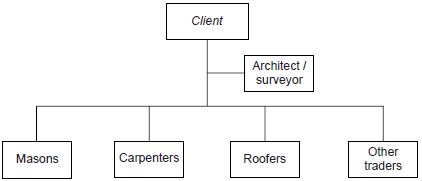
| + | Two kind of separated coalition are developed: traditional – trade contracting, and general contracting. In the first one the architect, in union with the client, is responsible unit for choosing and contracting suppliers of the construction services. Hierarchy is shown in the figure 3.1 | ||
| + | [[File:s170060separatedcoalition.PNG|600px|thumb|center|Figure 3.1: Trades contracting]] | ||
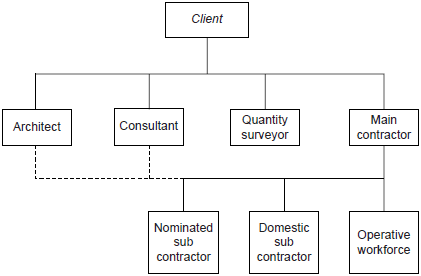
| + | The second type, very common now a days, introduces the position of Main contractor which is responsible for contracting all construction services. Architect, Consultant unit, Quality surveyor, and Main contractor are on the equal level in relation to the client. All this units has to cooperate together and provide effective service while each can be controlled be one of them. Coalition scheme is shown in the figure 3.2. In both models services are procured by competitive tendering or appointment. | ||
| + | [[File:s170060generalcontracting.PNG|600px|thumb|center|Figure 3.1: General contracting]] | ||
Revision as of 10:38, 12 June 2017
Contents |
Project Coalition
A coalition is defined as interaction of two o more members who adopt common strategy toward a common goal. The client’s task is to find the firms which will provide resources required and adopt most convenient cooperation-model to fulfil project mission. The process of procurement is used in the construction industry for selection and review of different suppliers and services. And the resource base is analysed based on the criteria such as price, value and reputation.
Client and suppliers
The client deals with the problem of asymmetry of information once, and what occurs most often, the suppliers knows more about its real competence in supplying required resources. The client needs a tools to investigate the supplier quality, reliability and price for resources. In the field of construction the asymmetry generates two problems defines as: Moral hazard and Adverse selection. Both are related to reliability of a supplier.
• Moral hazard – How can the client be sure that the firm will fully mobilise its capabilities on the client’s behalf.
• Adverse selection – How the client be sure that the most enthusiastic offer of the requested resources is not also the most desperate.
Selection of appropriate procurement
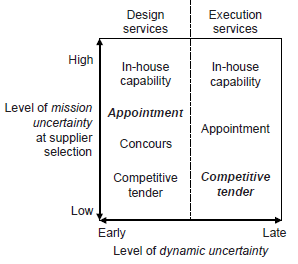
Selection of the supplier depends on the level of the uncertainty and the resources required in the time of making decision. According to the Graham M. Winch selection method can be illustrated as function of level of dynamic uncertainty and level of mission uncertainty, see figure 1. From the graph we can establish the most appropriate method of the procuring services for our project and stage in which it is. For example the client is planning to build simple multifamily building with repetitive structure and is at the early stage of the schedule. The level of mission uncertainty is low and dynamic uncertainty is at the early stage so most appropriate is the use of competitive tendering. The decision making is based on the two interacting dimensions defined as:
• The level of mission uncertainty – the uncertainty is increasing for the big and unique projects
• The phase in the project life cycle – defines the level of the dynamic uncertainty. It increases with the time propagation in the project schedule.
Processes of procuring construction services
A client have four ways to find most compatible supplier. Each method of procure is more convenient for different kids of the project stages: design, construction erection, resources/materials supply, quality surveys, estate maintenance. Selection is also related to the size of the project, uncertainties, phase in the project life cycle. These procure processes are:
• In-house capability:
A client is conducting an activity or operation within a company, instead of relying on outsourcing. A firm uses its own resources to perform the necessary tasks.
Advantages of in-house capability:
• Adjustable relation between client and supplier and no need of complete contract.
• Client has direct contact with a supplier and has full control on audit and evaluation of works.
• Aa
Disadvantages:
• Production inefficiency and rising production costs due to lack of competition.
• Low quality of the project maintains if construction is not the main business of the client.
• aa
• Appointment:
Supplier is nominated based on the reputation for having previously completed projects. This method is most common for the design and project management services. Also is used on construction site services while schedule is delayed.
Advantages:
• Easy and quick search for suppliers.
• Low risk of supplier no capabilities.
Disadvantages:
• Low effectiveness and high probability of misunderstandings between supplier and client due to lack of competition and close relations.
• Concours:
Method is dedicated for design services and mostly is used for the public investments or for unique needs of private client. The Concours can be open or close with invitation for particular designers. The aim of the concur is to select the individual, high standard project.
Advantages:
• Gives opportunity for all kind of designers.
• It reaches a large number of designers so the client network is growing.
• High competitions gives unique and exceptional designs.
Disadvantages:
• Long waiting time and high maintenance costs.
• Challenging designs of very high costs in construction.
• Possible significant differences between conceptual design and final result of a project.
• Competitive tendering
Sellers are presenting their valuations of the contract based on the detailed description provided by client. In general, the tender with the lowest price wins the order, although factors related to quality, shipping, timeliness, and efficiency, may also be a consideration.
Advantages:
• Promote high competition, provide transparency and gives all suppliers the opportunity to win a contract.
• Drives down the price.
Disadvantages:
• Selected supplier might not suit the project due to lack of experience.
• Risk of service failure/stop caused by too low price estimation by supplier.
The formation of project coalitions
Project coalition creates structures for organizations and individuals to share resources and common goals. Coalition tasks and responsibilities should be clearly defined and assignments equitably distributed on the basis of the members’ areas of expertise. At the heart of every successful coalition, there should be a small group of leaders who are deeply committed to both the issue, and to ensuring that the overall goals of the coalition take precedence over the narrow interest of individual member organizations. In the building industry where big number of suppliers is present, project coalition creates hierarchy of project participants, communication plan and ………. (management , design execution tool) COLABORATION
We can distinguish three main type of project coalitions: integrated, separated, and mediated. And fourth called unmediated coalition where client is in direct contact with all suppliers. Client selects most appropriate depend on the project risk and uncertainty. For the simple project where the uncertainty is small the integrated coalition is most comment. With the increase of project complexity the separated or mediate coalitions are more favourable. Dependence of the coalition type in respect to uncertainty and risk is show on the graph in figure 2.
• Separated project coalition
Two kind of separated coalition are developed: traditional – trade contracting, and general contracting. In the first one the architect, in union with the client, is responsible unit for choosing and contracting suppliers of the construction services. Hierarchy is shown in the figure 3.1
The second type, very common now a days, introduces the position of Main contractor which is responsible for contracting all construction services. Architect, Consultant unit, Quality surveyor, and Main contractor are on the equal level in relation to the client. All this units has to cooperate together and provide effective service while each can be controlled be one of them. Coalition scheme is shown in the figure 3.2. In both models services are procured by competitive tendering or appointment.